|
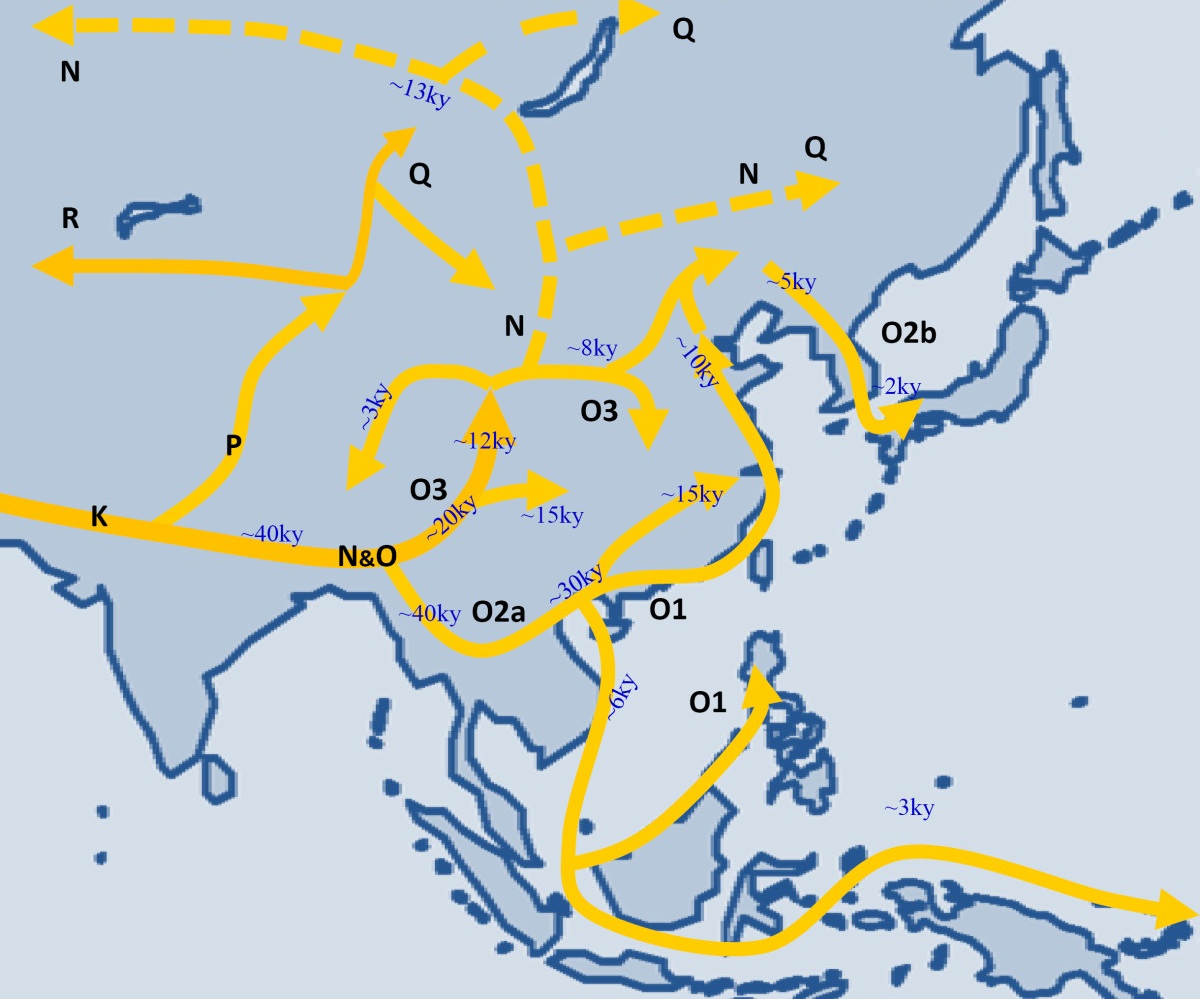
Q-M242
Haplogroup Q or Q-M242 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It has one primary subclade, Haplogroup Q1 (L232/S432), which includes numerous subclades that have been sampled and identified in males among modern populations. Q-M242 is the predominant Y-DNA haplogroup among Native Americans and several peoples of Central Asia and Northern Siberia. Origins Haplogroup Q-M242 is one of the two branches of P1-M45, the other being R-M207. P1, as well as R* and Q* were observed among Ancient North Eurasians, a deeply European hunter-gatherer related population. Q-M242 is believed to have arisen around the Altai Mountains area (or South Central Siberia), approximately 17,000 to 31,700 years ago. However, the matter remains unclear due to limited sample sizes and changing definitions of Haplogroup Q: early definitions used a combination of the SNPs M242, P36.2, and MEH2 as defining mutations. Technical specification of mutation The polymorphism, “M242”, is a C→T transition re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkmens
Turkmens ( tk, , , , ; historically "the Turkmen"), sometimes referred to as Turkmen Turks ( tk, , ), are a Turkic ethnic group native to Central Asia, living mainly in Turkmenistan, northern and northeastern regions of Iran and north-western Afghanistan. Sizeable groups of Turkmens are found also in Uzbekistan, Kazakhstan, and the North Caucasus ( Stavropol Krai). They speak the Turkmen language, which is classified as a part of the Eastern Oghuz branch of the Turkic languages. Examples of other Oghuz languages are Turkish, Azerbaijani, Qashqai, Gagauz, Khorasani, and Salar. In the early Middle ages, Turkmens called themselves Oghuz and in the Middle Ages they took the ethnonym Turkmen. These early Oghuz Turkmens moved westward from the Altai Mountains through the Siberian steppes, and settled in the region now known as Turkmenistan. Further westward migration of the Turkmen tribes from the territory of modern Turkmenistan and the rest of Central Asia started from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altaians
The Altai people ( alt, Алтай-кижи, Altai-kizhi), also the Altaians ( alt, Алтайлар, Altailar), are a Turkic ethnic group of indigenous peoples of Siberia mainly living in the Altai Republic, Russia. Several thousand of the Altaians also live in Mongolia (Mongolian Altai Mountains) and China (Altay Prefecture, northern Xinjiang) but are officially unrecognized as a distinct group and listed under the name "Oirats" as a part of the Mongols, as well as in Kazakhstan where they number around 200. For alternative ethnonyms see also Tele, Black Tatar, and Oirats. During the Northern Yuan Dynasty of Mongolia, they were ruled in the administrative area known as Telengid Province. Ethnic groups and subgroups The Altaians are represented by two ethnographic groups: *The Southern Altaians, who speak the Southern Altai language with its dialects, include the Altai-Kizhi, the Teleuts, the Telengits, and used to include the Telesy who are now assimilated within the Telen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup (haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (hap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup Q1
A haplotype is a group of alleles in an organism that are inherited together from a single parent, and a haplogroup ( haploid from the el, ἁπλοῦς, ''haploûs'', "onefold, simple" and en, group) is a group of similar haplotypes that share a common ancestor with a single-nucleotide polymorphism mutation. More specifically, a haplogroup is a combination of alleles at different chromosomal regions that are closely linked and that tend to be inherited together. As a haplogroup consists of similar haplotypes, it is usually possible to predict a haplogroup from haplotypes. Haplogroups pertain to a single line of descent. As such, membership of a haplogroup, by any individual, relies on a relatively small proportion of the genetic material possessed by that individual. Each haplogroup originates from, and remains part of, a preceding single haplogroup (or paragroup). As such, any related group of haplogroups may be precisely modelled as a nested hierarchy, in which each set (h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup R (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup R, or R-M207, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup. It is both numerous and widespread amongst modern populations. Some descendant subclades have been found since pre-history in Europe, Central Asia and South Asia. Others have long been present, at lower levels, in parts of West Asia and Africa. Some authorities have also suggested, more controversially, that R-M207 has long been present among Native Americans in North America – a theory that has not yet been widely accepted. According to geneticist Spencer Wells, haplogroup K, from which haplogroups P and Q descend, originated in the Middle East or Central Asia. "Given the widespread distribution of K, it probably arose somewhere in the Middle East or Central Asia, perhaps in the region of Iran or Pakistan." However, Karafet et al. (2014) proposed that "rapid diversification ... of K-M526", also known as K2, likely occurred in Southeast Asia (near Indonesia) and later expanded to mainland Asia, although they could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup P1 (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup P1, also known as P-M45 and K2b2a, is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup in human genetics. Defined by the SNPs M45 and PF5962, P1 is a primary branch (subclade) of P (P-P295; K2b2). The only primary subclades of P1 are Haplogroup Q (Q-M242) and Haplogroup R (R-M207). These haplogroups now comprise most of the male lineages among Native Americans, Europeans, Central Asia and South Asia, among other parts of the world. P1 (M45) likely originated in Central Asia or Siberia, with basal P1* (P1xQ,R) now most common among individuals in Siberia and Central Asia.Miroslava Derenko et al 2005 Contrasting patterns of Y-chromosome variation in South Siberian populations from Baikal and Altai-Sayan regionsZgms.cm.umk.plE. Heyer et al., 2013, "Genetic Diversity of Four Filipino Negrito Populations from Luzon: Comparison of Male and Female Effective Population Sizes and Differential Integration of Immigrants into Aeta and Agta Communities", ''Human Biology'', Vol. 85, Iss. 1, p. 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Y-chromosome DNA Haplogroup
In human genetics, a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup is a haplogroup defined by mutations in the non- recombining portions of DNA from the male-specific Y chromosome (called Y-DNA). Many people within a haplogroup share similar numbers of short tandem repeats (STRs) and types of mutations called single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The human Y-chromosome accumulates roughly two mutations per generation. "one mutation in every 30 million base pairs" Y-DNA haplogroups represent major branches of the Y-chromosome phylogenetic tree that share hundreds or even thousands of mutations unique to each haplogroup. The Y-chromosomal most recent common ancestor (Y-MRCA, informally known as Y-chromosomal Adam) is the most recent common ancestor (MRCA) from whom all currently living humans are descended patrilineally. Y-chromosomal Adam is estimated to have lived roughly 236,000 years ago in Africa. By examining other bottlenecks most Eurasian men (men from populations outside of Afri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haplogroup P (Y-DNA)
Haplogroup P also known as P-P295 and K2b2 is a Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup in human genetics. P-P295 is a branch of K2b (previously Haplogroup MPS; P331), which is a branch of Haplogroup K2 (K-M526). The only primary branches (clades) of P-P295 are P1 (P-M45) commonly found among Siberians and Central Asians, and P2 (P-B253) found in Oceanian populations. along with P* found among an Indian sample in Malayasia. P1 (P-M45) Many ethnic groups with high frequencies of P1, also known as P-M45 and K2b2a, are located in Central Asia and Siberia: 35.4% among Tuvans, 28.3% among Altai-Kizhi (PxQ-M3,R1), and 35% among Nivkh males. § ''May include members of haplogroup R2.'' Q Near universal in the Kets (95%) of Siberia. Very common in pre-modern Native American populations and Selkups, except for the Na-Dene peoples, where it reaches 50-90%. Also common, at 25-50% in Siberian populations such as the Siberian Tatars, Nivkh, Tuvans, Chukchi, Siberian Eskimos, Northern A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ket People
Kets (russian: Кеты; Ket: Ostygan) are a tribe of Yeniseian speaking people in Siberia. During the Russian Empire, they were known as Ostyaks, without differentiating them from several other Siberian people. Later, they became known as ''Yenisei Ostyaks'' because they lived in the middle and lower basin of the Yenisei River in the Krasnoyarsk Krai district of Russia. The modern Kets lived along the eastern middle stretch of the river before being assimilated politically into Russia between the 17th and 19th centuries. According to the 2010 census, there were 1,220 Kets in Russia. Origin The Ket people share their origin with other Yeniseian people and are closely related to other Indigenous people of Siberia and Indigenous peoples of the Americas. They belong mostly to Y-DNA haplogroup Q-M242. According to a 2016 study, the Ket and other Yeniseian people originated likely somewhere near the Altai Mountains or near Lake Baikal. It is suggested that parts of the Altaians a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selkup People
The Selkup (russian: селькупы), until the 1930s called Ostyak- Samoyeds (''остяко-самоеды''), are a Samoyedic speaking Uralic ethnic group native to Siberia. They live in the northern parts of Tomsk Oblast, Krasnoyarsk Krai and Tyumen Oblast (with Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug). History Selkups speak the Selkup language, which belongs to the Samoyedic languages of the Uralic language family. The Selkups originated in the middle basin of the Ob River, from interactions between the aboriginal Yeniseian population and Samoyedic peoples that came to the region from the Sayan Mountains during the early part of the first millennium CE. In the 13th century, the Selkups came under the sway of the Mongols. Around 1628, the Russians conquered the area and the Selkups were subjugated. The Selkups joined an uprising against Russian rule but were gunned down and defeated. In the 17th century, some of the Selkups relocated up north to live along the Taz River and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
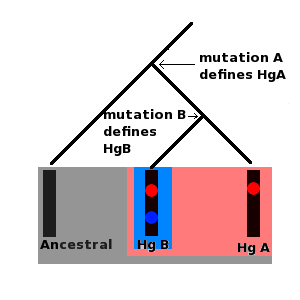
Subclade
In genetics, a subclade is a subgroup of a haplogroup. Naming convention Although human mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) and Y chromosome DNA (Y-DNA) haplogroups and subclades are named in a similar manner, their names belong to completely separate systems. mtDNA mtDNA haplogroups are defined by the presence of a series of single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) markers in the hypervariable regions and the coding region of mitochondrial DNA. They are named with the capital letters A through Z, with further subclades named using numbers and lower case letters. Y-DNA Y-DNA haplogroups are defined by the presence of a series of SNP markers on the Y chromosome. Subclades are defined by a ''terminal SNP'', the SNP furthest down in the Y chromosome phylogenetic tree. Human Y-DNA The Y Chromosome Consortium (YCC) developed a system of naming major human Y-DNA haplogroups with the capital letters A through T, with further subclades named using numbers and lower case letters (YCC longhand nomenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribes Of Assam
According to the 2001 census, the Scheduled Tribes population as in percentage of the total population of Assam was 12.4 percent. The Assam Tribune reported in 2009 that the tribal communities of Assam now officially account for 15.64 percent of the total population. The Constitution of India categorizes the tribes of Assam into two groups: Scheduled Tribes (Hills) and Scheduled Tribes (Plains). Since hills tribes living in the plains and plains tribes living in the hills in large numbers are not recognised as scheduled tribes in the respective places, the census data may not reflect the correct figures. The Assam Tribune has claimed that if these categories of tribes are counted the actual population. Assamese language is used as the lingua franca by almost all the tribes. Groups The main Scheduled Tribes (Plains) are Bodo , Deori, Sonowal, Mising, Hajong, etc and Karbi, Dimasa etc has Scheduled Tribes (hills) status. List of tribes * In the autonomous Districts of Karbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)