|
Proteopedia
Proteopedia is a wiki, 3D encyclopedia of proteins and other molecules. The site contains a page for every entry in the Protein Data Bank (>130,000 pages), as well as pages that are more descriptive of protein structures in general such as acetylcholinesterase, hemoglobin, and the photosystem II with a Jmol view that highlights functional sites and ligands. It employs a scene-authoring tool so that users do not have to learn JSmol script language to create customized molecular scenes. Custom scenes are easily attached to "green links" in descriptive text that display those scenes in JSmol. A web browser is all that is needed to access the site and the 3D information; no viewers are required to be installed. Proteopedia was the winner of the 2010 award for the best website by '' The Scientist'' magazine. Legal aspects Licensing terms All user-added content is free and covered by the GNU Free Documentation License. Proteopedia is hosted at the Israel Structural Proteomics Center at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
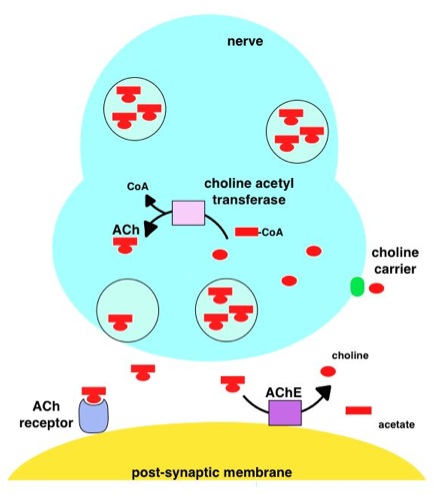
Acetylcholinesterase
Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ... that catalysis, catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters: : acetylcholine + H2O = choline + acetate It is found at mainly neuromuscular junctions and in chemical synapses of the cholinergic type, where its activity serves to terminate neurotransmission, synaptic transmission. It belongs to the carboxylesterase family of enzymes. It is the primary target of inhibition by organophosphorus compounds such as nerve agents and pesticides. Enzyme structure and mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hemoglobin
Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocytes) of almost all vertebrates (the exception being the fish family Channichthyidae) as well as the tissues of some invertebrates. Hemoglobin in blood carries oxygen from the respiratory organs (''e.g.'' lungs or gills) to the rest of the body (''i.e.'' tissues). There it releases the oxygen to permit aerobic respiration to provide energy to power functions of an organism in the process called metabolism. A healthy individual human has 12to 20grams of hemoglobin in every 100mL of blood. In mammals, the chromoprotein makes up about 96% of the red blood cells' dry content (by weight), and around 35% of the total content (including water). Hemoglobin has an oxygen-binding capacity of 1.34mL O2 per gram, which increases the total blood oxygen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jmol
Jmol is computer software for molecular modelling chemical structures in 3-dimensions. Jmol returns a 3D representation of a molecule that may be used as a teaching tool, or for research e.g., in chemistry and biochemistry. It is written in the programming language Java, so it can run on the operating systems Windows, macOS, Linux, and Unix, if Java is installed. It is free and open-source software released under a GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) version 2.0. A standalone application and a software development kit (SDK) exist that can be integrated into other Java applications, such as Bioclipse and Taverna. A popular feature is an applet that can be integrated into web pages to display molecules in a variety of ways. For example, molecules can be displayed as ball-and-stick models, space-filling models, ribbon diagrams, etc. Jmol supports a wide range of chemical file formats, including Protein Data Bank (pdb), Crystallographic Information File (cif), MDL Molfile (mol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy, and submitted by biologists and biochemists from around the world, are freely accessible on the Internet via the websites of its member organisations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB, and BMRB). The PDB is overseen by an organization called the Worldwide Protein Data Bank, wwPDB. The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other databases use protein structures deposited in the PDB. For example, SCOP and CATH classify protein structures, while PDBsum provides a graphic overview of PDB entries using information from other sources, such as Gene ontology. History Two force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GNU Free Documentation License
The GNU Free Documentation License (GNU FDL or simply GFDL) is a copyleft license for free documentation, designed by the Free Software Foundation (FSF) for the GNU Project. It is similar to the GNU General Public License, giving readers the rights to copy, redistribute, and modify (except for "invariant sections") a work and requires all copies and derivatives to be available under the same license. Copies may also be sold commercially, but, if produced in larger quantities (greater than 100), the original document or source code must be made available to the work's recipient. The GFDL was designed for manuals, textbooks, other reference and instructional materials, and documentation which often accompanies GNU software. However, it can be used for any text-based work, regardless of subject matter. For example, the free online encyclopedia Wikipedia uses the GFDL (coupled with the Creative Commons Attribution Share-Alike License) for much of its text, excluding text that was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Israeli Online Encyclopedias
Israeli may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel * Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel * Modern Hebrew, a language * ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008 * Guni Israeli (born 1984), Israeli basketball player See also * Israelites, the ancient people of the Land of Israel * List of Israelis Israelis ( he, ישראלים ''Yiśraʾelim'') are the citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel, a multiethnic state populated by people of different ethnic backgrounds. The largest ethnic groups in Israel are Jews (75%), foll ... {{disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creative Commons-licensed Databases
Creative may refer to: *Creativity, phenomenon whereby something new and valuable is created * "Creative" (song), a 2008 song by Leon Jackson * Creative class, a proposed socioeconomic class * Creative destruction, an economic term * Creative director, an occupation * Creative industries, exchange of finance for rights in intellectual properties * Creative nonfiction, a literary genre * Creative writing, an original, non-technical writing or composition * Creative Commons, an organization that deals with public copyright issues * Creative Labs, a brand owned by Creative Technology * Creative Technology Creative Technology Ltd. is a Singaporean multinational technology company headquartered with overseas offices in Shanghai, Tokyo, Dublin, and Silicon Valley (where in the US it is known as Creative Labs). The principal activities of the compa ..., Singapore-based manufacturer of computer products See also * Creativity (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Databases
Biological databases are libraries of biological sciences, collected from scientific experiments, published literature, high-throughput experiment technology, and computational analysis. They contain information from research areas including genomics, proteomics, metabolomics, microarray gene expression, and phylogenetics. Information contained in biological databases includes gene function, structure, localization (both cellular and chromosomal), clinical effects of mutations as well as similarities of biological sequences and structures. Biological databases can be classified by the kind of data they collect (see below). Broadly, there are molecular databases (for sequences, molecules, etc.), functional databases (for physiology, enzyme activities, phenotypes, ecology etc), taxonomic databases (for species and other taxonomic ranks), images and other media, or specimens (for museum collections etc.) Databases are important tools in assisting scientists to analyze and explain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a ''residue'' indicating a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weizmann Institute Of Science
The Weizmann Institute of Science ( he, מכון ויצמן למדע ''Machon Vaitzman LeMada'') is a public research university in Rehovot, Israel, established in 1934, 14 years before the State of Israel. It differs from other Israeli universities in that it offers only postgraduate degrees in the natural and exact sciences. It is a multidisciplinary research center, with around 3,800 scientists, postdoctoral fellows, Ph.D. and M.Sc. students, and scientific, technical, and administrative staff working at the institute. As of 2019, six Nobel laureates and three Turing Award winners have been associated with the Weizmann Institute of Science. History Founded in 1934 by Chaim Weizmann and his first team, among them Benjamin M. Bloch, as the Daniel Sieff Research Institute. Weizmann had offered the post of director to Nobel Prize laureate Fritz Haber, but took over the directorship himself after Haber's death en route to Palestine. Before he became President of the State o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonprofit
A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in contrast with an entity that operates as a business aiming to generate a profit for its owners. A nonprofit is subject to the non-distribution constraint: any revenues that exceed expenses must be committed to the organization's purpose, not taken by private parties. An array of organizations are nonprofit, including some political organizations, schools, business associations, churches, social clubs, and consumer cooperatives. Nonprofit entities may seek approval from governments to be tax-exempt, and some may also qualify to receive tax-deductible contributions, but an entity may incorporate as a nonprofit entity without securing tax-exempt status. Key aspects of nonprofits are accountability, trustworthiness, honesty, and openness to eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |