|
QF 13-pounder Gun
The Ordnance QF 13-pounder ( quick-firing) field gun was the standard equipment of the British and Canadian Royal Horse Artillery at the outbreak of World War I. History The QF 13-pounder was developed as a response to combat experience gained in the Boer War and entered service in 1904, replacing the Ehrhard QF 15-pounder and BL 12-pounder 6 cwt. It was intended as a rapid-firing and highly-mobile, yet reasonably powerful, field gun for Royal Horse Artillery (RHA) batteries supporting Cavalry brigades, and were expected to be engaged in mobile open warfare. It was developed in parallel with the QF 18-pounder used by Royal Field Artillery. The original Mk I barrel was wire wound. Later Mk II barrels had a tapered inner A tube which was pressed into the outer tube. A hydro-spring recoil system was mounted above the barrel. The carriage was a pole trail type with two seats for the gunners and a protective shield. The first British artillery round on the Western Front in Worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honourable Artillery Company
The Honourable Artillery Company (HAC) is a reserve regiment in the British Army. Incorporated by royal charter in 1537 by King Henry VIII, it is the oldest regiment in the British Army and is considered the second-oldest military unit in the world. Today, it is also a charity whose purpose is to attend to the "better defence of the realm", primarily through supporting the HAC regiment and a detachment of City of London Special Constabulary. The word "artillery" in "Honourable Artillery Company" does not have the current meaning that is generally associated with it, but dates from a time when in the English language that word meant any projectile, including for example arrows shot from a bow. The equivalent form of words in modern English would be either "Honourable Infantry Company" or "Honourable Military Company". In the 17th century, its members played a significant part in the formation of both the Royal Marines and the Grenadier Guards. More recently, regiments, battalions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of British Ordnance Terms
This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance (i.e.: weapons) and also ammunition. The terms may have slightly different meanings in the military of other countries. BD Between decks: applies to a naval gun mounting in which part of the rotating mass is below the deck, and part of it is above the deck. This allows for a lower profile of turret, meaning that turrets need not be superfiring (i.e. they can be mounted on the same deck and not obstruct each other at high angles of elevation.) BL The term BL, in its general sense, stood for breech loading, and contrasted with muzzle loading. The shell was loaded via the breech (i.e. the gunner's end of the barrel, which opened) followed by the propellant charge, and the breech mechanism was closed to seal the chamber. Breech loading, in its formal British ordnance sense, served to identify the gun as the type of rifled breechloading gun for which the powder charge was loaded in a silk or cloth bag and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trench Warfare
Trench warfare is a type of land warfare using occupied lines largely comprising military trenches, in which troops are well-protected from the enemy's small arms fire and are substantially sheltered from artillery. Trench warfare became archetypically associated with World War I (1914–1918), when the Race to the Sea rapidly expanded trench use on the Western Front starting in September 1914.. Trench warfare proliferated when a revolution in firepower was not matched by similar advances in mobility, resulting in a grueling form of warfare in which the defender held the advantage. On the Western Front in 1914–1918, both sides constructed elaborate trench, underground, and dugout systems opposing each other along a front, protected from assault by barbed wire. The area between opposing trench lines (known as " no man's land") was fully exposed to artillery fire from both sides. Attacks, even if successful, often sustained severe casualties. The development of armoured ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (World War I)
The Western Front was one of the main theatres of war during the First World War. Following the outbreak of war in August 1914, the German Army opened the Western Front by invading Luxembourg and Belgium, then gaining military control of important industrial regions in France. The German advance was halted with the Battle of the Marne. Following the Race to the Sea, both sides dug in along a meandering line of fortified trenches, stretching from the North Sea to the Swiss frontier with France, which changed little except during early 1917 and in 1918. Between 1915 and 1917 there were several offensives along this front. The attacks employed massive artillery bombardments and massed infantry advances. Entrenchments, machine gun emplacements, barbed wire and artillery repeatedly inflicted severe casualties during attacks and counter-attacks and no significant advances were made. Among the most costly of these offensives were the Battle of Verdun, in 1916, with a combined 700,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial War Museum
Imperial War Museums (IWM) is a British national museum organisation with branches at five locations in England, three of which are in London. Founded as the Imperial War Museum in 1917, the museum was intended to record the civil and military war effort and sacrifice of Britain and British Empire, its Empire during the First World War. The museum's remit has since expanded to include all conflicts in which British or Commonwealth forces have been involved since 1914. As of 2012, the museum aims "to provide for, and to encourage, the study and understanding of the history of modern war and 'wartime experience'." Originally housed in the Crystal Palace at Sydenham Hill, the museum opened to the public in 1920. In 1924, the museum moved to space in the Imperial Institute in South Kensington, and finally in 1936, the museum acquired a permanent home that was previously the Bethlem Royal Hospital in Southwark. The outbreak of the Second World War saw the museum expand both its coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Cross
The Victoria Cross (VC) is the highest and most prestigious award of the British honours system. It is awarded for valour "in the presence of the enemy" to members of the British Armed Forces and may be awarded posthumously. It was previously awarded by countries of the Commonwealth of Nations, most of which have established their own honours systems and no longer recommend British honours. It may be awarded to a person of any military rank in any service and to civilians under military command. No civilian has received the award since 1879. Since the first awards were presented by Queen Victoria in 1857, two-thirds of all awards have been personally presented by the British monarch. The investitures are usually held at Buckingham Palace. The VC was introduced on 29 January 1856 by Queen Victoria to honour acts of valour during the Crimean War. Since then, the medal has been awarded 1,358 times to 1,355 individual recipients. Only 15 medals, of which 11 to members of the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affair Of Néry
The Affair of Néry was a skirmish fought on 1 September 1914 between the British Army and the German Army, part of the Great Retreat from Mons during the early stages of the First World War. A British cavalry brigade preparing to leave their overnight bivouac were attacked by a German cavalry division of about twice their strength, shortly after dawn. Both sides fought dismounted; the British artillery was mostly put out of action in the first few minutes but a gun of L Battery, Royal Horse Artillery kept up a steady fire for two and a half hours, against a full battery of German artillery. British reinforcements arrived at around counter-attacked the Germans and forced them to retreat; the German division was routed and did not return to combat for several days. Three men of L Battery were awarded the Victoria Cross for their part in the battle, the battery was later awarded the honour title of "Néry", the only British Army unit to have this as a battle honour. Background ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L (Néry) Battery Royal Horse Artillery
L (Néry) Battery Royal Horse Artillery is the Tactical Group Battery of 1st Regiment Royal Horse Artillery. Previous role The Battery became a Tactical Group Battery in 2005, with its guns firing their last rounds in Otterburn in February 2005. *2006 – L/N (Nery) Battery (The Eagles Troop) RHA split to reform separately as L and N Batteries. N Battery returned to 3 RHA to become their Tactical Group Battery and L Battery became 1 RHA's Tactical Group Battery – supporting the HCR, 1st Mech Bde Formation Reconnaissance Regiment. Battery structure L (Nery) Battery are known as a Tactical Group Battery and they consist of approximately 30 personnel: * Battery Commanders FOO Party * FOO Party A - Commanded by the Battery Captain * FOO Party B - Commanded by a Captain. * Battery Commanders Tac Group Equipment L (Nery) Battery are currently equipped with CVRT, rather the Warrior OPV. They have Forward Air Controllers in each team. History Formation L (Nery) Battery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Mons
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force commitment. An engagement with only limited commitment between the forces and without decisive results is sometimes called a skirmish. The word "battle" can also be used infrequently to refer to an entire operational campaign, although this usage greatly diverges from its conventional or customary meaning. Generally, the word "battle" is used for such campaigns if referring to a protracted combat encounter in which either one or both of the combatants had the same methods, resources, and strategic objectives throughout the encounter. Some prominent examples of this would be the Battle of the Atlantic, Battle of Britain, and Battle of Stalingrad, all in World War II. Wars and military campaigns are guided by military strategy, wherea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
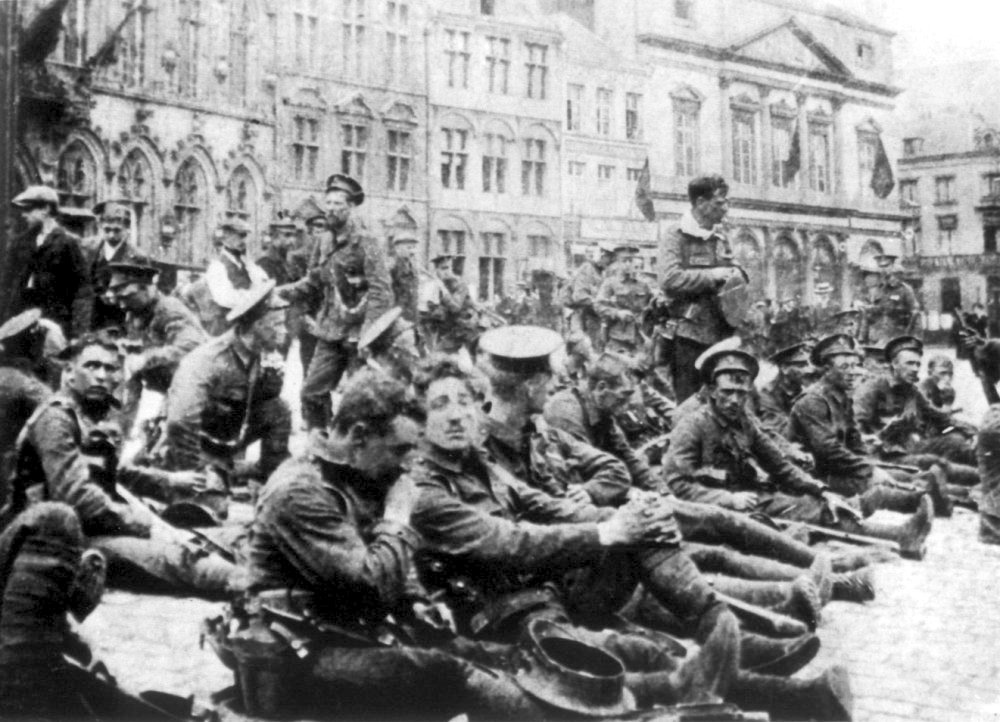
British Expeditionary Force (World War I)
The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) was the six-divisions the British Army sent to the Western Front during the First World War. Planning for a British Expeditionary Force began with the 1906–1912 Haldane reforms of the British Army carried out by the Secretary of State for War Richard Haldane following the Second Boer War (1899–1902). The term ''British Expeditionary Force'' is often used to refer only to the forces present in France prior to the end of the First Battle of Ypres on 22 November 1914. By the end of 1914—after the battles of Mons, Le Cateau, the Aisne and Ypres—the existent BEF had been almost exhausted, although it helped stop the German advance.Chandler (2003), p. 211 An alternative endpoint of the BEF was 26 December 1914, when it was divided into the First and Second Armies (a Third, Fourth and Fifth being created later in the war). "British Expeditionary Force" remained the official name of the British armies in France and Flanders thro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Le Cateau
The Battle of Le Cateau was fought on the Western Front during the First World War on 26 August 1914. The British Expeditionary Force (BEF) and the French Fifth Army had retreated after their defeats at the Battle of Charleroi (21–23 August) and the Battle of Mons (23 August). The British II Corps fought a delaying action at Le Cateau to slow the German pursuit. Most of the BEF was able to continue its retreat to Saint-Quentin. Prelude Having retreated from Mons two days earlier, Le Cateau and Mons being apart, the British II Corps (General Sir Horace Smith-Dorrien) was exhausted. The corps had become separated from the rest of the BEF because of the unexpected retreat by Sir Douglas Haig, the commander of I Corps, who had fought his own rearguard action at Landrecies on 25 August. Following that engagement, where Haig had rallied his troops, revolver in hand, he succumbed to panic, writing to the French High Command about the imminent debacle. He had greatly ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |