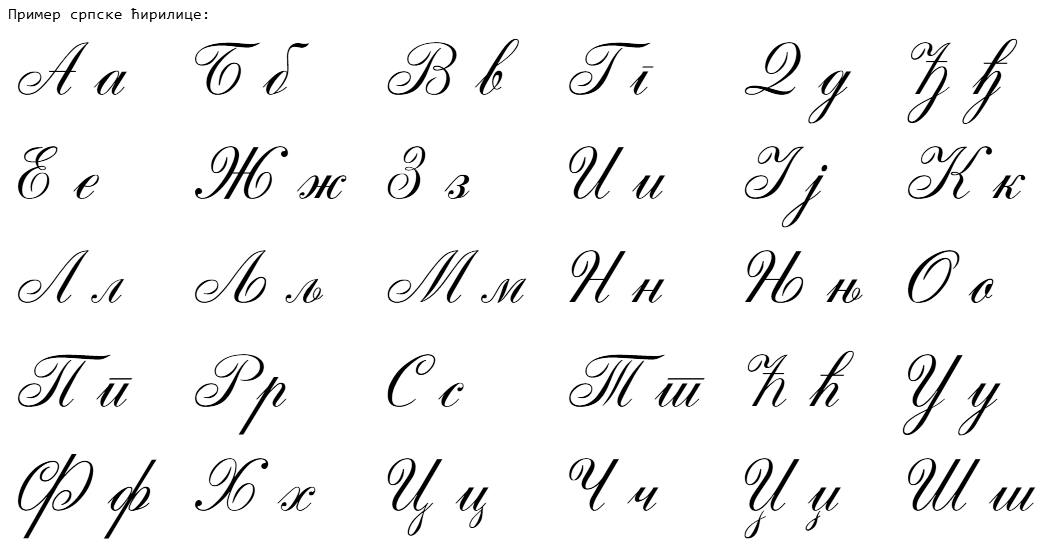|
Prokopije Ivačković
Prokopije or Procopius ( sr, Прокопије; ro, Procopie or ro, Procopiu, hu, Prokop; born Petar Ivačković, Serbian Cyrillic: Петар Ивачковић, ro, Petru Ivacicovici, hu, Ivácskovics Péter; August 8, 1808 – May 11, 1881) was an Austro-Hungarian cleric of the Romanian Orthodox and Serbian Orthodox churches who ultimately served as the latter's Patriarch at Karlovci. He was born in the Banat as a subject of the Austrian Empire, his ethnic affiliations alternating between the Serb and Romanian communities. Ivačković's early life was spent in Serbian Orthodox institutions, and he was seen as a Serb loyalist before he became Bishop of Arad. During the 1860s, he expressed support for Romanian nationalism, primarily as a founder of the National Aradian Association for Romanian Popular Culture. He backed Andrei Șaguna's bid to set up the Romanian-centered Metropolis of Transylvania, becoming its suffragan bishop; during the Serb–Romanian church partition, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patriarchate Of Karlovci
The Patriarchate of Karlovci ( sr, Карловачка патријаршија, Karlovačka patrijaršija) or Serbian Patriarchate of Sremski Karlovci ( sr, Српска патријаршија у Сремским Карловцима, Srpska patrijaršija u Sremskim Karlovcima), was a patriarchate of the Eastern Orthodox Church that existed between 1848 and 1920. It was formed when the Metropolitanate of Karlovci was elevated to the rank of patriarchate.Paul Robert Magocsi: Historical Atlas of Central Europe, University of Toronto Press, 2002 ''"Then, in 1766, when the Ottomans abolished Pec, the Karlovci province became an independent body, eventually with six suffragan bishops (Novi Sad, Timișoara, Vrsac, Buda, Pakrac, and Karlovac), known as the Serbian Orthodox Slav Oriental Church, which after 1848 was raised to the status of a patriarchate."'' The Patriarchate of Karlovci nominally existed until 1920, when along with several other Eastern Orthodox jurisdictions in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Cyrillic Alphabet
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet ( sr, / , ) is a variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language, updated in 1818 by Serbian linguist Vuk Stefanović Karadžić, Vuk Karadžić. It is one of the two alphabets used to write standard modern Serbian language, Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his alphabet on the previous Slavonic-Serbian script, following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written", removing obsolete letters and letters representing iotified vowels, introducing from the Latin alphabet instead, and adding several consonant letters for sounds specific to Serbian phonology. During the same period, linguists led by Ljudevit Gaj adapted the Latin alphabet, in use in western South Slavic areas, using the same principles. As a result of this joint effort, Serbian Cyrillic and Gaj's Latin alphabets for Serbian-Croatian have a complete one-to-one congruence, with the Latin Digraph (orthography), digraph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungary to the north, Romania to the northeast, Bulgaria to the southeast, North Macedonia to the south, Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina to the west, and Montenegro to the southwest, and claims a border with Albania through the Political status of Kosovo, disputed territory of Kosovo. Serbia without Kosovo has about 6.7 million inhabitants, about 8.4 million if Kosvo is included. Its capital Belgrade is also the List of cities in Serbia, largest city. Continuously inhabited since the Paleolithic Age, the territory of modern-day Serbia faced Slavs#Migrations, Slavic migrations in the 6th century, establishing several regional Principality of Serbia (early medieval), states in the early Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kovin
Kovin (, hu, Kevevára) is a town and municipality located in the South Banat District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a population of 13,515, while the municipality has 33,722 inhabitants. In Romanian, the town is known as Cuvin, in Hungarian as Kevevára or (until 1899) Temeskubin, and in German as Kubin or Temeschkubin. In the past, the town was also known as Donji Kovin ("lower Kovin") in contrast to the town with same name in Hungary that was known in Serbian as '' Gornji Kovin'' ("upper Kovin") and in Hungarian as ''Ráckeve'' ("the Serb Kovin"). History The Dacian tribe of Albocenses dwelled in this area in the second century AD. There are remains of the ancient Roman fortress called '' Contra Margum'', opposite to the Margum, a fortress on the other side of the Danube. In the ninth and tenth centuries, this area was populated by Slavs and Romanians and Voivode Glad ruled over the region. Glad was defeated by the Hungarians, and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ágoston Trefort
Dr. Ágoston Trefort (pronunciation: a:gɔʃtɔn 'trɛfɔrt 7 February 1817 – 22 August 1888) was a Hungarian politician, who served as Minister of Religion and Education from 1872 until his death. He was the President of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences from 1885. Family He was born into a Hungarian Catholic family of Walloon origin in Homonna, Zemplén County, Kingdom of Hungary (today Humenné, Slovakia). His great-grandfather worked as a lawyer in Belgium, his medical officer grandfather came to Hungary in the 1770s. Ágoston's father was Ignác Trefort (1770–1831), a famous surgeon, and his mother was Tekla Beldovics (died 1829). They married in 1816, when Ignác's first wife died. They had three children: Ágoston, Antal (died in his infancy) and István (born 1825, year of death unknown). On 14 March 1847 he married the Hungarian noble lady Ilona Rosty de Barkócz (1826–1870), who was the daughter of Albert Rosty de Barkócz (1779–1847), jurist, landowner, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kálmán Tisza
Kálmán Tisza de Borosjenő (archaic English: Coloman Tisza, or Koloman Tisza; 16 December 1830 – 23 March 1902) was the Hungarian prime minister between 1875 and 1890. He is credited with the formation of a consolidated Magyar government, the foundation of the new Liberal Party (1875) and major economic reforms that would both save and eventually lead to a government with popular support. He is the second longest-serving head of government in Hungarian history. Political career At the age of 18, Kálmán Tisza witnessed one of the greatest transformations of the political arena in Hungarian history. Hungary's political system changed from being a feudalistic state into a newly established constitutional monarchy that shared many components with modern-day governments. Legislation such as Public Law III abolished the Royal Chancellery and the Residential Council replacing them with a bicameral parliament (House of Lords and House of Representatives). Democratic princip ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suffragan Bishop
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations. In the Anglican Communion, a suffragan bishop is a bishop who is subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop (bishop ordinary) and so is not normally jurisdictional in their role. Suffragan bishops may be charged by a metropolitan to oversee a suffragan diocese and may be assigned to areas which do not have a cathedral of their own. In the Catholic Church, a suffragan bishop instead leads a diocese within an ecclesiastical province other than the principal diocese, the metropolitan archdiocese; the diocese led by the suffragan is called a suffragan diocese. Anglican Communion In the Anglican churches, the term applies to a bishop who is assigned responsibilities to support a diocesan bishop. For example, the Bishop of Jarrow is a suffragan to the diocesan Bishop of Durham. Suffragan bishops in the Anglican Communion are nearly identical in their role to auxiliary bishops in the Roman Catholic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrei Șaguna
Andrei Șaguna (; 20 January 1808, Miskolc, Hungary – 28 June 1873, Nagyszeben, Hungary) was a Metropolitan bishop of the Romanian Orthodox Church in Transylvania, and one of the Romanian community political leaders in the Habsburg monarchy, especially active during the 1848 Revolution. He was an honorary member of the Romanian Academy. Early life He was Aromanian in origin, his family having settled with Naum Șaguna (Andrei's father) in Hungary from Grabova, now Albania. With the guidance of local Piarists, Șaguna's parents had opted to convert to Roman Catholicism, seeking to obtain a better status than the second-class one reserved for most Eastern Orthodox subjects of the Habsburgs. However, the Șagunas most likely continued to practice their original religion in secret - the future Metropolitan was probably never a practising Catholic. After he rejoined the Orthodox Church while living and studying in Pest, Andrei Șaguna became a monk and started his ecclesia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanian Nationalism
Romanian nationalism is the nationalism which asserts that Romanians are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Romanians. Its extremist variation is the Romanian ultranationalism.Aristotle KallisGenocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Drive in Fascist Europe Routledge, 2008, p. 75 Parties Current *Greater Romania Party (1991–present) * New Generation Party (2000–present) *Noua Dreaptă (2000–present) *Social Democratic Party (2001–present) * Romanian Socialist Party (2003–present) *People's Movement Party (2014–present) *United Romania Party (2015–present) *National Identity Bloc in Europe (2017–present) *Alliance for the Union of Romanians (2019–present) *Romanian Nationhood Party (2019–present) *The Right Alternative (2019–present) * Alliance for the Homeland (2021–present) *Force of the Right (2021–present) Former *Romanian National Party (1881–1926) * Democratic Nationalist Party (1910–1946) *Bessarabian Peasants' Party (1918–1923) * De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym ''Vlachs'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Culture of Romania, Romanian culture and Cultural heritage, ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The Demographic history of Romania#20 October 2011 census, 2011 Romanian census found that just under 89% of Romania's citizens identified themselves as ethnic Romanians. In one interpretation of the 1989 census results in Moldova, the majority of Moldovans were counted as ethnic Romanians.''Ethnic Groups Worldwide: A Ready Reference Handbook By'' David Levinson (author), David Levinson, Published 1998 – Greenwood Publishing Group.At the time of the 1989 census, Moldova's total population was 4,335,400. The largest nationality in the republic, ethnic Romanians, numbered 2,795,000 persons, accounting for 64.5 percent of the population. Source U.S. Library of Congress "however it is one interpreta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbs In Vojvodina
The Serbs of Vojvodina are the largest ethnic group in this northern province of Serbia. For centuries, Vojvodina was ruled by several European powers, but Vojvodina Serbs never assimilated into cultures of those countries. Thus, they have consistently been a recognized indigenous ethnic minority with its own culture, language and religion. According to the 2011 census, there were 1,289,635 Serbs in Vojvodina or 66.76% of the population of the province. History Early medieval period Before the Roman conquest in the 1st century BC, Celtic tribes inhabited the territory of present-day Vojvodina region. During the Roman rule, the original inhabitants were heavily Romanized. The Slavs ( Severans, Abodrites, Braničevci and Timočani) settled today's Vojvodina during the early medieval migrations. Until the 13th century, the region had a dominant West Slavic and Hungarian population. In the 9th century the region of present-day Vojvodina was ruled by the two local Bulgaro-Slavic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |