|
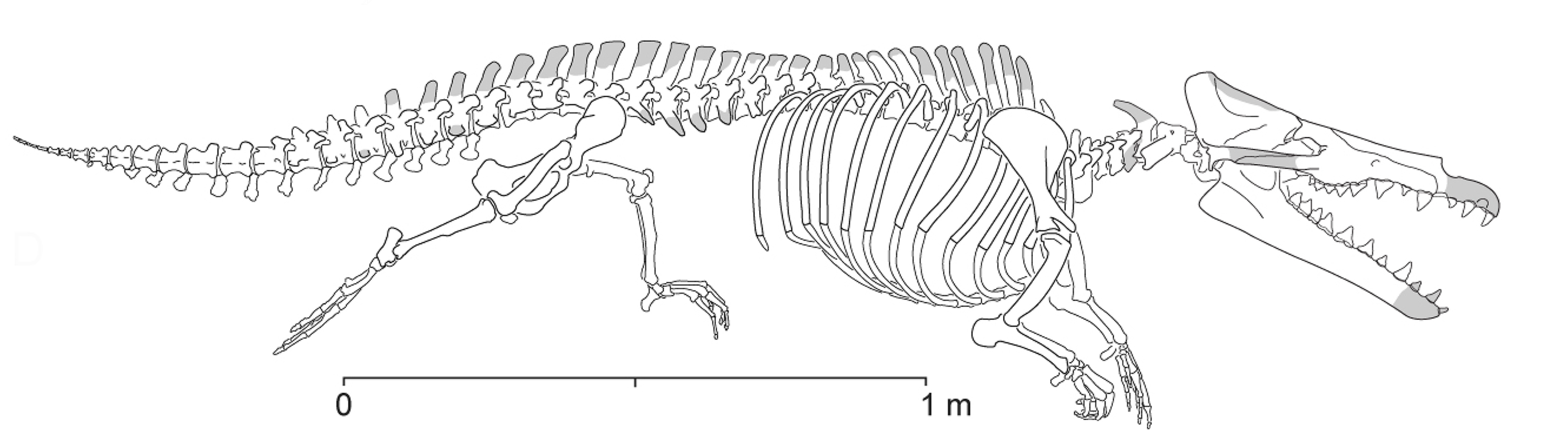
Qaisracetus
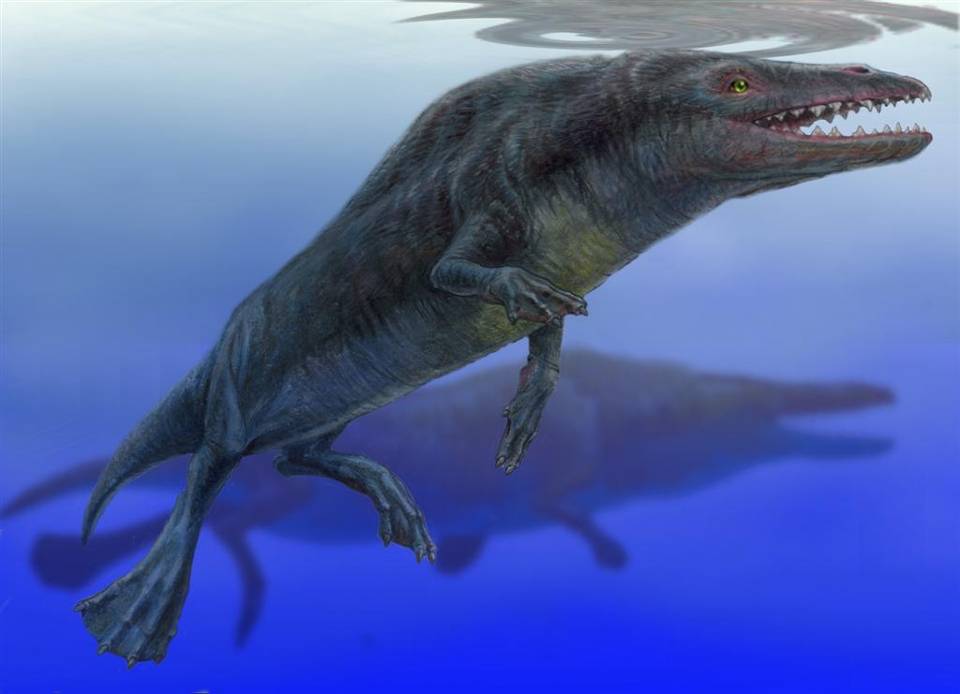
''Qaisracetus'' is an extinct Protocetidae, protocetid Archaeoceti, early whale known from the Eocene (Lutetian, ) of Baluchistan, Pakistan (, paleocoordinates ). Etymology The genus is named after the Qaisrani Baloch tribe which assisted Gingerich and his team during their field work. "Qaisra" is also etymologically close to the royal title used in Persian and many Indo-European languages (e.g. Kaiser, Czar, Caesar). The species is named for Muhammad Arif, former paleontologist at the Geological Survey of Pakistan who contributed significantly to archaeocete paleontology in Pakistan. Description ''Qaisracetus'' is known from a dozen specimens, all found in or near the type locality. Among them are several well-preserved elements, including a well-preserved skull, partial skulls and braincases, several vertebrae including an almost complete sacrum, a left innominate, ribs, and partial limb elements. ''Qaisracetus'' is smaller than ''Pappocetus'' and ''Babiacetus'' but larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeoceti
Archaeoceti ("ancient whales"), or Zeuglodontes in older literature, is a paraphyletic group of primitive cetaceans that lived from the Early Eocene to the late Oligocene (). Representing the earliest cetacean radiation, they include the initial amphibious stages in cetacean evolution, thus are the ancestors of both modern cetacean suborders, Mysticeti and Odontoceti. This initial diversification occurred in the shallow waters that separated India and Asia , resulting in some 30 species adapted to a fully oceanic life. Echolocation and filter-feeding evolved during a second radiation . All archaeocetes from the Ypresian (56–47.8 mya) and most from the Lutetian (47.8–41.3 mya) are known exclusively from Indo-Pakistan, but Bartonian (41.3–38.0 mya) and Priabonian (38.0–33.9 mya) genera are known from across Earth, including North America, Egypt, New Zealand, and Europe. Although no consensus exists regarding the mode of locomotion of which cetaceans were capable during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodhocetus
''Rodhocetus'' (from ''Rodho'', the geological anticline at the type locality, and ''cetus'', Latin for whale) is an extinct genus of protocetid early whale known from the Lutetian of Pakistan. The best-known protocetid, ''Rodhocetus'' is known from two partial skeletons that taken together give a complete image of an Eocene whale that had short limbs with long hands and feet that were probably webbed and a sacrum that was immobile with four partially fused sacral vertebrae. It is one of several extinct whale genera that possess land mammal characteristics, thus demonstrating the evolutionary transition from land to sea. Description left, Size of ''Rodhocetus'' relative to a human. ''Rodhocetus'' was a small whale measuring long. Throughout the 1990s, a close relationship between cetaceans and mesonychids, an extinct group of cursorial, wolf-like ungulates, was generally accepted based on morphological analyses. In the late 1990s, however, cladistic analyses based on molecula ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocetidae
Protocetidae, the protocetids, form a diverse and heterogeneous group of extinct cetaceans known from Asia, Europe, Africa, South America, and North America. Description There were many genera, and some of these are very well known (e.g., ''Rodhocetus''). Known protocetids had large fore- and hindlimbs that could support the body on land, and it is likely that they lived amphibiously: in the sea and on land. It is unclear at present whether protocetids had flukes (the horizontal tail fin of modern cetaceans). However, what is clear is that they are adapted even further to an aquatic life-style. In ''Rodhocetus'', for example, the sacrum – a bone that in land-mammals is a fusion of five vertebrae that connects the pelvis with the rest of the vertebral column – was divided into loose vertebrae. However, the pelvis retain a sacroiliac joint. Furthermore, the nasal openings are now halfway up the snout; a first step towards the telescoped condition in modern whales. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchondrosis
A synchondrosis (or primary cartilaginous joint) is a type of cartilaginous joint where hyaline cartilage completely joins together two bones. Synchondroses are different than symphyses (secondary cartilaginous joints) which are formed of fibrocartilage. Synchondroses are immovable joints and are thus referred to as synarthroses. Examples in the human body Permanent synchondroses * first sternocostal joint (where first rib meets the manubrium of the sternum) *petro-occipital synchondrosis Temporary synchondroses (fuse during development) * epiphyseal plates * apophyses * synchondroses in the developing hip bone The hip bone (os coxae, innominate bone, pelvic bone or coxal bone) is a large flat bone, constricted in the center and expanded above and below. In some vertebrates (including humans before puberty) it is composed of three parts: the ilium, isch ... composed of the ilium, ischium and pubis * spheno-occipital synchondrosis References {{Authority con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 2001
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive (phylogenetics)
In phylogenetics, a primitive (or ancestral) character, trait, or feature of a lineage or taxon is one that is inherited from the common ancestor of a clade (or clade group) and has undergone little change since. Conversely, a trait that appears ''within'' the clade group (that is, is present in any subgroup within the clade but not all) is called advanced or derived. A clade is a group of organisms that consists of a common ancestor and all its lineal descendants. A primitive trait is the original condition of that trait in the common ancestor; advanced indicates a notable change from the original condition. These terms in biology contain no judgement about the sophistication, superiority, value or adaptiveness of the named trait. "Primitive" in biology means only that the character appeared first in the common ancestor of a clade group and has been passed on largely intact to more recent members of the clade. "Advanced" means the character has evolved within a later subgroup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synapomorphy
In phylogenetics, an apomorphy (or derived trait) is a novel character or character state that has evolved from its ancestral form (or plesiomorphy). A synapomorphy is an apomorphy shared by two or more taxa and is therefore hypothesized to have evolved in their most recent common ancestor. ) In cladistics, synapomorphy implies homology. Examples of apomorphy are the presence of erect gait, fur, the evolution of three middle ear bones, and mammary glands in mammals but not in other vertebrate animals such as amphibians or reptiles, which have retained their ancestral traits of a sprawling gait and lack of fur. Thus, these derived traits are also synapomorphies of mammals in general as they are not shared by other vertebrate animals. Etymology The word —coined by German entomologist Willi Hennig—is derived from the Ancient Greek words (''sún''), meaning "with, together"; (''apó''), meaning "away from"; and (''morphḗ''), meaning "shape, form". Clade analysis T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocetus
''Eocetus'' is an extinct protocetid early whale known from the early late Eocene (Bartonian, ) Giushi Formation in Gebel Mokattam, (, paleocoordinates ) outside Cairo, Egypt. The specimen was first named by Fraas as ''Mesocetus schweinfurthi''. However, the name ''Mesocetus'' was previously used causing a change to the species name to ''Eocetus schweinfurthi''. Since the genus was first described in the early 20th century, several other specimens, mostly isolated vertebrae, have been attributed to ''Eocetus'', but the taxonomic status of these widely distributed specimens remain disputed. Discovery and taxonomy described "''Mesocetus schweinfurthi''" based on a dorsoventrally compressed skull with only I2 ''in situ'', a specimen supposedly originating from a 40 Ma Tethyan deposit at Mokattam. Fraas also referred two isolated teeth, P4 and M1, to the skull and the most important of his specimens is not the deformed skull, but the upper molar which retains three roots and a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachyostosis
Pachyostosis is a non-pathological condition in vertebrate animals in which the bones experience a thickening, generally caused by extra layers of lamellar bone. It often occurs together with bone densification (osteosclerosis), reducing inner cavities. This joint occurrence is called pachyosteosclerosis. However, especially in the older literature, "pachyostosis" is often used loosely, referring to all osseous specializations characterized by an increase in bone compactness and/or volume. It occurs in both terrestrial and, especially, aquatic or semi-aquatic vertebrates. In aquatic animals, such as seacows (manatees and dugongs), ''Thalassocnus'', and plesiosaurs, pachyostosis in the thoracic region provides (or provided) ballast against the air-filled lungs. This maintains neutral buoyancy in aquatic habitats. Most giant deer showed pronounced pachyostosis of the mandible and skull. It has been suggested that this served to store minerals for antler growth. Many Pachycephalosau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgiacetus
''Georgiacetus'' is an extinct genus of ancient whale known from the Eocene period of the United States. Fossils are known from Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi and protocetid fossils from the right time frame, but not yet confirmed as ''Georgiacetus'', have been found in Texas () and South Carolina (). created a new clade, Pelagiceti, for the common ancestor of Basilosauridae and all of its descendants, including Neoceti, the living cetaceans. He placed ''Georgiacetus'' near the base of this clade together with ''Eocetus'' and perhaps ''Babiacetus'' because of the assumed presence of a fluke and very compressed posterior caudal vertebrae in these genera. ''Georgiacetus'' is an extinct protocetid (early whale) which lived about and hunted the rich, Suwannee Current powered coastal sea which once covered the Southeastern United States. This was during the earliest Bartonian Stage of the Eocene Epoch (). Current research puts ''Georgiacetus'' as the link between the protoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natchitochia
''Natchitochia'' is an extinct protocetid early whale known from the Middle Eocene (Bartonian, ) Cook Mountain Formation in Natchitoches Parish, Louisiana (, paleocoordinates ).. Retrieved July 2013. ''Natchitochia'' is known from three incomplete ribs and thirteen vertebrae of which four are thoracics, five lumbars, one sacral, two caudals, and one of indeterminable position. ''Natchitochia'' is significantly larger than most other early protocetids, except ''Eocetus'' and ''Pappocetus''. The vertebrae of ''Natchitochia'' are smaller than those of ''Eocetus'' and lack (1) elongated lumbar centra and (2) the ventral keel seen on the vertebrae of ''Pappocetus''. The ribs are smaller than those of ''Pappocetus''. The fragmentary specimen was collected in 1943 during a ground water survey and then sent to the United States National Museum where Remington Kellogg Arthur Remington Kellogg (5 October 1892 – 8 May 1969) was an American naturalist and a director of the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |