|
Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture
Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA) is a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture, developed by Theodore J. Williams and members of the Industry-Purdue University Consortium for Computer Integrated Manufacturing. Overview PERA is a reference architecture that can model the enterprise in multiple layers and in multiple stages of the architectural life cycle. Initially PERA was part of the PERA methodology, which consisted of three main building blocks: * Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture, * Purdue Reference Model, and * Purdue implementation procedures manual PERA has been further developed, and according to Gary Rathwell, PERA nowadays consists of the following components: :* ''The PERA Enterprise Life-cycle Framework or Model or Architecture...'' :* ''Concepts of maximum and minimum lines of automation...'' :* ''Concepts explaining the effect of recycle and time delays on the design and operation of facilities.'' :* ''The PERA Master Planning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
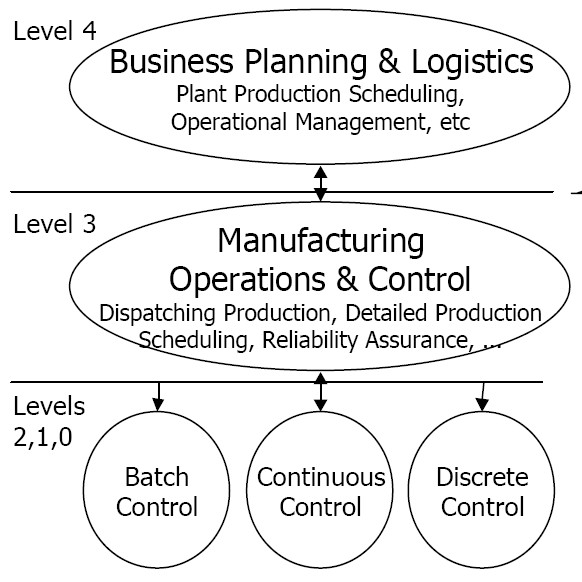
PERA Decision-making And Control Hierarchy
Pera may refer to: Places * Pera (Beyoğlu), a district in Istanbul formerly called Pera, now called Beyoğlu ** Galata, a neighbourhood of Beyoğlu, often referred to as Pera in the past * Pêra (Caparica), a Portuguese locality in the district of Setúbal * Pera (San Giovanni di Fassa), an Italian hamlet in the municipality of San Giovanni di Fassa, in Trentino * Pêra (Silves), a Portuguese parish in the district of Faro in the Algarve * Pera Orinis, a village in Cyprus Other uses * Pera (surname) * The '' Pera'', a ship of the Dutch East India Company * Peda or Pera, a dessert in Pakistan and India * ''Pera'' (plant), a plant genus in the family Peraceae * Public Employees Retirement Association, the name of several public employee pension plans in the United States * Peripheral ERA, a baseball statistic * Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA) is a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture, developed by Theodore J. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Control
Enterprise control is the ability to combine control, intelligence and process management to enable business optimization that is inclusive of business and production operations. It combines the strength of both business processes and production operations processes. It is the deliberate act of synchronizing business strategy with operational execution in real-time to enable closed loop business control across an enterprise. Key elements * Enterprise resource planning (ERP) * Supply chain * Environment and safety systems * Assets * People Interoperating enterprise and industrial service-oriented architectures (SOA) provide industrial companies with the potential for problem solutions that cover entire plants and entire industrial enterprises. This enterprise-wide system can be developed using systems and technologies previously installed. The resulting system, consisting of multiple vendor products acquired over many years working as a single system, is what is referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy Doumeingts
Guy Doumeingts (born 1938) is a French engineer, Emeritus professor at the University of Bordeaux 1 and former Director of "Laboratoire d’Automatique, Productique Signal et Image" control theory, known for the development of the GRAI method and his contributions to the field of Enterprise modelling. Biography Doumeingts received his MS at the University of Bordeaux 1, where in 1984 he also received his PhD in Control Theory with the thesis, entitled ''La Méthode GRAI''. Doumeingts spend his academic career at the University Bordeaux I, where he was appointed professor and initiated and directed the GRAI/LAP (Laboratory of Automation and Productics). He chaired the Technical Committee on Computer Application in Technology at the IFIP (International Federation for Information Processing), and was member of the Editorial Board of several journals. In 2012 Doumeingts was elected General Manager of INTEROP-VLab (International Virtual Laboratory for Enterprise Interoperability), a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bruno Vallespir
Bruno Vallespir (born 1960) is a French engineer, and Professor of Enterprise Modelling at the University of Bordeaux, working in the fields of production management, performance evaluation and enterprise modeling.Ejub Kajan eds. (2011) ''Electronic Business Interoperability.'' p. 733 Biography Vallespir received his PhD in at the University of Bordeaux with the thesis, entitled "Exploitation des systèmes de production discrets-continus: contribution à une méthode de conception." Vallespir started his academic career at the University of Bordeaux, where in 2004 he was appointed Professor of Enterprise Modelling as successor of Guy Doumeingts. He is member of several IFIP working groups, including the WG 5.7 workgroup on Integrated Production Management. He has participated in the INTEROP NoE and the development of the Model Driven Interoperability (MDI) Framework. Selected publications Vallespir published several books and articles in his field of expertise.: * Bruno Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Bernus
Peter Bernus (born 1949) is a Hungarian Australian scientist and Associate Professor of Enterprise Architecture at the School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia.Peter Bernus Accessed 10 January 2009. Biography Peter Bernus graduated from as an engineer in electronic technology in 1976. He started working at the Mechanical Engineering Automation Division Computer and Automation Institute of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. In 1990 he became a research of ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manufacturing Execution System
Manufacturing execution systems (MES) are computerized systems used in manufacturing to track and document the transformation of raw materials to finished goods. MES provides information that helps manufacturing decision-makers understand how current conditions on the plant floor can be optimized to improve production output. MES works as real-time monitoring system to enable the control of multiple elements of the production process (e.g. inputs, personnel, machines and support services). MES may operate across multiple function areas, for example management of product definitions across the product life-cycle, resource scheduling, order execution and dispatch, production analysis and downtime management for overall equipment effectiveness (OEE), product quality, or materials track and trace. MES creates the "as-built" record, capturing the data, processes and outcomes of the manufacturing process. This can be especially important in regulated industries, such as food and bever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Integration
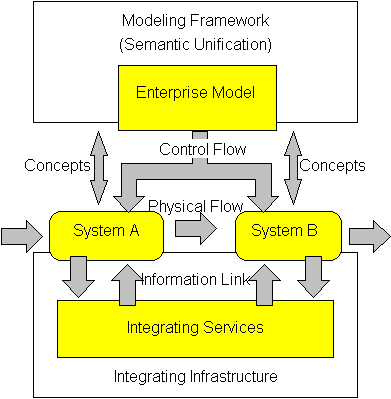
Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments. It is a concept in enterprise engineering to provide the relevant information and thereby enable communication between people, machines and computers and their efficient co-operation and co-ordination. The Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) framework defined by the IFAC/IFIP Task Force provides the necessary guidance of the modelling process, see figure, and enables semantic unification of the model contents as well. The framework identifies the set of components necessary and helpful for enterprise modelling. The general concepts identified and defined in the reference architecture consist of life cycle, life history, model views among others. These concept help the user to create and maintain the process models ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ANSI/ISA-95
ANSI/ISA-95, or ISA-95 as it is more commonly referred, is an international standard from the International Society of Automation for developing an automated interface between enterprise and control systems. This standard has been developed for global manufacturers. It was developed to be applied in all industries, and in all sorts of processes, like batch processes, continuous and repetitive processes. The objectives of ISA-95 are to provide consistent terminology that is a foundation for supplier and manufacturer communications, provide consistent information models, and to provide consistent operations models which is a foundation for clarifying application functionality and how information is to be used. There are 5 parts of the ISA-95 standard. ANSI/ISA-95.00.01-2000, Enterprise-Control System Integration Part 1: Models and Terminology consists of standard terminology and object models, which can be used to decide which information should be exchanged. The models help defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Resource Planning
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is the integrated management of main business processes, often in real time and mediated by software and technology. ERP is usually referred to as a category of Business management tools, business management software—typically a suite of integrated application software, applications—that an organization can use to collect, store, manage and interpret data from many business sector, business activities. ERP systems can be local based or Cloud computing, cloud-based. Cloud-based applications have grown in recent years due to information being readily available from any location with Internet access. Traditional On-premises software, on-premise ERP systems are now considered Legacy system, legacy technology. ERP provides an integrated and continuously updated view of core business processes using common databases maintained by a database management system. ERP systems track business resources—cash, raw materials, production capacity—and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operational Historian
Operational historian refers to a complementary set of time-series database applications that are developed for operational process data. Historian software is often embedded or used in conjunction with standard DCS and PLC control systems to provide enhanced data capture, validation, compression, and aggregation capabilities. Historians have been deployed in almost every industry and contribute to functions such as supervisory control, performance monitoring, quality assurance, and, more recently, machine learning applications which can learn from vast quantities of historical data. These systems were originally developed to capture instrumentation and control data, which led many to use the term "tag" for a stream of process data, referring to the physical "tags" which had been placed on instrumentation for manually capturing data. Raw data may be accessed via OPC HDA, SQL, or REST API interfaces.{{cite web, url= https://www.parasyn.com.au/operational-historian-vs-enterpris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
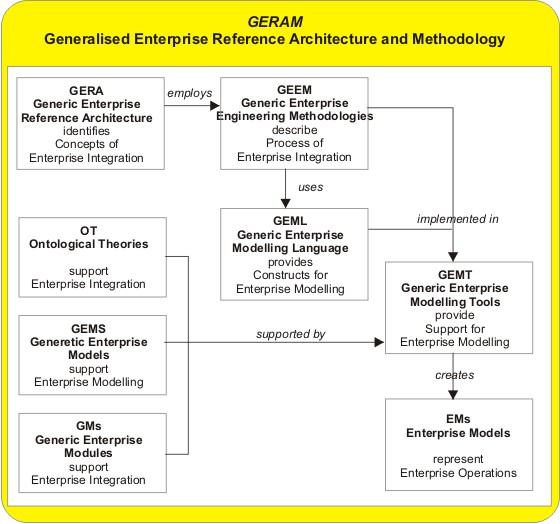
Generic Enterprise Reference Architecture And Methodology
Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) is a generalised enterprise architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering. J.G. Nell, NIST (1997).An Overview of GERAM ICEIMT'97 International Conference on Enterprise Integration Modelling Technology 1997. Updated 30 January 1997 This framework was developed in the 1990s by a joint task force of both the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC) and the International Federation of Information Processing (IFIP) on enterprise architectures for enterprise integration. The development started with the evaluation of then-existing frameworks for enterprise application integration, which was developed into an overall definition of a so-called "generalised architecture". P. Bernus, and L. Nemes (1994). "A Framework to Define a Generic Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology". In: ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |