|
Propionyl-CoA Carboxylase
Propionyl-CoA carboxylase (, PCC) catalyses the carboxylation reaction of propionyl-CoA in the mitochondrial matrix. PCC has been classified both as a ligase and a lyase. The enzyme is biotin-dependent. The product of the reaction is (S)-methylmalonyl CoA. : ATP + propionyl-CoA + HCO3− ADP + phosphate + (S)-methylmalonyl-CoA (S)-Methylmalonyl-CoA cannot be directly utilized by animals. It is acted upon by a racemase, yielding (R)-methylmalonyl-CoA, which is then converted into succinyl-CoA by methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (one of the few metabolic enzymes which requires vitamin B12 as a cofactor). Succinyl-CoA, a Krebs cycle intermediate, is further metabolized into fumarate, then malate, and then oxaloacetate. Oxaloacetate may be transported into the cytosol to form phosphoenol pyruvate and other gluconeogenic intermediates. Propionyl-CoA is therefore an important precursor to glucose. Propionyl-CoA is the end product of odd-chain fatty acid metabolism, including most methylated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
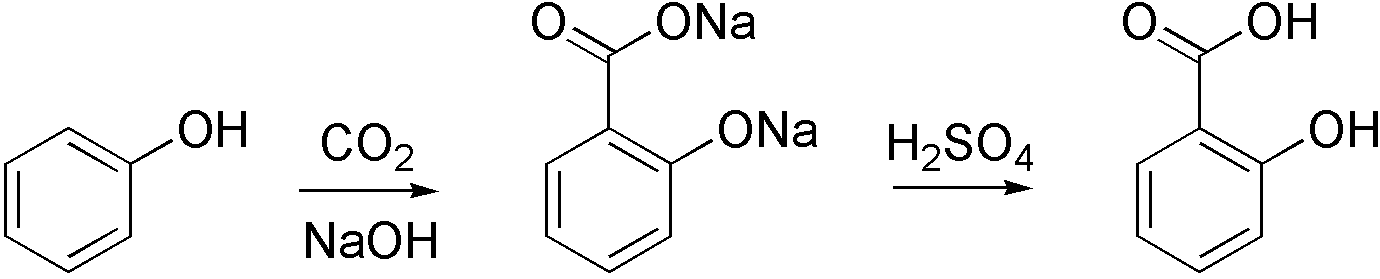
Carboxylation
Carboxylation is a chemical reaction in which a carboxylic acid is produced by treating a substrate with carbon dioxide. The opposite reaction is decarboxylation. In chemistry, the term carbonation is sometimes used synonymously with carboxylation, especially when applied to the reaction of carbanionic reagents with CO2. More generally, carbonation usually describes the production of carbonates. Organic chemistry Carboxylation is a standard conversion in organic chemistry. Specifically carbonation (i.e. carboxylation) of Grignard reagents and organolithium compounds is a classic way to convert organic halides into carboxylic acids. Sodium salicylate, precursor to aspirin, is commercially prepared by treating sodium phenolate (the sodium salt of phenol) with carbon dioxide at high pressure (100 atm) and high temperature (390 K) – a method known as the Kolbe-Schmitt reaction. Acidification of the resulting salicylate salt gives salicylic acid. : Many detailed procedures are des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valine
Valine (symbol Val or V) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated −NH3+ form under biological conditions), an α- carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −COO− form under biological conditions), and a side chain isopropyl group, making it a non-polar aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans, meaning the body cannot synthesize it: it must be obtained from the diet. Human dietary sources are foods that contain protein, such as meats, dairy products, soy products, beans and legumes. It is encoded by all codons starting with GU (GUU, GUC, GUA, and GUG). History and etymology Valine was first isolated from casein in 1901 by Hermann Emil Fischer. The name valine comes from valeric acid, which in turn is named after the plant valerian due to the presence of the acid in the roots of the plant. Nomenclature According to IUPAC, carbon atoms forming valine are numbered sequentially s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isoelectric Point
The isoelectric point (pI, pH(I), IEP), is the pH at which a molecule carries no net electrical charge or is electrically neutral in the statistical mean. The standard nomenclature to represent the isoelectric point is pH(I). However, pI is also used. For brevity, this article uses pI. The net charge on the molecule is affected by pH of its surrounding environment and can become more positively or negatively charged due to the gain or loss, respectively, of protons (H+). Surfaces naturally charge to form a double layer. In the common case when the surface charge-determining ions are H+/HO−, the net surface charge is affected by the pH of the liquid in which the solid is submerged. The pI value can affect the solubility of a molecule at a given pH. Such molecules have minimum solubility in water or salt solutions at the pH that corresponds to their pI and often precipitate out of solution. Biological amphoteric molecules such as proteins contain both acidic and basic function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michaelis–Menten Kinetics
In biochemistry, Michaelis–Menten kinetics is one of the best-known models of enzyme kinetics. It is named after German biochemist Leonor Michaelis and Canadian physician Maud Menten. The model takes the form of an equation describing the rate of enzymatic reactions, by relating reaction rate v (rate of formation of product, ce P/math>) to ce S/math>, the concentration of a substrate ''S''. Its formula is given by : v = \frac = V_\max \frac This equation is called the Michaelis–Menten equation. Here, V_\max represents the maximum rate achieved by the system, happening at saturating substrate concentration for a given enzyme concentration. When the value of the Michaelis constant K_\mathrm is numerically equal to the substrate concentration, then the reaction rate is half of V_\max. Biochemical reactions involving a single substrate are often assumed to follow Michaelis–Menten kinetics, without regard to the model's underlying assumptions. Model In 1901, French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Triphosphate
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) is an organic compound that provides energy to drive many processes in living cells, such as muscle contraction, nerve impulse propagation, condensate dissolution, and chemical synthesis. Found in all known forms of life, ATP is often referred to as the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. When consumed in metabolic processes, it converts either to adenosine diphosphate (ADP) or to adenosine monophosphate (AMP). Other processes regenerate ATP. The human body recycles its own body weight equivalent in ATP each day. It is also a precursor to DNA and RNA, and is used as a coenzyme. From the perspective of biochemistry, ATP is classified as a nucleoside triphosphate, which indicates that it consists of three components: a nitrogenous base (adenine), the sugar ribose, and the Polyphosphate, triphosphate. Structure ATP consists of an adenine attached by the 9-nitrogen atom to the 1′ carbon atom of a sugar (ribose), which i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylglyoxal
Phenylglyoxal is the organic compound with the formula C6H5C(O)C(O)H. It contains both an aldehyde and a ketone functional group. It is yellow liquid when anhydrous but readily forms a colorless crystalline hydrate. It has been used as a reagent to modify the amino acid, arginine. It has also been used to attach chemical payload (probes) to the amino acid citrulline and to peptides/proteins. Properties Like some other aldehydes, phenylglyoxal polymerizes upon standing, as indicated by solidification of the liquid. Upon heating, this polymer "cracks" to give back the yellow aldehyde. Dissolution of phenylglyoxal in water gives crystals of the hydrate: : C6H5C(O)COH + H2O → C6H5C(O)CH(OH)2 Upon heating, the hydrate loses water and regenerates the anhydrous liquid. Preparation Phenylglyoxal was first prepared by thermal decomposition of the sulfite derivative of the oxime: : C6H5C(O)CH(NOSO2H) + 2 H2O → C6H5C(O)CHO + NH4HSO4 More conveniently, it can be prepared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Site-directed Mutagenesis
Site-directed mutagenesis is a molecular biology method that is used to make specific and intentional mutating changes to the DNA sequence of a gene and any gene products. Also called site-specific mutagenesis or oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis, it is used for investigating the structure and biological activity of DNA, RNA, and protein molecules, and for protein engineering. Site-directed mutagenesis is one of the most important laboratory techniques for creating DNA libraries by introducing mutations into DNA sequences. There are numerous methods for achieving site-directed mutagenesis, but with decreasing costs of oligonucleotide synthesis, artificial gene synthesis is now occasionally used as an alternative to site-directed mutagenesis. Since 2013, the development of the CRISPR/Cas9 technology, based on a prokaryotic viral defense system, has also allowed for the editing of the genome, and mutagenesis may be performed ''in vivo'' with relative ease. History Early attempt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyanion Hole
An oxyanion hole is a pocket in the active site of an enzyme that stabilizes transition state negative charge on a deprotonated oxygen or alkoxide. The pocket typically consists of backbone amides or positively charged residues. Stabilising the transition state lowers the activation energy necessary for the reaction, and so promotes catalysis. For example, proteases such as chymotrypsin contain an oxyanion hole to stabilise the tetrahedral intermediate anion formed during proteolysis and protects substrate's negatively charged oxygen from water molecules. Additionally, it may allow for insertion or positioning of a substrate, which would suffer from steric hindrance Steric effects arise from the spatial arrangement of atoms. When atoms come close together there is a rise in the energy of the molecule. Steric effects are nonbonding interactions that influence the shape ( conformation) and reactivity of ions ... if it could not occupy the hole (such as 2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Barrel
In protein structures, a beta barrel is a beta sheet composed of tandem repeats that twists and coils to form a closed toroidal structure in which the first strand is bonded to the last strand (hydrogen bond). Beta-strands in many beta-barrels are arranged in an antiparallel fashion. Beta barrel structures are named for resemblance to the barrels used to contain liquids. Most of them are water-soluble proteins and frequently bind hydrophobic ligands in the barrel center, as in lipocalins. Others span cell membranes and are commonly found in porins. Porin-like barrel structures are encoded by as many as 2–3% of the genes in Gram-negative bacteria. It has been shown that more than 600 proteins with various function (e.g., oxidase, dismutase, amylase) contain the beta barrel structure. In many cases, the strands contain alternating polar and non-polar (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) amino acids, so that the hydrophobic residues are oriented into the interior of the barrel to form a hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotin Carboxyl Carrier Protein
Biotin Carboxyl Carrier Protein (BCCP) refers to proteins containing a biotin attachment domain that carry biotin and carboxybiotin throughout the ATP-dependent carboxylation by biotin-dependent carboxylases. In the case of '' E. coli'' Acetyl-CoA carboxylase, the BCCP is a separate protein known as ''accB'' (). On the other hand, in '' Haloferax mediterranei'' Propionyl-CoA carboxylase, the BCCP ''pccA'' () is fused with biotin carboxylase In enzymology, a biotin carboxylase () is an enzyme that Catalysis, catalyzes the chemical reaction : ATP + biotin-carboxyl-carrier protein + CO2 \rightleftharpoons ADP + phosphate + carboxybiotin-carboxyl-carrier protein The three Substrate .... Coenzymes Enzymes Metabolism Proteins {{Protein-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |