|
QBD (electronics)
QBD is the term applied to the charge-to-breakdown measurement of a semiconductor device. It is a standard destructive test method used to determine the quality of gate oxides in MOS devices. It is equal to the total charge passing through the dielectric layer (i.e. electron or hole fluence multiplied by the elementary charge) just before failure. Thus QBD is a measure of time-dependent gate oxide breakdown. As a measure of oxide quality, QBD can also be a useful predictor of product reliability under specified electrical stress conditions. Test method Voltage is applied to the MOS structure to force a controlled current through the oxide, i.e. to inject a controlled amount of charge into the dielectric layer. By measuring the time after which the measured voltage drops towards zero (when electrical breakdown occurs) and integrating the injected current over time, the charge needed to break the gate oxide is determined. This gate charge integral is defined as: Q_\text = \in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity value falling between that of a electrical conductor, conductor, such as copper, and an insulator (electricity), insulator, such as glass. Its electrical resistivity and conductivity, resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. Its conducting properties may be altered in useful ways by introducing impurities ("doping (semiconductor), doping") into the crystal structure. When two differently doped regions exist in the same crystal, a semiconductor junction is created. The behavior of charge carriers, which include electrons, ions, and electron holes, at these junctions is the basis of diodes, transistors, and most modern electronics. Some examples of semiconductors are silicon, germanium, gallium arsenide, and elements near the so-called "metalloid staircase" on the periodic table. After silicon, gallium arsenide is the second-most common s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integral
In mathematics Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ..., an integral assigns numbers to functions in a way that describes Displacement (geometry), displacement, area, volume, and other concepts that arise by combining infinitesimal data. The process of finding integrals is called integration. Along with Derivative, differentiation, integration is a fundamental, essential operation of calculus,Integral calculus is a very well established mathematical discipline for which there are many sources. See and , for example. and serves as a tool to solve problems in mathematics and physics involving the area of an arbitrary shape, the length of a curve, and the volume of a solid, among others. The integrals enumerated here are those termed definite integrals, which can be int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capacitor
A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals. The effect of a capacitor is known as capacitance. While some capacitance exists between any two electrical conductors in proximity in a circuit, a capacitor is a component designed to add capacitance to a circuit. The capacitor was originally known as the condenser, a term still encountered in a few compound names, such as the ''condenser microphone''. The physical form and construction of practical capacitors vary widely and many types of capacitor are in common use. Most capacitors contain at least two electrical conductors often in the form of metallic plates or surfaces separated by a dielectric medium. A conductor may be a foil, thin film, sintered bead of metal, or an electrolyte. The nonconducting dielectric acts to increase the capacitor's c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weibull Chart
Weibull is a Swedish locational surname. The Weibull family share the same roots as the Danish / Norwegian noble family of Falsenbr>They originated from and were named after the village of Weiböl in Widstedts parish, Jutland, but settled in Skåne, Sweden in the 17th century.''Släkten Weibulls Hemsida''"Family Weibull Ancestry" Retrieved on 14 January 2016. The surname Weibull may refer to: *Curt Weibull (1886–1991), Swedish historian *Lauritz Weibull (1873–1960), Swedish historian * Marie Weibull Kornias (born 1954), Swedish politician *Waloddi Weibull (1887–1979), Swedish scientist and mathematician Other uses A number of statistical concepts are named after Waloddi Weibull: * Exponentiated Weibull distribution * Poly-Weibull distribution *Q-Weibull distribution *Weibull distribution * Weibull fading *Weibull modulus The Weibull modulus is a dimensionless parameter of the Weibull distribution which is used to describe variability in measured material strength of brittl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cumulative Distribution Function
In probability theory and statistics, the cumulative distribution function (CDF) of a real-valued random variable X, or just distribution function of X, evaluated at x, is the probability that X will take a value less than or equal to x. Every probability distribution supported on the real numbers, discrete or "mixed" as well as continuous, is uniquely identified by an ''upwards continuous'' ''monotonic increasing'' cumulative distribution function F : \mathbb R \rightarrow ,1/math> satisfying \lim_F(x)=0 and \lim_F(x)=1. In the case of a scalar continuous distribution, it gives the area under the probability density function from minus infinity to x. Cumulative distribution functions are also used to specify the distribution of multivariate random variables. Definition The cumulative distribution function of a real-valued random variable X is the function given by where the right-hand side represents the probability that the random variable X takes on a value less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured. An ammeter usually has low resistance so that it does not cause a significant voltage drop in the circuit being measured. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as ''milliammeters'' or ''microammeters''. Early ammeters were laboratory instruments that relied on the Earth's magnetic field for operation. By the late 19th century, improved instruments were designed which could be mounted in any position and allowed accurate measurements in electric power systems. It is generally represented by letter 'A' in a circuit. History The relation between electric current, magnetic fields and physical forces was first noted by Hans Christian Ør ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RC Time Constant
The RC time constant, also called tau, the time constant (in seconds) of an RC circuit, is equal to the product of the circuit resistance (in ohms) and the circuit capacitance (in farads), i.e. : \tau = RC econds It is the time required to charge the capacitor, through the resistor, from an initial charge voltage of zero to approximately 63.2% of the value of an applied DC voltage, or to discharge the capacitor through the same resistor to approximately 36.8% of its initial charge voltage. (These values are derived from the mathematical constant '' e'': 63.2\% \approx 1-e^ and 36.8\% \approx e^.) The following formulae use it, assuming a constant voltage applied across the capacitor and resistor in series, to determine the voltage across the capacitor against time: :Charging toward applied voltage (initially zero voltage across capacitor, constant across resistor and capacitor together) V_0: \quad V(t) = V_0(1-e^) :Discharging toward zero from initial voltage (initially ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constant Current
A constant current (steady current, time-independent current, stationary current) is a type of direct current (DC) that does not change its intensity with time. Sources If the load is constant, a steady current can be obtained via a constant voltage source. If the load is varying, a steady current can be obtained via a constant current supply source. Constant voltage sources An electrochemical cell is a device capable of either generating electrical energy from chemical reactions or facilitating chemical reactions through the introduction of electrical energy. A common example of an electrochemical cell is a standard 1.5-volt cell meant for consumer use. This type of device is known as a single Galvanic cell, so an obsolete name for steady current was galvanic current. A ''battery'' consists of two or more cells, connected in either parallel or series pattern. A homopolar generator is an electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc or cylinder rotating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
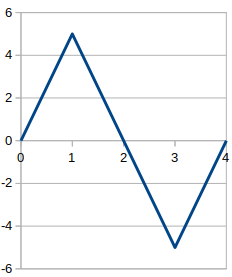
Triangle Wave
A triangular wave or triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape. It is a periodic, piecewise linear, continuous real function. Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics. However, the higher harmonics roll-off, roll off much faster than in a square wave (proportional to the inverse square of the harmonic number as opposed to just the inverse). Definitions Definition A triangle wave of period ''p'' that spans the range [0,1] is defined as: x(t)= 2 \left, \frac - \left \lfloor \frac + \frac \right \rfloor \ where \lfloor\,\ \rfloor is the Floor and ceiling functions, floor function. This can be seen to be the absolute value of a shifted sawtooth wave. For a triangle wave spanning the range the expression becomes: x(t)= 2 \left , 2 \left ( \frac - \left \lfloor + \right \rfloor \right) \right , - 1. A more general equation for a triangle wave with amplitude a and period p using the modulo operation and absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawtooth Wave
The sawtooth wave (or saw wave) is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based on its resemblance to the teeth of a plain-toothed saw with a zero rake angle. A single sawtooth, or an intermittently triggered sawtooth, is called a ramp waveform. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse (or inverse) sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. The equivalent piecewise linear functions x(t) = t - \lfloor t \rfloor x(t) = t \bmod 1 based on the floor function of time ''t'' is an example of a sawtooth wave with period 1. A more general form, in the range −1 to 1, and with period ''p'', is 2\left( - \left\lfloor + \right\rfloor\right) This sawtooth function has the same phase as the sine function. While a square wave is constructed from only odd harmonics, a sawtooth wave's sound is harsh and clear and its spectrum contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current%E2%80%93voltage Characteristic
A current–voltage characteristic or I–V curve (current–voltage curve) is a relationship, typically represented as a chart or graph, between the electric current through a circuit, device, or material, and the corresponding voltage, or potential difference across it. In electronics In electronics, the relationship between the direct current ( DC) through an electronic device and the DC voltage across its terminals is called a current–voltage characteristic of the device. Electronic engineers use these charts to determine basic parameters of a device and to model its behavior in an electrical circuit. These characteristics are also known as I–V curves, referring to the standard symbols for current and voltage. In electronic components with more than two terminals, such as vacuum tubes and transistors, the current-voltage relationship at one pair of terminals may depend on the current or voltage on a third terminal. This is usually displayed on a more complex curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avalanche Breakdown
Avalanche breakdown (or avalanche effect) is a phenomenon that can occur in both insulating and semiconducting materials. It is a form of electric current multiplication that can allow very large currents within materials which are otherwise good insulators. It is a type of electron avalanche. The avalanche process occurs when carriers in the transition region are accelerated by the electric field to energies sufficient to create mobile or free electron-hole pairs via collisions with bound electrons. Explanation Materials conduct electricity if they contain mobile charge carriers. There are two types of charge carriers in a semiconductor: free electrons (mobile electrons) and electron holes (mobile holes which are missing electrons from the normally occupied electron states). A normally bound electron (e.g., in a bond) in a reverse-biased diode may break loose due to a thermal fluctuation or excitation, creating a mobile electron-hole pair. If there is a voltage gradient (el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)