|
Psoas Sign
The psoas sign, also known as Cope's sign (or Cope's psoas test) or Obraztsova's sign, is a medical sign that indicates irritation to the iliopsoas group of hip flexors in the abdomen, and consequently indicates that the inflamed appendix is retrocaecal in orientation (as the iliopsoas muscle is retroperitoneal). The technique for detecting the psoas sign is carried out on the patient's right leg. The patient lies on his/her left side with the knees extended. The examiner holds the patient's right thigh and passively extends the hip. Alternatively, the patient lies on their back, and the examiner asks the patient to actively flex the right hip against the examiner's hand. If abdominal pain results, it is a "positive psoas sign". The pain results because the psoas borders the peritoneal cavity, so stretching (by hyperextension at the hip) or contraction (by flexion of the hip) of the muscles causes friction against nearby inflamed tissues. In particular, the right iliopsoas muscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boas' Sign
Boas' or Boas's sign is hyperaesthesia (increased or altered sensitivity) below the right Hypochondrium or 12th rib region, which can be a symptom in acute cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder). It is one of many signs a medical provider may look for during an abdominal examination. Originally this sign referred to point tenderness in the region to the right of the 10th to 12th thoracic vertebrae. It is less than 7% sensitive. Its namesake is Ismar Isidor Boas (1858–1938), a German physician and the first licensed GI specialist in his country. Boas' sign can also indicate stomach and duodenal disease. When the transverse processes of thoracic vertebrae T10-T12 are pressed or effleuraged with the bottom of the hand, pain can appear at the left of spinous processes (in stomach's lesser curvature ulcer) or at the right (in pyloric or duodenal ulcer Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supine Position
The supine position ( or ) means lying horizontally with the face and torso facing up, as opposed to the prone position, which is face down. When used in surgical procedures, it grants access to the peritoneal, thoracic and pericardial regions; as well as the head, neck and extremities. Using anatomical terms of location, the dorsal side is down, and the ventral side is up, when supine. Semi-supine In scientific literature "semi-supine" commonly refers to positions where the upper body is tilted (at 45° or variations) and not completely horizontal. Relation to sudden infant death syndrome The decline in death due to sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) is said to be attributable to having babies sleep in the supine position. The realization that infants sleeping face down, or in a prone position, had an increased mortality rate re-emerged into medical awareness at the end of the 1980s when two researchers, Susan Beal in Australia and Gus De Jonge in the Netherlands, indep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rovsing's Sign
Rovsing's sign, named after the Danish surgeon Niels Thorkild Rovsing (1862–1927), is a sign of appendicitis. If palpation of the left lower quadrant of a person's abdomen increases the pain felt in the right lower quadrant, the patient is said to have a positive Rovsing's sign and may have appendicitis. The phenomenon was first described by Swedish surgeon Emil Samuel Perman (1856-1945) writing in the journal ''Hygiea'' in 1904. In acute appendicitis, palpation in the left iliac fossa may produce pain in the right iliac fossa. Referral of pain This anomaly occurs because the pain nerves deep in the intestines do not localize well to an exact spot on the abdominal wall, unlike pain nerves in muscles. Pain from a stomach ulcer or gallstone can be interpreted by the brain as pain from the stomach, liver, gall bladder, duodenum, or first part of the small intestine. It will "refer" pain often to the mid upper abdomen, the epigastrum. Because the appendix is a piece of inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obturator Sign
The obturator sign, also called Cope's obturator test, is an indicator of irritation to the obturator internus muscle. The technique for detecting the obturator sign, called the ''obturator test'', is carried out on each leg in succession. The patient lies on her/his back with the hip and knee both flexed at ninety degrees. The examiner holds the patient's ankle with one hand and knee with the other hand. The examiner internally rotates the hip by moving the patient's ankle away from the patient's body while allowing the knee to move only inward. This is flexion and internal rotation of the hip. In the clinical context, it is performed when acute appendicitis is suspected. In this condition, the appendix becomes inflamed and enlarged. The appendix may come into physical contact with the obturator internus muscle, which will be stretched when this maneuver is performed on the right leg. This causes pain and is evidence in support of an inflamed appendix. The principles of the obtu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamburger Sign
The hamburger sign is used in the diagnosis of appendicitis. The sign is used to rule out that disease, with the physician inquiring if the patient would like to consume his/her favourite food. If a patient wants to eat, consider a diagnosis other than appendicitis. Anorexia is 80% sensitive for appendicitis. A positive hamburger sign is demonstrated by a patient declining food. See also * Blumberg's sign * Obturator sign * Psoas sign * Rovsing's sign * McBurney's point McBurney's point is the name given to the point over the right side of the abdomen that is one-third of the distance from the anterior superior iliac spine to the umbilicus (navel). This is near the most common location of the appendix. Locati ... References {{Digestive system diseases Diseases of appendix Medical signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blumberg's Sign
Blumberg's sign (also referred to as rebound tenderness or Shchetkin–Blumberg's sign) is a clinical sign in which there is pain upon removal of pressure rather than application of pressure to the abdomen. (The latter is referred to simply as ''abdominal tenderness''.) It is indicative of peritonitis. It was named after German surgeon Jacob Moritz Blumberg. Procedure The abdominal wall is compressed slowly and then rapidly released. A positive sign is indicated by presence of pain upon removal of pressure on the abdominal wall. Clinical significance The sign indicates aggravation of the parietal peritoneum by stretching or moving. Positive Blumberg's sign is indicative of peritonitis, which can occur in diseases like appendicitis, and may occur in ulcerative colitis with rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. However, in recent years the value of rebound tenderness has been questioned, since it may not add any diagnostic value beyond the observation that the patient ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zachary Cope
Sir Vincent Zachary Cope MD MS FRCS (14 February 1881 – 28 December 1974) was an English physician, surgeon, author, historian and poet perhaps best known for authoring the book ''Cope's Early Diagnosis of the Acute Abdomen'' from 1921 until 1971. The work remains a respected and standard text of general surgery, and new editions continue being published by editors long after his death, the most recent one being the 22nd edition, published in 2010. Cope also wrote widely on the history of medicine and of public dispensaries. Early life Cope was the youngest of ten children of a minister, Thomas John Cope and his wife Celia Anne Crowle. He was head boy at Westminster City School where he was awarded a gold medal in 1899 and then a scholarship to go to St Mary's Hospital Medical School. He passed surgery and forensic medicine with distinction in 1905 and became house physician to David Lees, author of ''The Abdominal Inflammations.'' Lees influenced Cope in his lifelong in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliac Vessels (other)
Iliac vessels can refer to: * Iliac artery * Iliac vein In human anatomy, iliac vein refers to several anatomical structures located in the pelvis: * Common iliac vein, formed by the external and internal iliac veins, drains into the inferior vena cava * Deep circumflex iliac vein, formed by the union ... {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemorrhage
Bleeding, hemorrhage, haemorrhage or blood loss, is blood escaping from the circulatory system from damaged blood vessels. Bleeding can occur internally, or externally either through a natural opening such as the mouth, nose, ear, urethra, vagina or anus, or through a puncture in the skin. Hypovolemia is a massive decrease in blood volume, and death by excessive loss of blood is referred to as exsanguination. Typically, a healthy person can endure a loss of 10–15% of the total blood volume without serious medical difficulties (by comparison, blood donation typically takes 8–10% of the donor's blood volume). The stopping or controlling of bleeding is called hemostasis and is an important part of both first aid and surgery. Types * Upper head ** Intracranial hemorrhage – bleeding in the skull. ** Cerebral hemorrhage – a type of intracranial hemorrhage, bleeding within the brain tissue itself. ** Intracerebral hemorrhage – bleeding in the brain caused by the ruptu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
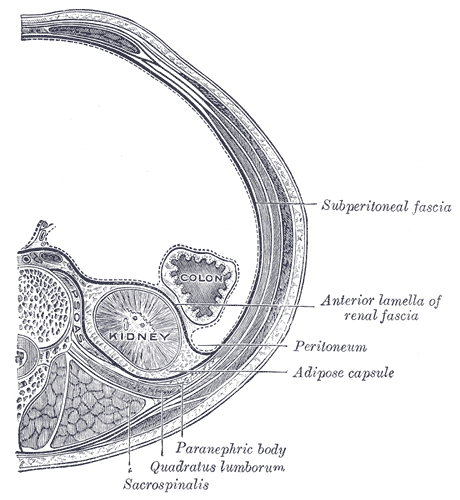
Retroperitoneal
The retroperitoneal space (retroperitoneum) is the anatomical space (sometimes a potential space) behind (''retro'') the peritoneum. It has no specific delineating anatomical structures. Organs are retroperitoneal if they have peritoneum on their anterior side only. Structures that are not suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity and that lie between the parietal peritoneum and abdominal wall are classified as retroperitoneal. This is different from organs that are not retroperitoneal, which have peritoneum on their posterior side and are suspended by mesentery in the abdominal cavity. The retroperitoneum can be further subdivided into the following: *Perirenal (or perinephric) space *Anterior pararenal (or paranephric) space *Posterior pararenal (or paranephric) space Retroperitoneal structures Structures that lie behind the peritoneum are termed "retroperitoneal". Organs that were once suspended within the abdominal cavity by mesentery but migrated posterior to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoas Abscess
An abscess in the psoas muscle of the abdomen may be caused by lumbar tuberculosis. Owing to the proximal attachments of the iliopsoas, such an abscess may drain inferiorly into the upper medial thigh and present as a swelling in the region. The sheath of the muscle arises from the lumbar vertebrae and the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae. The disc is more susceptible to infection, from tuberculosis and ''Salmonella discitis''. The infection can spread into the psoas muscle sheath. Treatment may involve drainage and antibiotics. Additional images See also * Femoral hernia * Transient synovitis Transient synovitis of hip (also called toxic synovitis; see below for more synonyms) is a self-limiting condition in which there is an inflammation of the inner lining (the synovium) of the capsule of the hip joint. The term irritable hip refer ... References External links Muscular disorders Peritoneum disorders {{endocrine-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vermiform Appendix
The appendix (or vermiform appendix; also cecal r caecalappendix; vermix; or vermiform process) is a finger-like, blind-ended tube connected to the cecum, from which it develops in the embryo. The cecum is a pouch-like structure of the large intestine, located at the junction of the small and the large intestines. The term "vermiform" comes from Latin and means "worm-shaped". The appendix was once considered a vestigial organ, but this view has changed since the early 2000s. Research suggests that the appendix may serve an important purpose. In particular, it may serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria. Structure The human appendix averages in length but can range from . The diameter of the appendix is , and more than is considered a thickened or inflamed appendix. The longest appendix ever removed was long. The appendix is usually located in the lower right quadrant of the abdomen, near the right hip bone. The base of the appendix is located beneath the ileoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |