|
Publius Cornelius Scipio Asina
Publius Cornelius Scipio Asina (c. 260 BC – after 211 BC) was a Roman politician and general who served as consul in 221 BC, and as such campaigned against the Histri, a people in the northern Adriatic. Asina belonged to the Scipionic-Aemilian faction which dominated Roman politics at the beginning of the Second Punic War, and advocated for an aggressive policy against Hannibal. This stance led him to oppose the more prudent strategy of Fabius Maximus. He was notably appointed Interrex in 216 BC, probably in order to manipulate the elections. Asina was also a founder of Piacenza. Family background Asina was a member of the patrician gens Cornelia, one of the leading gentes throughout the Republic. Members of the gens had held 29 consulships before him. The Scipiones were one of the stirpes of the Cornelii that emerged during the fourth century, and by Asina's time it had become very influential. All his known relatives were consul in the third century: Asina's father Gnaeus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and greatest naval war of antiquity, the two powers struggled for supremacy. The war was fought primarily on the Mediterranean island of Sicily and its surrounding waters, and also in North Africa. After immense losses on both sides, the Carthaginians were defeated. The war began in 264 BC with the Romans gaining a foothold on Sicily at Messana (modern Messina). The Romans then pressed Syracuse, the only significant independent power on the island, into allying with them and laid siege to Carthage's main base at Akragas. A large Carthaginian army attempted to lift the siege in 262 BC but was heavily defeated at the Battle of Akragas. The Romans then built a navy to challenge the Carthaginians', and using novel tactics inflicted severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient Indo-European people, reached the apogee of their influence and territorial expansion during the 4th century bc, extending across the length of Europe from Britain to Asia Minor."; . " e Celts, were Indo-Europeans, a fact that explains a certain compatibility between Celtic, Roman, and Germanic mythology."; . "The Celts and Germans were two Indo-European groups whose civilizations had some common characteristics."; . "Celts and Germans were of course derived from the same Indo-European stock."; . "Celt, also spelled Kelt, Latin Celta, plural Celtae, a member of an early Indo-European people who from the 2nd millennium bce to the 1st century bce spread over much of Europe."; in Europe and Anatolia, identified by their use of Celtic langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Istria
Istria ( ; Croatian language, Croatian and Slovene language, Slovene: ; ist, Eîstria; Istro-Romanian language, Istro-Romanian, Italian language, Italian and Venetian language, Venetian: ; formerly in Latin and in Ancient Greek) is the largest peninsula within the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Kvarner Gulf. It is shared by three countries: Croatia, Slovenia, and Italy.Marcel Cornis-Pope, John Neubauer''History of the literary cultures of East-Central Europe: junctures and disjunctures in the 19th And 20th Centuries'' John Benjamins Publishing Co. (2006), Alan John Day, Roger East, Richard Thomas''A political and economic dictionary of Eastern Europe'' Routledge, 1sr ed. (2002), Croatia encapsulates most of the Istrian peninsula with its Istria County. Geography The geographical features of Istria include the Učka/Monte Maggiore mountain range, which is the highest portion of the Ćićarija/Cicceria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaius Terentius Varro
Gaius Terentius Varro ( 218–200 BC) was a Roman politician and general active during the Second Punic War. A plebeian son of a butcher, he was a populist politician who was elected consul for the year 216 BC. While holding that office, he was decisively defeated by Hannibal at the Battle of Cannae. Early years Varro was a member of a plebeian family, the '' gens Terentia'', and the first man of note in his family. His father was reportedly a butcher who had "employed his son in the menial tasks associated with that profession." Despite this low birth, on his father's death he used the inheritance to embark on a public career, making his name by prosecuting those of higher status and progressing through the various magistracies of the ''cursus honorum'', holding the quaestorship and both the plebeian and curule aedileships.Livy. 22.26.1. When discussing the provenance of his cognomen, Servius suggests that this Varro served in the First Illyrian War. His first time in office for w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
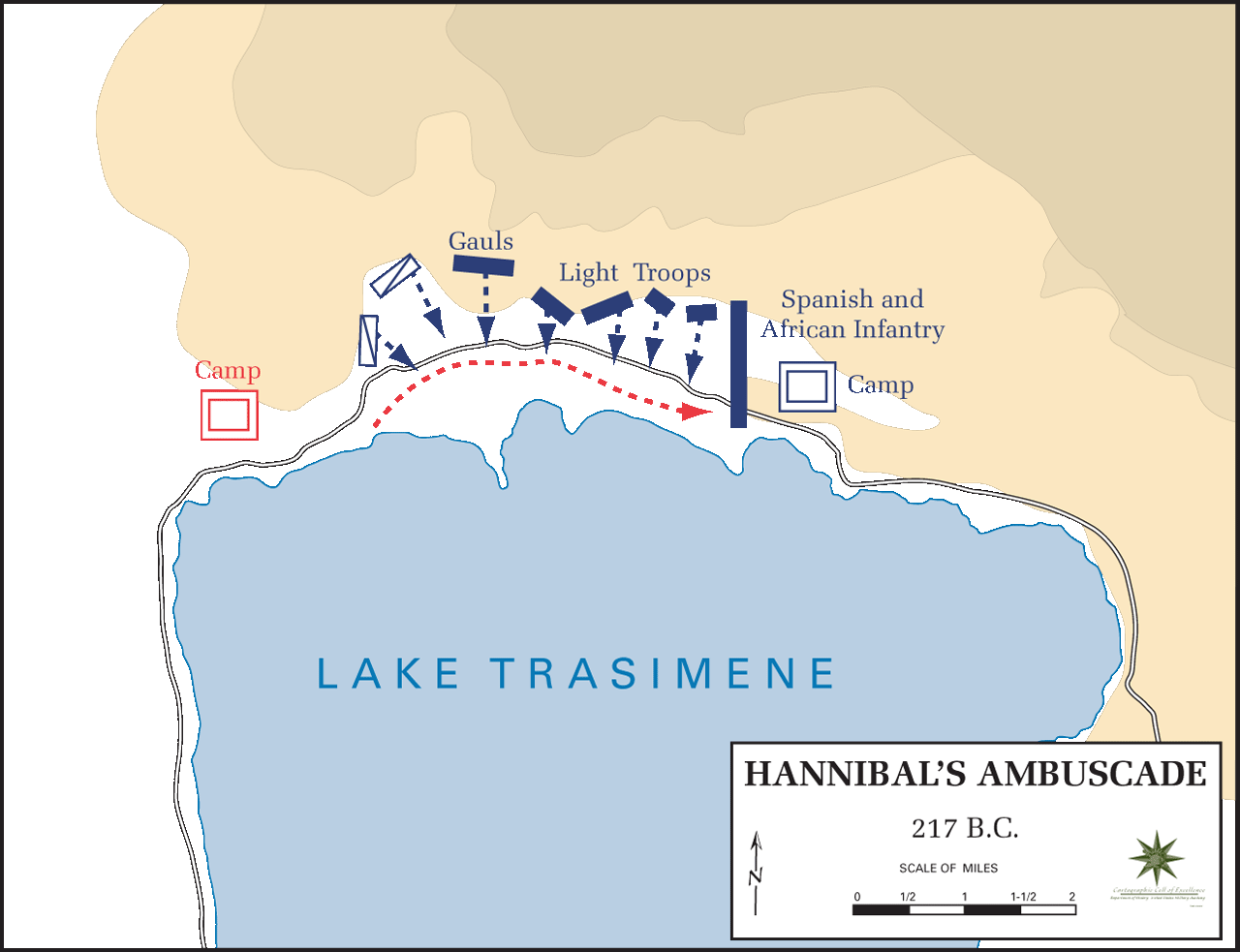
Gaius Flaminius (consul 223 BC)
Gaius Flaminius (c. 275 BC217 BC) was a leading Roman politician in the third century BC. Twice consul, in 223 and 217, Flaminius is notable for the ''Lex Flaminia'', a land reform passed in 232, the construction of the Circus Flaminius in 221, and his death at the hands of Hannibal's army at the Battle of Lake Trasimene in 217, during the Second Punic War. Flaminius is celebrated by ancient sources as being a skilled orator and a man possessed of great piety, strength, and determination. He is, however, simultaneously criticised by ancient writers such as Cicero and Livy for his popular policies and disregard of Roman traditions, particularly during the terms of his tribunate and second consulship. Tribunate and the ''Lex Flaminia'', 232 BC Flaminius was elected as tribune of the plebs in 232 BC. Cicero writes that Flaminius was an accomplished orator before the people, a skill that likely helped him achieve the tribunate. During his term Flaminius proposed the ''Lex Flaminia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiberius Sempronius Longus (consul 218 BC)
Tiberius Sempronius Longus (''c.'' 260 BC – unknown) was a Roman consul during the Second Punic War and a contemporary of Publius Cornelius Scipio (father of Scipio Africanus). In 218 BC, Sempronius was sent to Sicily with 160 quinqueremes to gather forces and supplies, while Scipio was sent to Iberia to intercept Hannibal. It was at this time, striking from Lilybaeum, on the island of Sicily, that Sempronius Longus captured Malta from the Carthaginians. Shortly thereafter, with Scipio wounded and pursued by Hannibal's forces after the Battle of Ticinus, the Senate sent for Tiberius Sempronius Longus. Upon his arrival in December, and reportedly against Scipio's advice, Sempronius Longus led an ambitious attack at the Battle of the Trebia. His army charged into a trap and was enveloped by the forces of Hannibal's brother, Mago. Although it was a crushing Roman defeat, Tiberius Sempronius Longus and a force of 10,000 infantrymen fought their way through the rear Carthaginian li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Livius Salinator
Marcus Livius Salinator (254 – c. 191 BC) was a Roman general and politician who fought in the Second Punic War, most notably during the Battle of the Metaurus. Born in 254 BC, Livius was elected consul of the Roman Republic with Lucius Aemilius Paullus (consul 219 BC), Lucius Aemilius Paulus shortly before the Second Illyrian War in 219 BC. After leading a successful campaign against the Illyrians, he was charged with malfeasance concerning war spoils during a mission to Carthage and was tried and found guilty on his return to Rome. After his removal as consul, he retired from public life for several years, until 210 BC. In 207 BC, during the Second Punic War, he was again elected consul (supposedly against his wishes) with Gaius Claudius Nero. Arriving in Narni, Livius attempted to block the advance of the Carthaginian army invading the Italian peninsula. Encountering Carthaginians near Fano, Fanum in the spring of 207 BC, Livius, reinforced by the army of his colleague Nero, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Centuriate Assembly
The Centuriate Assembly (Latin: ''comitia centuriata'') of the Roman Republic was one of the three voting assemblies in the Roman constitution. It was named the Centuriate Assembly as it originally divided Roman citizens into groups of one hundred men by classes. The centuries initially reflected military status, but were later based on the wealth of their members. The centuries gathered into the Centuriate Assembly for legislative, electoral, and judicial purposes. The majority of votes in any century decided how that century voted. Each century received one vote, regardless of how many electors each Century held. Once a majority of centuries voted in the same way on a given measure, the voting ended, and the matter was decided.Taylor, 40 Only the Centuriate Assembly could declare war or elect the highest-ranking Roman magistrates: consuls, praetors and censors.Abbott, 257 The Centuriate Assembly could also pass a law that granted constitutional command authority, or "Imperium", to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cassiodorus
Magnus Aurelius Cassiodorus Senator (c. 485 – c. 585), commonly known as Cassiodorus (), was a Roman statesman, renowned scholar of antiquity, and writer serving in the administration of Theodoric the Great, king of the Ostrogoths. ''Senator'' was part of his surname; not his rank. He also founded a monastery, Vivarium, where he spent the last years of his life. Life Cassiodorus was born at Scylletium, near Catanzaro in Calabria, Italy. Some modern historians speculate that his family was of Syrian origin based on his Greek name. His ancestry included some of the most prominent ministers of the state extending back several generations. His great-grandfather held a command in the defense of the coasts of southern Italy from Vandal sea-raiders in the middle of the fifth century; his grandfather appears in a Roman embassy to Attila the Hun, and his father (who bore the same name) served as ''comes sacrarum largitionum'' and ''comes rerum privatarum'' to Odovacer and as Praetorian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Minucius Rufus
Marcus Minucius Rufus (died August 2, 216 BC) was a Roman consul in 221 BC. He was also Magister Equitum during the dictatorship of Quintus Fabius Maximus Verrucosus known as ''Cunctator''. He was a political enemy of Fabius Maximus. He was against his delaying defensive strategy during the Second Punic War. While the Carthaginians had been busy at Geronium, Fabius had left Minucius in charge of the Roman army with instructions to follow the "Fabian strategy" and journeyed to Rome to observe some religious duties. Minucius, who had always advocated a more forward strategy against Hannibal, moved down from the hills after a few days and set up a new camp in the plain of Larinum to the north of Geronium. The Romans then began harassing the Carthaginian foragers from their new camp as Minucius sought to provoke Hannibal into battle. Hannibal in response moved near the Roman camp from Geronium with two thirds of his army, built a temporary camp and occupied a hill overlooking the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sicilia (Roman Province)
Sicilia (; , Ancient Greek: Σικελία) was the first province acquired by the Roman Republic, encompassing the island of Sicily. The western part of the island was brought under Roman control in 241 BC at the conclusion of the First Punic War with Carthage. A praetor was regularly assigned to the island from c.227 BC. The Kingdom of Syracuse under Hieron II remained an independent ally of Rome until its defeat in 212 BC during the Second Punic War. Thereafter the province included the whole of the island of Sicily, the island of Malta, and the smaller island groups (the Egadi islands, the Lipari islands, Ustica, and Pantelleria). During the Roman Republic, the island was the main source of grain for the city of Rome. Extraction was heavy, provoking armed uprisings known as the First and Second Servile Wars in the second century BC. In the first century, the Roman governor, Verres, was famously prosecuted for his corruption by Cicero. In the civil wars which brought the Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |