|
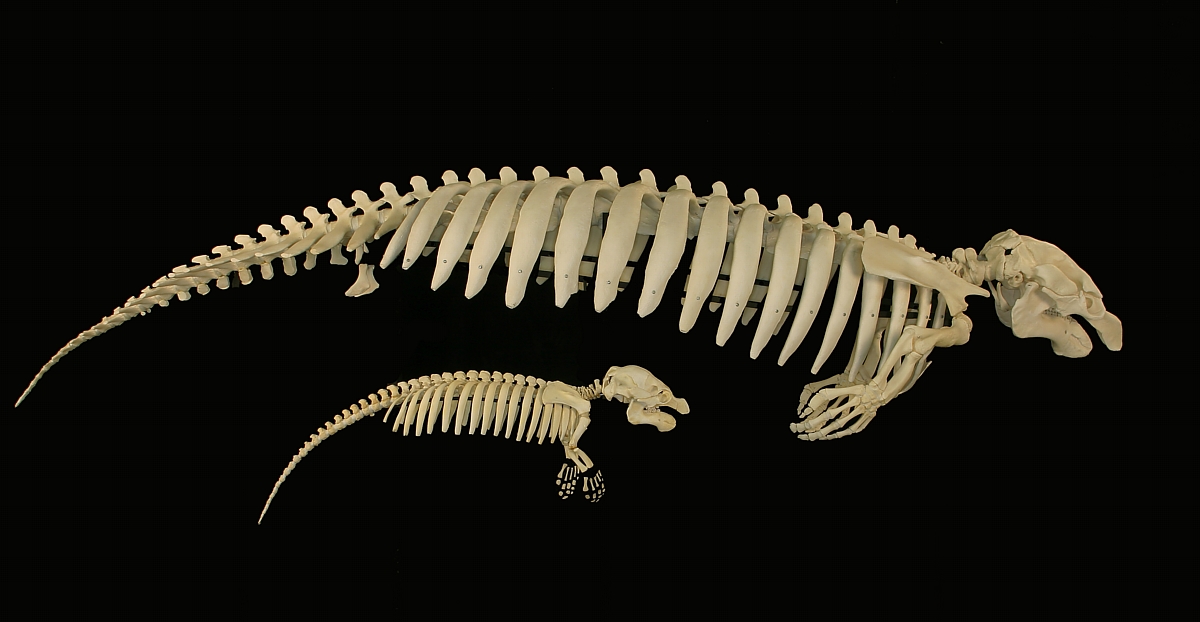
Protosirenidae
Protosirenidae is an extinct primitive family of the order Sirenia. Protosirenids are thought to have been amphibious quadrupeds, meaning that they spent their time both on land and in the water and had four legs. See also *Dugongidae * Evolution of sirenians *Manatee References External links ''Protosiren''at The Paleobiology Database The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Pale .... Eocene sirenians Prehistoric mammal families {{Paleo-sirenian-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sirenia
The Sirenia (), commonly referred to as sea-cows or sirenians, are an order of fully aquatic, herbivorous mammals that inhabit swamps, rivers, estuaries, marine wetlands, and coastal marine waters. The Sirenia currently comprise two distinct families: Dugongidae (the dugong and the now extinct Steller's sea cow) and Trichechidae (manatees, namely the Amazonian manatee, West Indian manatee, and West African manatee) with a total of four species. The Protosirenidae (Eocene sirenians) and Prorastomidae (terrestrial sirenians) families are extinct. Sirenians are classified in the clade Paenungulata, alongside the elephants and the hyraxes, and evolved in the Eocene 50 million years ago (mya). The Dugongidae diverged from the Trichechidae in the late Eocene or early Oligocene (30–35 mya). Sirenians grow to between in length and in weight. The historic Steller's sea cow was the largest known sirenian to have lived, and could reach lengths of and weights of . Sirenians have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolution Of Sirenians
Sirenia is the order of placental mammals which comprises modern "sea cows" (manatees and the Dugong) and their extinct relatives. They are the only extant herbivorous marine mammals and the only group of herbivorous mammals to have become completely aquatic. Sirenians are thought to have a 50-million-year-old fossil record (early Eocene-recent). They attained modest diversity during the Oligocene and Miocene, but have since declined as a result of climatic cooling, oceanographic changes, and human interference. Two genera and four species are extant: ''Trichechus'', which includes the three species of manatee that live along the Atlantic coasts and in rivers and coastlines of the Americas and western Africa, and ''Dugong'', which is found in the Indian and Pacific oceans. Origins Sirenians, along with Proboscidea (elephants), group together with the extinct Desmostylia and likely the extinct Embrithopoda to form the Tethytheria. Tethytheria is thought to have evolved f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protosiren
''Protosiren'' is an extinct early genus of the order Sirenia. ''Protosiren'' existed throughout the Lutetian to Priabonian stages of the Middle Eocene. Fossils have been found in the far-flung locations like the United States (South Carolina, North Carolina and Florida), Africa (Egypt), Europe (France, Germany and Hungary) and Asia (India and Pakistan). So far, five species have been named. From comparative anatomy and chronological order,Gingerich P.D., Arif M, Bhatti M.A., Anwar M & Sanders W.J. (1997). "''Basilosaurus drazindai'' and ''Basiloterus hussaini'', New Archaeoceti (Mammalia, Cetacea) from the Middle Eocene Drazinda Formation, with a Revised Interpretation of Ages of Whale-Bearing Strata in the Kirthar Group of the Sulaiman Range, Punjab (Pakistan)". ''Contributions from the Museum of Paleontology, University of Michigan'' 30(2): p. 55–81Gingerich P.D., Muhammad A, Bhatti M.A., Raza H.A. & Raza S.M. (1995). "''Protosiren'' and ''Babiacetus'' (Mammalia, Sirenia and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dugongidae
Dugongidae is a family in the order of Sirenia. The family has one surviving species, the dugong (''Dugong dugon''), one recently extinct species, Steller's sea cow (''Hydrodamalis gigas''), and a number of extinct genera known from fossil records. Dugongidae's body weight ranges from 217 to 307 kg for juveniles, 334 to 424 kg for subadults, and 435 to 568.5 kg for adults. Oral temperatures for individual dugongs is determined from 24° to 34.2 °C. Heart rate readings are from 40 to 96 bpm and vary between individual dugongs. Respiration rate during the out-of-water phase is from 1 to 33. Taxonomy * Family DUGONGIDAE ** Genus †''Anisosiren'' ** Genus †''Caribosiren'' ** Genus †'' Indosiren'' ** Genus †''Lentiarenium'' ** Genus †''Kaupitherium'' ** Genus †'' Paralitherium'' ** Genus †''Priscosiren'' ** Genus †'' Prohalicore'' ** Genus †''Sirenavus'' ** Subfamily †Halitheriinae *** Genus †''Halitherium'' (''nomen dubium'') ** Subfamily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manatee
Manatees (family Trichechidae, genus ''Trichechus'') are large, fully aquatic, mostly herbivorous marine mammals sometimes known as sea cows. There are three accepted living species of Trichechidae, representing three of the four living species in the order Sirenia: the Amazonian manatee (''Trichechus inunguis''), the West Indian manatee (''Trichechus manatus''), and the West African manatee (''Trichechus senegalensis''). They measure up to long, weigh as much as , and have paddle-like tails. Manatees are herbivores and eat over 60 different freshwater and saltwater plants. Manatees inhabit the shallow, marshy coastal areas and rivers of the Caribbean Sea, the Gulf of Mexico, the Amazon basin, and West Africa. The main causes of death for manatees are human-related issues, such as habitat destruction and human objects. Their slow-moving, curious nature has led to violent collisions with propeller-driven boats and ships. Some manatees have been found with over 50 scars on them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Paleobiology Database
The Paleobiology Database is an online resource for information on the distribution and classification of fossil animals, plants, and microorganisms. History The Paleobiology Database (PBDB) originated in the NCEAS-funded Phanerozoic Marine Paleofaunal Database initiative, which operated from August 1998 through August 2000. From 2000 to 2015, PBDB received funding from the National Science Foundation. PBDB also received support form the Australian Research Council. From 2000 to 2010 it was housed at the National Center for Ecological Analysis and Synthesis, a cross-disciplinary research center within the University of California, Santa Barbara. It is currently housed at University of Wisconsin-Madison and overseen by an international committee of major data contributors. The Paleobiology Database works closely with the Neotoma Paleoecology Database, which has a similar intellectual history, but has focused on the Quaternary (with an emphasis on the late Pleistocene and Holoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene Sirenians
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Siberia and in what is now Chesapeake Bay. As with other geologic periods, the strata that define the start and end of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
_colourised.png)