|
Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Primary hyperparathyroidism (or PHPT) is a medical condition where the parathyroid gland (or a benign tumor within it) produce excess amounts of parathyroid hormone (PTH). The symptoms of the condition relate to the resulting elevated serum calcium (hypercalcemia), which can cause digestive symptoms, kidney stones, psychiatric abnormalities, and bone disease. The diagnosis is initially made on blood tests; an elevated level of calcium together with a raised (or inappropriately high) level of parathyroid hormone are typically found. To identify the source of the excessive hormone secretion, medical imaging may be performed. Parathyroidectomy, the surgical removal of one or more parathyroid glands, may be required to control symptoms. Signs and symptoms The signs and symptoms of primary hyperparathyroidism are those of hypercalcemia. They are classically summarized by "stones, bones, abdominal groans, thrones and psychiatric overtones". * "Stones" refers to kidney stones, nephroca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrinology
Endocrinology (from '' endocrine'' + '' -ology'') is a branch of biology and medicine dealing with the endocrine system, its diseases, and its specific secretions known as hormones. It is also concerned with the integration of developmental events proliferation, growth, and differentiation, and the psychological or behavioral activities of metabolism, growth and development, tissue function, sleep, digestion, respiration, excretion, mood, stress, lactation, movement, reproduction, and sensory perception caused by hormones. Specializations include behavioral endocrinology and comparative endocrinology. The endocrine system consists of several glands, all in different parts of the body, that secrete hormones directly into the blood rather than into a duct system. Therefore, endocrine glands are regarded as ductless glands. Hormones have many different functions and modes of action; one hormone may have several effects on different target organs, and, conversely, one target orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constipation
Constipation is a bowel dysfunction that makes bowel movements infrequent or hard to pass. The stool is often hard and dry. Other symptoms may include abdominal pain, bloating, and feeling as if one has not completely passed the bowel movement. Complications from constipation may include hemorrhoids, anal fissure or fecal impaction. The normal frequency of bowel movements in adults is between three per day and three per week. Babies often have three to four bowel movements per day while young children typically have two to three per day. Constipation has many causes. Common causes include slow movement of stool within the colon, irritable bowel syndrome, and pelvic floor disorders. Underlying associated diseases include hypothyroidism, diabetes, Parkinson's disease, celiac disease, non-celiac gluten sensitivity, colon cancer, diverticulitis, and inflammatory bowel disease. Medications associated with constipation include opioids, certain antacids, calcium channel blockers, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (abbreviated MEN) is a condition which encompasses several distinct syndromes featuring tumors of endocrine glands, each with its own characteristic pattern. In some cases, the tumors are malignant, in others, benign. Benign or malignant tumors of nonendocrine tissues occur as components of some of these tumor syndromes. MEN syndromes are inherited as autosomal dominant disorders. Presentation Related conditions Although not officially categorized as multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes, Von Hippel–Lindau disease and Carney complex are two other autosomal dominant endocrine tumor syndromes with features that overlap the clinical features of the MEN syndromes. Although not transmitted in the germline, McCune–Albright syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by endocrine neoplastic features involving endocrine glands that overlap with those involved in MEN1 or MEN2. Comparison Percentages in the table below refer to the percentage of peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
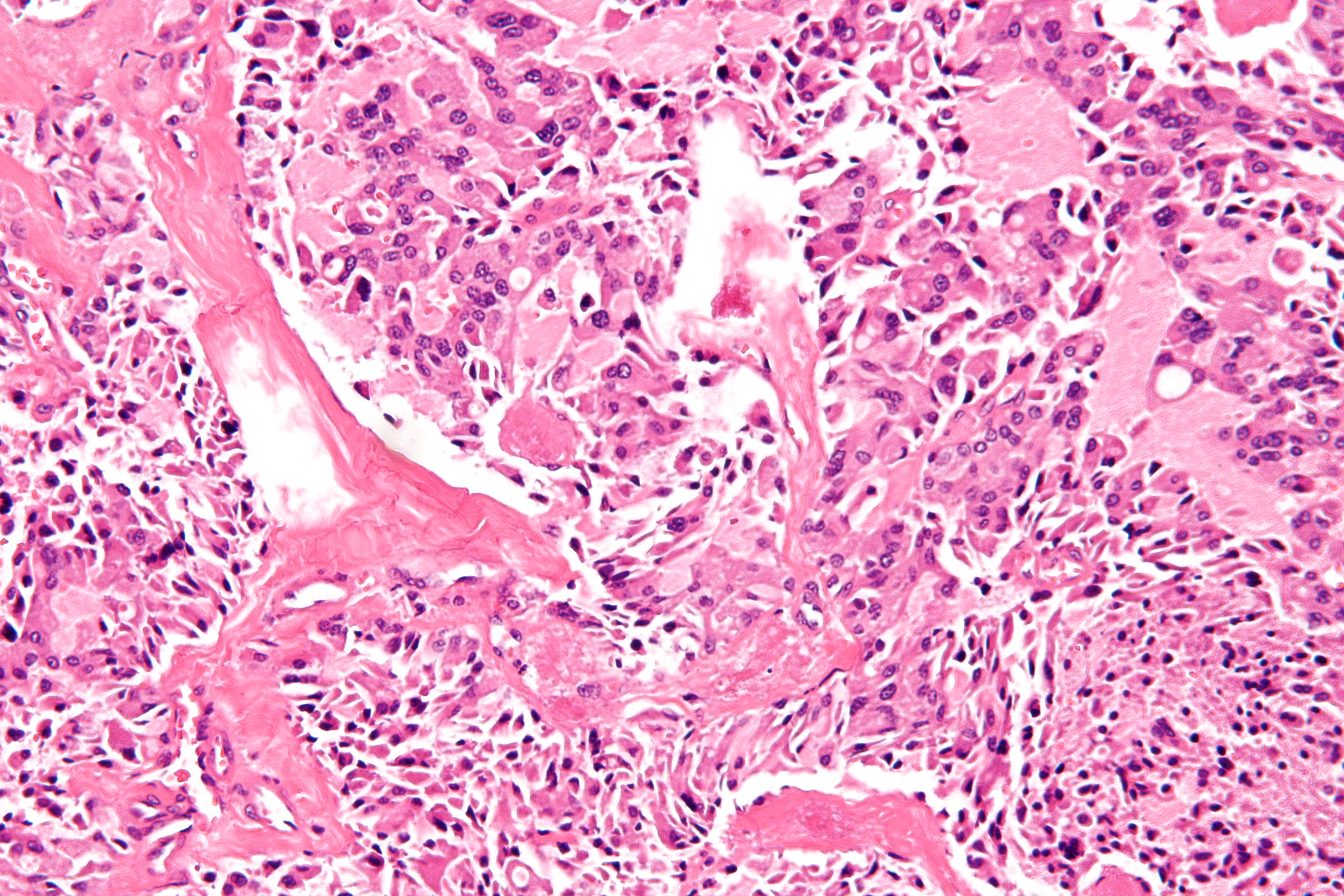
Parathyroid Carcinoma
Parathyroid carcinoma is a rare cancer resulting in parathyroid adenoma to carcinoma progression.Hu MI, Vassilopoulou-Sellin R, Lustig R, Lamont JP"Thyroid and Parathyroid Cancers"in Pazdur R, Wagman LD, Camphausen KA, Hoskins WJ (EdsCancer Management: A Multidisciplinary Approach 11 ed. 2008. It forms in tissues of one or more of the parathyroid glands (four pea-sized glands in the neck that make parathyroid hormone (PTH). PTH helps the body maintain normal levels of serum calcium by promoting calcium reabsorption from bone. It is antagonized by the hormone calcitonin, which prompts calcium storage.). It is rare, with documented cases of less than one thousand since its first discovery in 1904; and much less common than parathyroid adenoma. It can be difficult to excise. The rate of occurrence of parathyroid carcinoma is between 0.5% to 5% Signs and symptoms Most patients experience moderate to severe hypercalcemia and high parathyroid hormone levels. A large mass in the neck is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Hyperplasia
Parathyroid hormone (PTH), also called parathormone or parathyrin, is a peptide hormone secreted by the parathyroid glands that regulates the serum calcium concentration through its effects on bone, kidney, and intestine. PTH influences bone remodeling, which is an ongoing process in which bone tissue is alternately resorbed and rebuilt over time. PTH is secreted in response to low blood serum calcium (Ca2+) levels. PTH indirectly stimulates osteoclast activity within the bone matrix (osteon), in an effort to release more ionic calcium (Ca2+) into the blood to elevate a low serum calcium level. The bones act as a (metaphorical) "bank of calcium" from which the body can make "withdrawals" as needed to keep the amount of calcium in the blood at appropriate levels despite the ever-present challenges of metabolism, stress, and nutritional variations. PTH is "a key that unlocks the bank vault" to remove the calcium. PTH is secreted primarily by the chief cells of the parathyroid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parathyroid Adenoma
A parathyroid adenoma is a benign tumor of the parathyroid gland. It generally causes hyperparathyroidism; there are very few reports of parathyroid adenomas that were not associated with hyperparathyroidism. A human being usually has four parathyroid glands located on the posterior surface of the thyroid in the neck. In order to maintain calcium metabolism, the parathyroid glands secrete parathyroid hormone (PTH) which stimulates the bones to release calcium and the kidneys to reabsorb it from the urine into the blood, thereby increasing its serum level. The action of calcitonin opposes PTH. When a parathyroid adenoma causes hyperparathyroidism, more parathyroid hormone is secreted, causing the calcium concentration of the blood to rise, resulting in hypercalcemia. Signs and symptoms The first signs of a parathyroid adenoma and the resulting primary hyperparathyroidism can include bone fractures and urinary calculi such as kidney stones. Often, a parathyroid adenoma is diagnosed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Keratopathy
Band keratopathy is a corneal disease derived from the appearance of calcium on the central cornea. This is an example of metastatic calcification, which by definition, occurs in the presence of hypercalcemia. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms of band keratopathy include eye pain and decreased visual acuity. Causes Band keratopathy has several causes. These causes include uveitis, interstitial keratitis, superficial keratitis, phthisis, sarcoidosis, trauma, intraocular silicone oil, systemic diseases ( high levels of calcium in the blood, vitamin D intoxication, Fanconi's Syndrome, low levels of phosphorus in the blood, gout, milk-alkali syndrome, myotonic dystrophy, and chronic mercury exposure). Pathology Band keratopathy is seen when there is calcification of the epithelial basement membrane, Bowman's membrane, and the anterior stroma with destruction of Bowman's membrane. The calcium salts are intracellular when the process is due to alteration of systemic calcium me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) is thickening of the heart muscle of the left ventricle of the heart, that is, left-sided ventricular hypertrophy and resulting increased left ventricular mass. Causes While ventricular hypertrophy occurs naturally as a reaction to aerobic exercise and strength training, it is most frequently referred to as a pathological reaction to cardiovascular disease, or high blood pressure. It is one aspect of ventricular remodeling. While LVH itself is not a disease, it is usually a marker for disease involving the heart. Disease processes that can cause LVH include any disease that increases the afterload that the heart has to contract against, and some primary diseases of the muscle of the heart. Causes of increased afterload that can cause LVH include aortic stenosis, aortic insufficiency and hypertension. Primary disease of the muscle of the heart that cause LVH are known as hypertrophic cardiomyopathies, which can lead into heart failure. Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Acid
Gastric acid, gastric juice, or stomach acid is a digestive fluid formed within the stomach lining. With a pH between 1 and 3, gastric acid plays a key role in digestion of proteins by activating digestive enzymes, which together break down the long chains of amino acids of proteins. Gastric acid is regulated in feedback systems to increase production when needed, such as after a meal. Other cells in the stomach produce bicarbonate, a base, to buffer the fluid, ensuring a regulated pH. These cells also produce mucus – a viscous barrier to prevent gastric acid from damaging the stomach. The pancreas further produces large amounts of bicarbonate and secretes bicarbonate through the pancreatic duct to the duodenum to neutralize gastric acid passing into the digestive tract. The active components of gastric acid are protons and chloride. Often simplistically described as hydrochloric acid, these species are produced by parietal cells in the gastric glands in the stomach. The sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis (AP) is a sudden inflammation of the pancreas. Causes in order of frequency include: 1) a gallstone impacted in the common bile duct beyond the point where the pancreatic duct joins it; 2) heavy alcohol use; 3) systemic disease; 4) trauma; 5) and, in minors, mumps. Acute pancreatitis may be a single event; it may be recurrent; or it may progress to chronic pancreatitis. Mild cases are usually successfully treated with conservative measures: hospitalization, pain control, nothing by mouth, intravenous nutritional support, and intravenous fluid rehydration. Severe cases often require admission to an intensive care unit to monitor and manage complications of the disease. Complications are associated with a high mortality, even with optimal management. Signs and symptoms Common *severe epigastric pain (upper abdominal pain) radiating to the back in 50% of cases *nausea *vomiting *loss of appetite *fever * chills (shivering) *hemodynamic instability, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
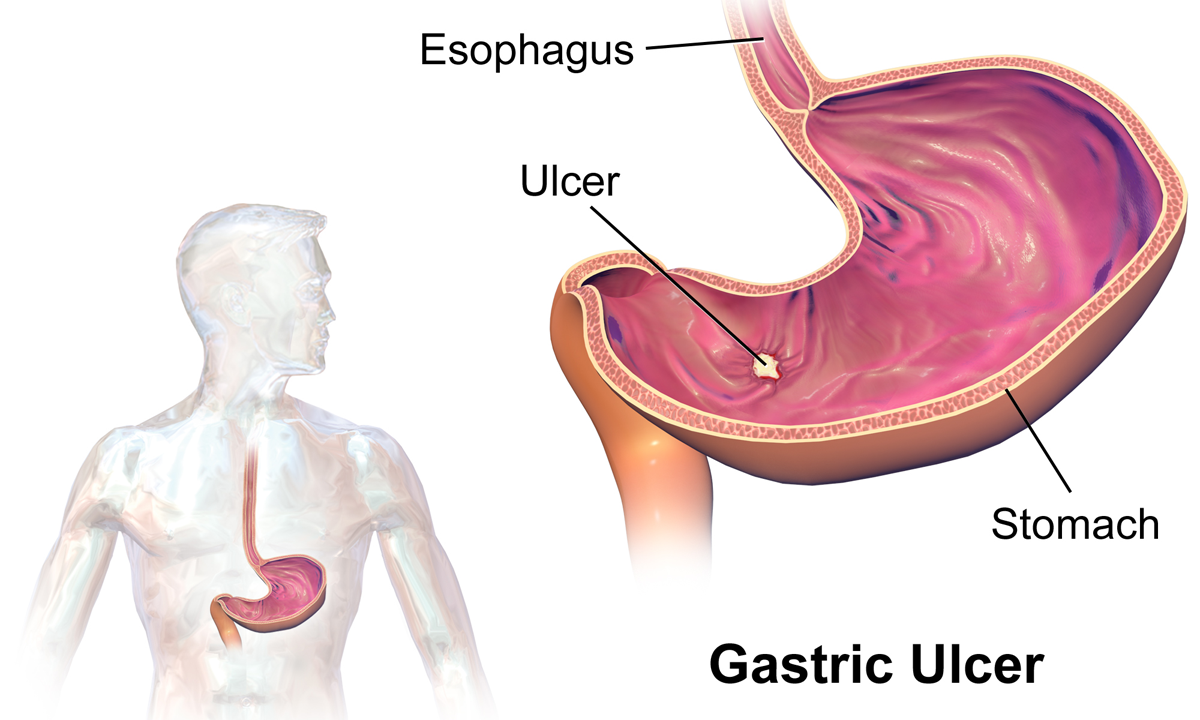
Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines is a duodenal ulcer. The most common symptoms of a duodenal ulcer are waking at night with upper abdominal pain and upper abdominal pain that improves with eating. With a gastric ulcer, the pain may worsen with eating. The pain is often described as a burning or dull ache. Other symptoms include belching, vomiting, weight loss, or poor appetite. About a third of older people have no symptoms. Complications may include bleeding, perforation, and blockage of the stomach. Bleeding occurs in as many as 15% of cases. Common causes include the bacteria ''Helicobacter pylori'' and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Other, less common causes include tobacco smoking, stress as a result of other serious health conditions, Behçet's di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |