|
Publius Aelius Aelianus
Publius Aelianus Aelianus was a senior officer in the Imperial Roman army in the mid-Third Century AD who rose from relatively lowly origins to become the prefect of a legion under the Emperor Gallienus He was one of the earliest beneficiaries of Gallienus's policy that effectively excluded senators from army commands in favour of career-soldiers of equestrian rank. His later life is obscure. He was possibly ''procurator'' (i.e. Chief Financial Officer) of Epirus in the late-260s, but the foremost authorities query this identification. However, there are stronger grounds for believing that he was appointed a ''praeses'' (provincial governor of equestrian rank) in ''Africa'', most likely under the Emperor Probus. Sources The sum total of our knowledge of this man derives from five epigraph inscriptions from: (a) A fragment of an epigraphic inscription from ''Poetovio'' (now Ptuj in Slovenia) that indicates that one ''AEL...I'' (a '' Vir Egregius'', presumed to be Aelianus) comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial Roman Army
The Imperial Roman army was the military land force of the Roman Empire from about 30 BC to 476 AD, and the final incarnation in the long history of the Roman army. This period is sometimes split into the Principate (30 BC – 284 AD) and the Dominate (285–476) periods. Under Augustus (), the army consisted of '' legions'', eventually ''auxilia'' and also '' numeri''. By the end of Augustus' reign, the imperial army numbered some 250,000 men, equally split between 25 legions and 250 units of auxiliaries. The numbers grew to a peak of about 450,000 by 211, in 33 legions and about 400 auxiliary units. By then, auxiliaries outnumbered legionaries substantially. From this peak, numbers probably underwent a steep decline by 270 due to plague and losses during multiple major barbarian invasions. Numbers were restored to their early 2nd-century level of c. 400,000 (but probably not to their 211 peak) under Diocletian (r. 284–305). After the Empire's borders became settled (on the R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
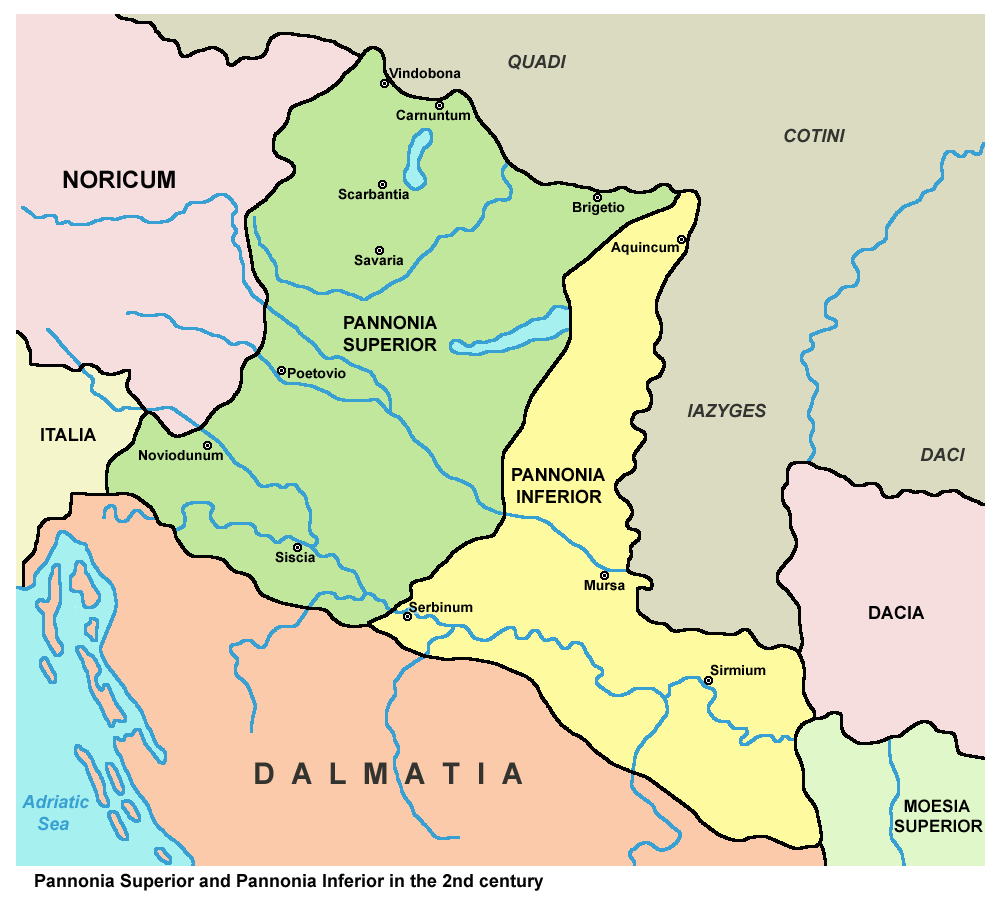
Pannonia Inferior
Pannonia Inferior, lit. Lower Pannonia, was a province of the Roman Empire. Its capital was Sirmium. It was one of the border provinces on the Danube. It was formed in the year 103 AD by Emperor Trajan who divided the former province of Pannonia into two parts: Pannonia Superior and Pannonia Inferior. The province included parts of present-day states of Hungary, Serbia, Croatia, and Bosnia and Herzegovina. The province was bordered to the east (across the Danube) by a Sarmatian tribe—the Iazyges. Later, the Vandals appeared to the north-east. Settlements Major settlements in Pannonia Inferior included: * ''Sirmium'' (Sremska Mitrovica) which several times served as an imperial residence for several emperors. * ''Aquincum'' ( Buda), the provincial capital. * ''Cuccium'' (Ilok) * ''Cibalae'' (Vinkovci) * ''Mursa'' ( Osijek) * ''Certissa'' (Đakovo) * ''Marsonia'' (Slavonski Brod) * ''Sopianae'' (Pécs) Aftermath and legacy The province was yet again split during the reign of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principate
The Principate is the name sometimes given to the first period of the Roman Empire from the beginning of the reign of Augustus in 27 BC to the end of the Crisis of the Third Century in AD 284, after which it evolved into the so-called Dominate. The Principate is characterised by the reign of a single emperor (''princeps'') and an effort on the part of the early emperors, at least, to preserve the illusion of the formal continuance, in some aspects, of the Roman Republic. Etymology and anticipations *'Principate' is etymologically derived from the Latin word ''princeps'', meaning ''chief'' or ''first'', and therefore represents the political regime dominated by such a political leader, whether or not he is formally head of state or head of government. This reflects the principate emperors' assertion that they were merely "first among equals" among the citizens of Rome. *Under the Republic, the ''princeps senatus'', traditionally the oldest or most honoured member of the Senate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noricum
Noricum () is the Latin name for the Celts, Celtic kingdom or federation of tribes that included most of modern Austria and part of Slovenia. In the first century AD, it became a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire. Its borders were the Danube to the north, Raetia and Vindelici to the west, Pannonia to the east and south-east, and Roman Italy, Italia (Triveneto, Venetia et Histria) to the south. The kingdom was founded around 400 BC, and had its capital at the royal residence at Virunum on the Magdalensberg. Area and population Around 800 BC, the region was inhabited mostly by the people of the local Celtic Hallstatt culture. Around 450 BC, they merged with the people of the other core Celtic areas in the south-western regions of Germany and La Tène culture, eastern France. The country is mountainous and rich in iron and salt. It supplied material for the manufacturing of arms in Pannonia, Moesia, and northern Italy. The famous Noric steel was largely used in the maki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Comitatenses
The comitatenses and later the palatini were the units of the field armies of the late Roman Empire. They were the soldiers that replaced the legionaries, who had formed the backbone of the Roman military since the Marian reforms. Organization Units such as the Joviani and Herculiani had 5,000 soldiers and 726–800 cavalrymen. Many units' sizes would vary. There were three types of units. They were the heavy infantry, medium infantry, and light infantry. The ''comitatenses'' were the heavy infantry. The Auxiliaries, Auxilia Palatina, and the Peltasts were the medium infantry, and the psiloi were the light infantry. Comitatenses regiments consisted of 1,024 soldiers. Comitatenses legions could consist of 6,000 to 7,000 soldiers. Some of these soldiers would be lightly armed, while others would be heavily armed. During a battle the army would divide into 3-4 divisions. The army might use a double phalanx to protect its rear. Reserves would be located behind or between each di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protectores Augusti Nostri
''Protector Augusti Nostri'' (''lit'' 'Protector of Our Augustus') was a title given to individual officers of the Roman army as a mark of their devotion to and approval by the Emperor himself. The term first appears with this meaning in the joint-reign of Valerian and Gallienus. Lucius Petronius Taurus Volusianus was the first recorded ''Protector'' appointed by Gallienus. Imperial Guards of Gallienus The use of the title ''protector'' in the sense of a 'bodyguard of a Great Man' long preceded the appointment of Volusianus. In addition, the title was not only bestowed by Emperors. However, it does seem to be the case that Gallienus was the originator of the ''Protectores Augusti Nostri''. It seems that, when it was first bestowed, this title signified an honour conferred on rather than a function carried out by the recipient. It seems to have been granted to officers who had distinguished themselves serving directly under Gallienus in his wars against barbarian invaders of the Bal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valerian (emperor)
Valerian (; la, Publius Licinius Valerianus; c. 199 – 260 or 264) was Roman emperor from 253 to spring 260 AD. He persecuted Christians and was later taken captive by the Persian emperor Shapur I after the Battle of Edessa, becoming the first Roman emperor to be captured as a prisoner of war, causing shock and instability throughout the Roman Empire. The unprecedented event and the unknown fate of the captured emperor generated a variety of different reactions and "new narratives about the Roman Empire in diverse contexts". Biography Origins and rise to power Unlike many of the would-be emperors and rebels who vied for imperial power during the Crisis of the Third Century of the Roman Empire, Valerian was of a noble and traditional senatorial family. Details of his early life are sparse, except for his marriage to Egnatia Mariniana, with whom he had two sons: later emperor Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus and Licinius Valerianus. He was Consul for the first time either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martialis
Marcus Valerius Martialis (known in English as Martial ; March, between 38 and 41 AD – between 102 and 104 AD) was a Roman poet from Hispania (modern Spain) best known for his twelve books of ''Epigrams'', published in Rome between AD 86 and 103, during the reigns of the emperors Domitian, Nerva and Trajan. In these short, witty poems he cheerfully satirises city life and the scandalous activities of his acquaintances, and romanticises his provincial upbringing. He wrote a total of 1,561 epigrams, of which 1,235 are in elegiac couplets. Martial has been called the greatest Latin epigrammatist, and is considered the creator of the modern epigram. Early life Knowledge of his origins and early life are derived almost entirely from his works, which can be more or less dated according to the well-known events to which they refer. In Book X of his ''Epigrams'', composed between 95 and 98, he mentions celebrating his fifty-seventh birthday; hence he was born during March 38, 39, 4 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regalianus
P. C. Regalianus (died 260/261), also known as Regalian, was Roman usurper for a few months in 260 and/or 261, during the Crisis of the Third Century, a period of intense political instability in the Roman Empire. Regalianus was acclaimed emperor by the troops along the Danube river, a region of the empire that frequently experienced barbarian raids, probably in the hope that he might be able to secure the frontier. Accounts by surviving literary sources concerning Regalianus are brief and few in number, and are mostly considered unreliable. The ''Historia Augusta'' relates that he was of Dacian descent, and a descendant of the Dacian king Decebalus, but this is mostly rejected in modern scholarship. Regalianus was married to Sulpicia Dryantilla, a woman from a prestigious senatorial family, which instead points to Regalianus also being of high-ranking Roman descent. Regalianus' acclamation as emperor was in the wake of a previous usurpation attempt by Ingenuus, also proclaimed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roxolani
The Roxolani or Rhoxolāni ( grc, Ροξολανοι , ; la, Rhoxolānī) were a Sarmatian people documented between the 2nd century BC and the 4th century AD, first east of the Borysthenes (Dnieper) on the coast of Lake Maeotis (Sea of Azov), and later near the borders of Roman Dacia and Moesia. They are believed to be an offshoot of the Alans. Name The name ''Roxolani'' is generally interpreted as a compound formed with the Alanic root *''rox''- (modern Osset. or 'light, luminous'; Avest. ''raox''-''šna-'' 'luminous, shining') attached to the tribal name ''Alān''. This would make ''Roxolani'' an endonym translatable as the 'luminous' or the 'shining Alans'. The name could be linked to aspects of worship or the supernatural, as suggested by the modern Ossetian expression ''rūxsag ū'' ('may you be blessed'), addressed to the deceased, or the name ''Wacyrūxs'' ('divine light'), mentioned in the Nart sagas.' Historian George Vernadsky suggested that the ''Rocas'' (or '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vexillationes
A ''vexillatio'' (plural ''vexillationes'') was a detachment of a Roman legion formed as a temporary task force created by the Roman army of the Principate. It was named from the standard carried by legionary detachments, the ''vexillum'' (plural ''vexilla''), which bore the emblem and name of the parent legion. Although commonly associated with legions, it is likely that ''vexillationes'' included auxiliaries. The term is found in the singular, referring to a single detachment, but is usually used in the plural to refer to an army made up of picked detachments. ''Vexillationes'' were assembled ad hoc to meet a crisis on Rome's extensive frontiers, to fight in a civil war, or to undertake an offensive against Rome's neighbours. They varied in size and composition, but usually consisted of about 1000 infantry and/or 500 cavalry. Purpose Most of the Roman Army (around 400,000 strong at the beginning of the 3rd century) was stationed along the frontiers from the time of Hadrian, if n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primus Pilus
The ''primus pilus'' or ''primipilus'' was the senior centurion of the first cohort in a Roman legion, a formation of five double-strength centuries of 160 men, was called the ''primus pilus''; he was a career soldier and advisor to the legate. The ''Primus Pilus'' would remain in command for one year. They could continue to serve in the army after their term ended if there was a vacancy in command or if they wished to become an independent commander of an ''auxilia'' unit or the ''praefectus castrorum''. During the Roman Empire, emperor Claudius created the office of ''primus pilus iterum''. To become the ''primus pilus iterum'' an officer must have formerly served as a tribune in the ''vigiles'', ''cohortes urbanae'', or Praetorian Guard. The ''primus pilus iterum'' would hold the responsibility of a Praefectus castrorum but with higher pay. The ''primus pilus'' was a well paid position. They could accumulate enough wealth to become part of the equestrian class. Even if ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



_obverse.jpg)


