|
Pseudodiploria Strigosa
''Pseudodiploria strigosa'', the symmetrical brain coral, is a colonial species of stony coral in the family Mussidae. It occurs on reefs in shallow water in the West Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea. It grows slowly and lives to a great age. Description The symmetrical brain coral forms smooth flat plates or massive hemispherical domes up to in diameter. The surface is covered with interlinking convoluted valleys in which the polyps sit in cup-shaped depressions known as corallites. Each of these has a number of radially arranged ridges known as septa which continue outside the corallite as costae and link with those of neighbouring corallites. The ridges separating the valleys are smoothly rounded and do not usually have a groove running along their apex as does the rather similar grooved brain coral (''Diploria labyrinthiformis''). The coral has symbiotic dinoflagellate alga called zooxanthella in its tissues and it is these which give the coral its colour of yellowish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Dwight Dana
James Dwight Dana Royal Society of London, FRS FRSE (February 12, 1813 – April 14, 1895) was an American geologist, mineralogist, volcanologist, and zoologist. He made pioneering studies of mountain-building, volcano, volcanic activity, and the origin and structure of continents and oceans around the world. His zoological author abbreviation is Dana. Early life and career Dana was born February 12, 1813, in Utica, New York. His father was merchant James Dana (1780–1860) and his mother was Harriet Dwight (1792–1870). Through his mother he was related to the Dwight New England family of missionaries and educators including uncle Harrison Gray Otis Dwight and first cousin Henry Otis Dwight. He showed an early interest in science, which had been fostered by Fay Edgerton, a teacher in the Utica high school, and in 1830 he entered Yale College in order to study under Benjamin Silliman the elder. Graduating in 1833, for the next two years he was teacher of mathematics to midshi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
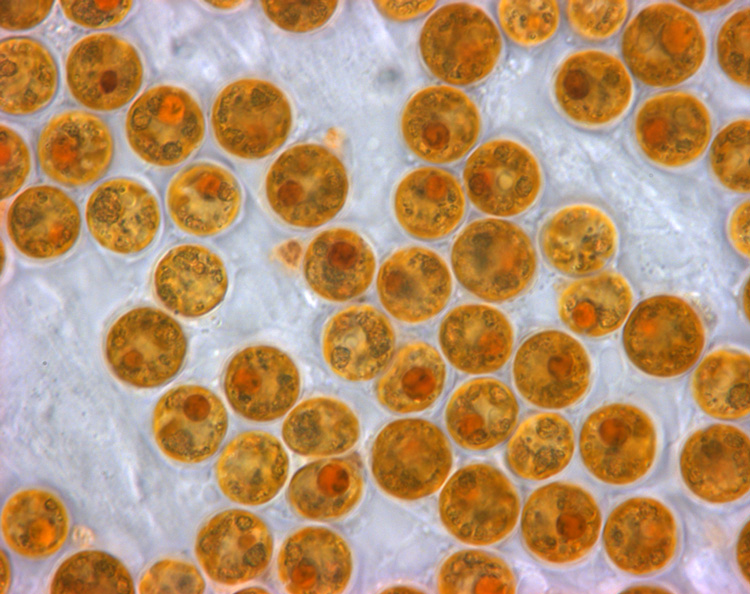
Dinoflagellate
The dinoflagellates (Greek δῖνος ''dinos'' "whirling" and Latin ''flagellum'' "whip, scourge") are a monophyletic group of single-celled eukaryotes constituting the phylum Dinoflagellata and are usually considered algae. Dinoflagellates are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. Their populations vary with sea surface temperature, salinity, and depth. Many dinoflagellates are photosynthetic, but a large fraction of these are in fact mixotrophic, combining photosynthesis with ingestion of prey (phagotrophy and myzocytosis). In terms of number of species, dinoflagellates are one of the largest groups of marine eukaryotes, although substantially smaller than diatoms. Some species are endosymbionts of marine animals and play an important part in the biology of coral reefs. Other dinoflagellates are unpigmented predators on other protozoa, and a few forms are parasitic (for example, ''Oodinium'' and ''Pfiesteria''). Some dinoflagellates pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooxanthellae
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus '' Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological Epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing Great American Interchang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Río Grande De Manatí
The Manatí River (Spanish: Río Grande de Manatí) is a river in Puerto Rico, which flows through several northern municipalities of the island. The river is named after the municipality of Manatí where the river mouth is located. Description The river travels in sequence through Barranquitas, the municipal boundaries of Orocovis, Corozal and Naranjito, Ciales, Morovis, Barceloneta and Manatí in Puerto Rico. The river flows into the Atlantic Ocean in the municipal boundary between Barceloneta and Manatí. History In the 1898 ''Military Notes on Puerto Rico'' by the U.S. it is written that the "Manatí River is bounded on the east 'south by the Sierra Grande and on the west by the Siales ridge. It rises in the Sierra Grande, and parallel with the preceding river, it flows through Siales and Manatí, to the north of which latter town it empties into the Atlantic." USACE project In mid 2018, the United States Army Corps of Engineers announced it had earmarked $1.2 milli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siderastrea Siderea
''Siderastrea siderea'', commonly known as massive starlet coral or round starlet coral, is a stony coral in the family Siderastreidae. It is found in shallow parts of the western Atlantic Ocean as solid boulder-shaped or domed structures. Description ''Siderastrea siderea'' is a colonial coral that forms low domes or boulder-shaped structures with a smooth dimpled surface as much as wide on the seabed. It can be encrusting when young. The corallites, the calcareous cup-shaped depressions in which the polyps sit, are about wide with about 50 or 60 little ridges called septa. The general colour is reddish brown. This species can be confused with the closely related lesser starlet coral ('' Siderastrea radians'') but that is usually smaller and has deeper, more angular corallites, each with 30 to 40 septa. Distribution and habitat ''Siderastrea siderea'' is found in the Caribbean Sea and the northern Gulf of Mexico and round the coasts of southern Florida, the Bahamas and Berm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pseudodiploria Clivosa
''Pseudodiploria clivosa'', the knobby brain coral, is a colonial species of stony coral in the family Mussidae. It occurs in shallow water in the West Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea. Description The knobby brain coral is a massive coral that either forms hemispherical domes or, particularly in areas of high wave action, forms plates and encrusts the seabed. It can grow to a diameter of about . The surface of the dome usually has a number of bulges or knobs but this species is not easy to distinguish from the symmetrical brain coral which tends to have a smoother outline. The surface consists of sharply delineated, convoluted ridges with valleys in between. There is no trough-like groove in the top of the ridge as is the case in the rather similar grooved brain coral ''(Diploria labyrinthiformis)''. The coral polyps are strung along the valley bottoms, each sitting in a little stony cup or corallite. The sides of these have minute walls called septa which come in four differ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooxanthella
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus ''Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algae
Algae (; singular alga ) is an informal term for a large and diverse group of photosynthetic eukaryotic organisms. It is a polyphyletic grouping that includes species from multiple distinct clades. Included organisms range from unicellular microalgae, such as ''Chlorella,'' ''Prototheca'' and the diatoms, to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelp, a large brown alga which may grow up to in length. Most are aquatic and autotrophic (they generate food internally) and lack many of the distinct cell and tissue types, such as stomata, xylem and phloem that are found in land plants. The largest and most complex marine algae are called seaweeds, while the most complex freshwater forms are the ''Charophyta'', a division of green algae which includes, for example, ''Spirogyra'' and stoneworts. No definition of algae is generally accepted. One definition is that algae "have chlorophyll ''a'' as their primary photosynthetic pigment and lack a sterile covering of cells around thei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |