|
Postpartum Infections
Postpartum infections, also known as childbed fever and puerperal fever, are any bacterial infections of the female reproductive tract following childbirth or miscarriage. Signs and symptoms usually include a fever greater than , chills, lower abdominal pain, and possibly bad-smelling vaginal discharge. It usually occurs after the first 24 hours and within the first ten days following delivery. The most common infection is that of the uterus and surrounding tissues known as puerperal sepsis, postpartum metritis, or postpartum endometritis. Risk factors include Caesarean section (C-section), the presence of certain bacteria such as group B streptococcus in the vagina, premature rupture of membranes, multiple vaginal exams, manual removal of the placenta, and prolonged labour among others. Most infections involve a number of types of bacteria. Diagnosis is rarely helped by culturing of the vagina or blood. In those who do not improve, medical imaging may be required. Other causes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptococcus Pyogenes
''Streptococcus pyogenes'' is a species of Gram-positive, aerotolerant bacteria in the genus ''Streptococcus''. These bacteria are extracellular, and made up of non-motile and non-sporing cocci (round cells) that tend to link in chains. They are clinically important for humans, as they are an infrequent, but usually pathogenic, part of the skin microbiota that can cause Group A streptococcal infection. ''S. pyogenes'' is the predominant species harboring the Lancefield group A antigen, and is often called group A ''Streptococcus'' (GAS). However, both '' Streptococcus dysgalactiae'' and the '' Streptococcus anginosus'' group can possess group A antigen as well. Group A streptococci, when grown on blood agar, typically produce small (2–3 mm) zones of beta-hemolysis, a complete destruction of red blood cells. The name group A (beta-hemolytic) ''Streptococcus'' (GABHS) is thus also used. The species name is derived from Greek words meaning 'a chain' () of berries ( a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vaginal Exam
A pelvic examination is the physical examination of the external and internal female pelvic organs. It is frequently used in gynecology for the evaluation of symptoms affecting the female reproductive and urinary tract, such as pain, bleeding, discharge, urinary incontinence, or trauma (e.g. sexual assault). It can also be used to assess a woman's anatomy in preparation for procedures. The exam can be done awake in the clinic and emergency department, or under anesthesia in the operating room. The most commonly performed components of the exam are 1) the external exam, to evaluate the external genitalia 2) the internal exam with palpation (commonly called the bimanual exam) to examine the uterus, ovaries, and fallopian tubes, and 3) the internal exam using the speculum to visualize the vaginal walls and cervix. During the pelvic exam, sample of cells and fluids may be collected to screen for sexually transmitted infections or cancer. Some clinicians perform a pelvic exam as part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends beyond the swelling. Carbuncles and boils are types of abscess that often involve hair follicles, with carbuncles being larger. They are usually caused by a bacterial infection. Often many different types of bacteria are involved in a single infection. In many areas of the world, the most common bacteria present is ''methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus''. Rarely, parasites can cause abscesses; this is more common in the developing world. Diagnosis of a skin abscess is usually made based on what it looks like and is confirmed by cutting it open. Ultrasound imaging may be useful in cases in which the diagnosis is not clear. In abscesses around the anus, computer tomography (CT) may be important to look for deeper infection. Standa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clindamycin
Clindamycin is an antibiotic medication used for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections, including osteomyelitis (bone) or joint infections, pelvic inflammatory disease, strep throat, pneumonia, acute otitis media (middle ear infections), and endocarditis. It can also be used to treat acne, and some cases of methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA). In combination with quinine, it can be used to treat malaria. It is available by mouth, by injection into a vein, and as a cream or a gel to be applied to the skin or in the vagina. Common side effects include nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, rashes, and pain at the site of injection. It increases the risk of hospital-acquired ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis about fourfold and thus is only recommended when other antibiotics are not appropriate. Alternative antibiotics may be recommended as a result. It appears to be generally safe in pregnancy. It is of the lincosamide class and works by blocking bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gentamicin
Gentamicin is an antibiotic used to treat several types of bacterial infections. This may include bone infections, endocarditis, pelvic inflammatory disease, meningitis, pneumonia, urinary tract infections, and sepsis among others. It is not effective for gonorrhea or chlamydia infections. It can be given intravenously, by intramuscular injection, or topically. Topical formulations may be used in burns or for infections of the outside of the eye. It is often only used for two days until bacterial cultures determine what specific antibiotics the infection is sensitive to. The dose required should be monitored by blood testing. Gentamicin can cause inner ear problems and kidney problems. The inner ear problems can include problems with balance and hearing loss. These problems may be permanent. If used during pregnancy, it can cause harm to the developing baby. However, it appears to be safe for use during breastfeeding. Gentamicin is a type of aminoglycoside. It works by disru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consumpti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ampicillin
Ampicillin is an antibiotic used to prevent and treat a number of bacterial infections, such as respiratory tract infections, urinary tract infections, meningitis, salmonellosis, and endocarditis. It may also be used to prevent group B streptococcal infection in newborns. It is used by mouth, by injection into a muscle, or intravenously. Common side effects include rash, nausea, and diarrhea. It should not be used in people who are allergic to penicillin. Serious side effects may include ''Clostridium difficile'' colitis or anaphylaxis. While usable in those with kidney problems, the dose may need to be decreased. Its use during pregnancy and breastfeeding appears to be generally safe. Ampicillin was discovered in 1958 and came into commercial use in 1961. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The World Health Organization classifies ampicillin as critically important for human medicine. It is available as a generic medication. Medical uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atelectasis
Atelectasis is the collapse or closure of a lung resulting in reduced or absent gas exchange. It is usually unilateral, affecting part or all of one lung. It is a condition where the alveoli are deflated down to little or no volume, as distinct from pulmonary consolidation, in which they are filled with liquid. It is often called a ''collapsed lung'', although that term may also refer to pneumothorax. It is a very common finding in chest X-rays and other radiological studies, and may be caused by normal exhalation or by various medical conditions. Although frequently described as a ''collapse of lung tissue'', atelectasis is not synonymous with a pneumothorax, which is a more specific condition that can cause atelectasis. Acute atelectasis may occur as a post-operative complication or as a result of surfactant deficiency. In premature babies, this leads to infant respiratory distress syndrome. The term uses combining forms of ''atel-'' + ''ectasis'', from el, ἀτελής, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
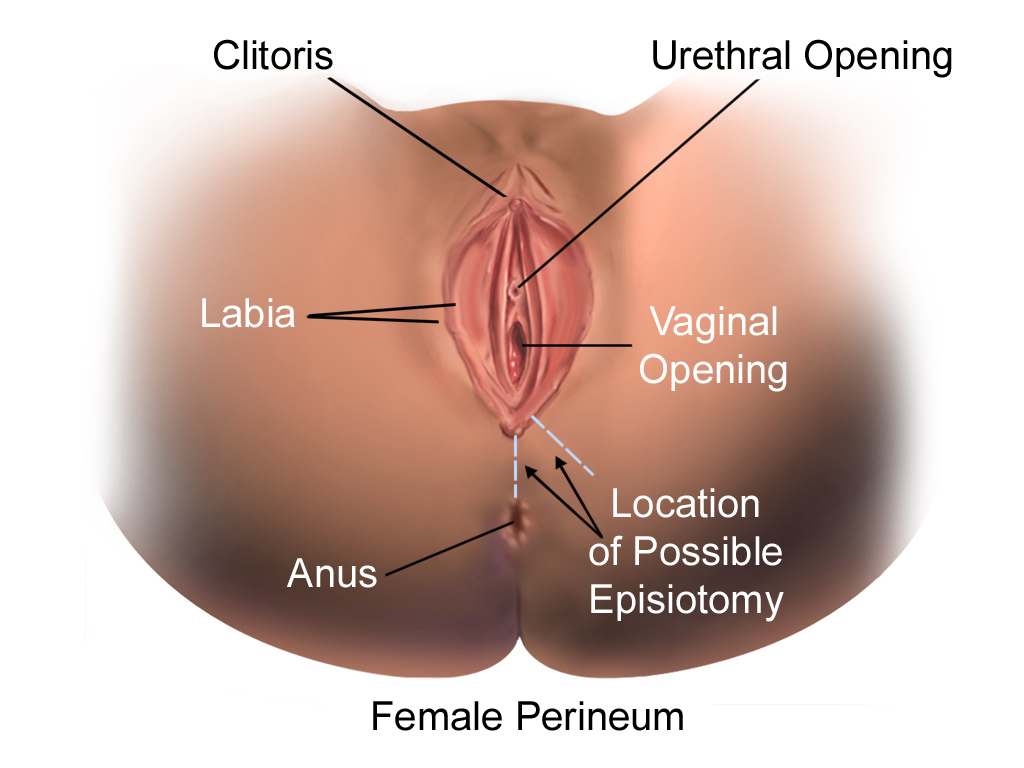
Episiotomy
Episiotomy, also known as perineotomy, is a surgical incision of the perineum and the posterior vaginal wall generally done by a midwife or obstetrician. Episiotomy is usually performed during second stage of labor to quickly enlarge the opening for the baby to pass through. The incision, which can be done from the posterior midline of the vulva straight toward the anus or at an angle to the right or left (medio-lateral episiotomy), is performed under local anesthetic (pudendal anesthesia), and is sutured after delivery. Its routine use is no longer recommended, as perineal massage is an alternative painless method of enlarging the opening for baby. Despite this, it is one of the most common surgical procedures specific to women. In the United States, as of 2012, it was performed in 12% of vaginal births. It is still widely practiced in many parts of the world, including Korea, Japan, Taiwan, China, and Spain. Uses Vaginal tears can occur during childbirth, most often at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breast Engorgement
Breast engorgement occurs in the mammary glands due to expansion and pressure exerted by the synthesis and storage of breast milk. It is also a main factor in altering the ability of the infant to latch-on. Engorgement changes the shape and curvature of the nipple region by making the breast inflexible, flat, hard, and swollen. The nipples on an engorged breast are flat or inverted. Sometimes it may lead to striae on nipples, mainly a preceding symptom of septation mastitis. Engorgement usually happens when the breasts switch from colostrum to mature milk (often referred to as when the milk "comes in"). However, engorgement can also happen later if lactating women miss several nursings and not enough milk is expressed from the breasts. It can be exacerbated by insufficient breastfeeding and/or blocked milk ducts. When engorged the breasts may swell, throb, and cause mild to extreme pain. Engorgement may lead to mastitis (inflammation of the breast) and untreated engorgement p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |