|
Qalunya
Qalunya (, also transliterated Qaluniya) was a Palestinian village located west of Jerusalem. Prior to the village's destruction in 1948, with the exception of 166 dunams, Qalunya's land was privately owned: 3,594 dunams were owned by Arabs, while 1,084 dunams were owned by Jews. Location Qalunya stood on a mountain slope, facing southwest; Wadi Qalunya passed through its eastern edge. The village lay on the Jerusalem-Jaffa highway, and a dirt path linked it to its neighboring villages.Khalidi, 1992, p. 309 Qalunya was located where the Israelite and Jewish town of Motza was believed to have been. The Modern Motza is now an outlying neighborhood of Jerusalem, and ruins of demolished buildings from Qalunya are present near Motza, covered in vegetation, just off the main highway between Jerusalem and Tel Aviv. The town of Mevaseret Zion today is expanding upon some of the territory of former Qalunya. History Ancient history Roman and Byzantine periods Qalunya preserves the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motza
Motza, also Mozah or Motsa, (, ) is a neighbourhood on the western edge of Jerusalem. It is located in the Judaean Mountains, 600 metres above sea level, connected to Jerusalem by the Jerusalem–Tel Aviv highway, Highway 16, and the winding mountain road to Har Nof. Established in 1854, Motza was the first Jewish farm founded outside the walls of the Old City in the modern era. It is situated near Tel Motza, an archaeological site and the location of the Biblical village of the same name mentioned in . History Tel Motza Motza is the site of the Canaanite and later Israelite town of Mozah, which according to the Hebrew Bible was allotted by Joshua to the Tribe of Benjamin (). The name Mozah was found stamped on pottery handles in Tell en-Nasbeh, a site identified with the biblical city of Mizpah, also in the territory of Benjamin. Sherds from the Late Bronze Age (only one), Iron Age II (58%), Persian/Hellenistic (16%), and Early Islamic period (16%) have been found; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
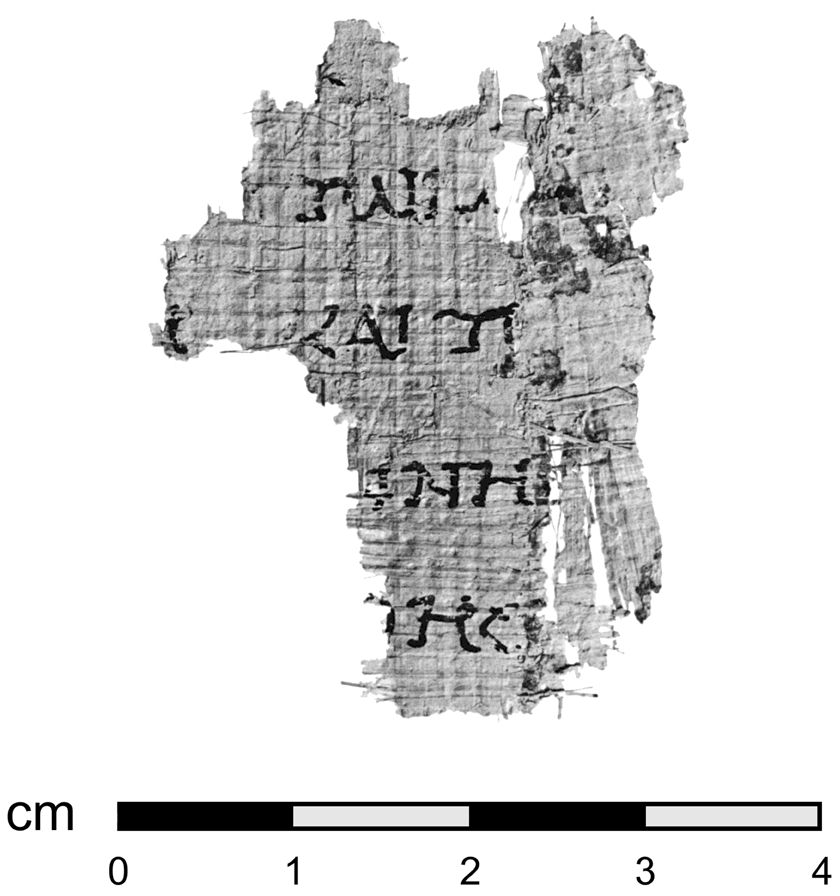
Emmaus-Nicopolis
Emmaus ( ; ; ; ) is a town mentioned in the Gospel of Luke of the New Testament. Luke reports that Jesus appeared, after his death and Resurrection of Jesus, resurrection, before two of his disciples while they were walking on the road to Emmaus. Although its geographical identification is not certain, several locations have been suggested throughout history, chiefly Imwas and Al-Qubeiba, Jerusalem, Al-Qubeiba, both in the West Bank. It is known only that it was connected by a road to Jerusalem; the distance given by Luke varies in different manuscripts and the figure given has been made even more ambiguous by interpretations. Names and location The place-name Emmaus is relatively common in classical sources about the Levant and is usually derived through Greek and Latin from the Semitic languages, Semitic word for "warm spring", the Hebrew form of which is ''hamma'' or ''hammat'' (חמת). In the ancient and present-day Middle East, many sites are named Hama (other), H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emmaus
Emmaus ( ; ; ; ) is a town mentioned in the Gospel of Luke of the New Testament. Luke reports that Jesus appeared, after his death and resurrection, before two of his disciples while they were walking on the road to Emmaus. Although its geographical identification is not certain, several locations have been suggested throughout history, chiefly Imwas and Al-Qubeiba, both in the West Bank. It is known only that it was connected by a road to Jerusalem; the distance given by Luke varies in different manuscripts and the figure given has been made even more ambiguous by interpretations. Names and location The place-name Emmaus is relatively common in classical sources about the Levant and is usually derived through Greek and Latin from the Semitic word for "warm spring", the Hebrew form of which is ''hamma'' or ''hammat'' (חמת). In the ancient and present-day Middle East, many sites are named Hama Hamath and variations thereof. The name for Emmaus was hellenized during the 2nd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevaseret Zion
Mevaseret Zion () is a town and local council located to the west of Jerusalem, straddling both sides of the Jerusalem–Tel Aviv highway. Mevaseret Zion is composed of two distinct older townships, Maoz Zion and Mevaseret Yerushalayim, under the jurisdiction of one local council. The newer neighborhoods of Mevaseret Zion were not part of either township. Mevaseret Zion is located on a mountain ridge above sea level, on the outskirts of Jerusalem. In it had a population of 24,409, spread over 15 neighborhoods. It is the wealthiest municipality per capita in the Jerusalem District. Mevaseret Zion's current mayor is Yoram Shimon. History Castel area Due to its strategic location, settlement in the area of Mevasseret Zion goes back to antiquity. The Romans built a fortress there, known as Castellum. On the ruins of this fortress, the Crusaders built a castle, Castellum Belveer, of which no trace remains. Belveer is mentioned in a letter from Eraclius, Patriarch of Jerusale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–74 CE), also known as the Great Jewish Revolt, the First Jewish Revolt, the War of Destruction, or the Jewish War, was the first of three major Jewish rebellions against the Roman Empire. Fought in the province of Judaea, it resulted in the destruction of Jerusalem and the Jewish Temple, mass displacement, land appropriation, and the dissolution of the Jewish polity. Judaea, once independent under the Hasmoneans, fell to Rome in the first century BCE. Initially a client kingdom, it later became a directly ruled province, marked by the rule of oppressive governors, socioeconomic divides, nationalist aspirations, and rising religious and ethnic tensions. In 66 CE, under Nero, unrest flared when a local Greek sacrificed a bird at the entrance of a Caesarea synagogue. Tensions escalated as Governor Gessius Florus looted the temple treasury and massacred Jerusalem's residents, sparking an uprising in which rebels killed the Roman garrison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonia (Roman)
A Roman (: ) was originally a settlement of Roman citizens, establishing a Roman outpost in federated or conquered territory, for the purpose of securing it. Eventually, however, the term came to denote the highest status of a Roman city. It is also the origin of the modern term "colony". Characteristics Under the Roman Republic, which had no standing army, their own citizens were planted in conquered towns as a kind of garrison. There were two types: * Roman colonies, ''coloniae civium Romanorum'' or ''coloniae maritimae'', as they were often built near the sea, e.g. Ostia (350 BC) and Rimini (268 BC). The colonists consisted of about three hundred Roman veterans with their families who were assigned from 1 to 2.5 hectares of agricultural land from the ''ager colonicus'' (state land), as well as free use of the ''ager compascus scripturarius'' (common state land) for pasture and woodland. * Latin colonies (''coloniae Latinae'') were considerably larger than Roman colonies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jerusalem Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine
The Jerusalem Subdistrict was one of the subdistricts of Mandatory Palestine. It was located in and around the city of Jerusalem. After the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, on the Israeli side of the Green Line, the district was integrated into the Jerusalem District. On the other side, the West Bank was annexed into Jordan, the subdistrict was merged with Ramallah Subdistrict to form Jerusalem Governorate, one of three Jordanian governorates in the West Bank. The city of Jerusalem under British rule In 1917 after the Battle of Jerusalem, the British Army, led by General Edmund Allenby, captured the city. In 1922, the League of Nations at the Conference of Lausanne entrusted the United Kingdom to administer Palestine, neighbouring Transjordan, and Iraq beyond it. The British had to deal with a conflicting demand that was rooted in Ottoman rule. Agreements for the supply of water, electricity, and the construction of a tramway system—all under concessions granted by the Otto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yishuv
The Yishuv (), HaYishuv Ha'ivri (), or HaYishuv HaYehudi Be'Eretz Yisra'el () was the community of Jews residing in Palestine prior to the establishment of the State of Israel in 1948. The term came into use in the 1880s, when there were about 25,000 Jews living in that region, and continued to be used until 1948, by which time there were some 630,000 Jews there. The term is still in use to denote the pre-1948 Jewish residents in Palestine, corresponding to the southern part of Ottoman Syria until 1918, OETA South in 1917–1920, and Mandatory Palestine in 1920–1948. A distinction is sometimes drawn between the '' Old Yishuv'' and the '' New Yishuv''. The Old Yishuv refers to all the Jews living in Palestine before the first Zionist immigration wave (''aliyah'') of 1882, and to their descendants until 1948. The Old Yishuv residents were religious Jews, living mainly in Jerusalem, Safed, Tiberias, and Hebron. There were smaller communities in Jaffa, Haifa, Peki'in, Acre, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defter
A ''defter'' was a type of tax register and land cadastre in the Ottoman Empire. Etymology The term is derived from Greek , literally 'processed animal skin, leather, fur', meaning a book, having pages of goat parchment used along with papyrus as paper in Ancient Greece, borrowed into Arabic as '':'' , meaning a register or a notebook. Description The information collected could vary, but ''tahrir defterleri'' typically included details of villages, dwellings, household heads (adult males and widows), ethnicity/religion (because these could affect tax liabilities/exemptions), and land use. The defter-i hakâni was a land registry, also used for tax purposes. Each town had a defter and typically an officiator or someone in an administrative role to determine whether the information should be recorded. The officiator was usually some kind of learned man who had knowledge of state regulations. The defter was used to record family interactions such as marriage and inheritance. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vallis Therebinthi - Zuallart Jean - 1587
{{disambiguation ...
Vallis (plural Valles) is Latin for valley, vale; it may refer to the following : ;Places and jurisdictions on Earth * the Swiss canton Wallis * Vallis (see), an ancient city, former bishopric and Latin Catholic titular see in Africa Proconsularis * Vallis Vale in Somerset ;Astronomy * Vallis (planetary geology) * Vallis Alpes on the Moon * Vallis Rheita on the Moon * Vallis Snellius on the Moon * Valles Marineris on Mars See also * Valles (other) Valles may refer to: Places * Interandean Valles, a region that is home to most of the human population and agricultural production of the central Andes of Peru, Bolivia, and northwest Argentina *Vallès, a region in Catalonia, Spain, comprising t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitschrift Für Antikes Christentum
The ''Zeitschrift für Antikes Christentum / Journal of Ancient Christianity'' is an academic journal published by Walter de Gruyter. It covers topics related to early Christianity and Patristics Patristics, also known as Patrology, is a branch of theological studies focused on the writings and teachings of the Church Fathers, between the 1st to 8th centuries CE. Scholars analyze texts from both orthodox and heretical authors. Patristics e .... References External links * De Gruyter academic journals Multilingual journals Journals about ancient Christianity Academic journals established in 1997 Triannual journals {{christianity-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carsten Peter Thiede
Carsten Peter Thiede OCF KStJ (8 August 1952 – 14 December 2004) was a German archaeologist and New Testament scholar. He was also a member of PEN and appointed a Knight of Justice of the Order of St John. He taught as professor of New Testament times and history at the Staatsunabhängige Theologische Hochschule (STH) in Basel and at the Ben-Gurion University of the Negev in Beersheba, Israel. He often advanced theories that conflicted with the consensus of academic and theological scholarship. Early life and career Born in West Berlin, Thiede studied comparative literature and history there before procuring a German National Scholarship Foundation Research Fellow position at Queen's College at Oxford University in 1976, where he attained a Blue for volleyball, which he had played in the German Volleyball Premier League. In 1978, he became a senior lecturer in comparative literature at Geneva, where he drew inspiration from his fellow "comparativist", George Steiner. Drawn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |