|
Posterior Spinal Artery Syndrome
Posterior spinal artery syndrome (PSAS), also known as ''posterior spinal cord syndrome'', is a type of incomplete spinal cord injury. PSAS is the least commonly occurring of the six clinical spinal cord injury syndromes, with an incidence rate of less than 1%. PSAS originates from an infarct in the posterior spinal artery and is caused by lesions on the posterior portion of the spinal cord, specifically the posterior column, posterior horn, and posterolateral region of the lateral column. These lesions can be caused by trauma to the neck, occlusion of the spinal artery, tumors, disc compression, vitamin B12 deficiency, syphilis, or multiple sclerosis. Despite these numerous pathological pathways, the result is an interruption in transmission of sensory information and motor commands from the brain to the periphery. Causes Trauma to the spinal cord, such as neck hyperflexion injuries, are often the result of car accidents or sports-related injuries. In such injuries, posterio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spinal Cord Injury
A spinal cord injury (SCI) is damage to the spinal cord that causes temporary or permanent changes in its function. Symptoms may include loss of muscle function, sensation, or autonomic function in the parts of the body served by the spinal cord below the level of the injury. Injury can occur at any level of the spinal cord and can be ''complete'', with a total loss of sensation and muscle function at lower sacral segments, or ''incomplete'', meaning some nervous signals are able to travel past the injured area of the cord up to the Sacral S4-5 spinal cord segments. Depending on the location and severity of damage, the symptoms vary, from numbness to paralysis, including bowel or bladder incontinence. Long term outcomes also range widely, from full recovery to permanent tetraplegia (also called quadriplegia) or paraplegia. Complications can include muscle atrophy, loss of voluntary motor control, spasticity, pressure sores, infections, and breathing problems. In the majority of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astrocytoma
Astrocytomas are a type of brain tumor. They originate in a particular kind of glial cells, star-shaped brain cells in the cerebrum called astrocytes. This type of tumor does not usually spread outside the brain and spinal cord and it does not usually affect other organs. Astrocytomas are the most common glioma and can occur in most parts of the brain and occasionally in the spinal cord. Within the astrocytomas, two broad classes are recognized in literature, those with: * Narrow zones of infiltration (mostly noninvasive tumors; e.g., pilocytic astrocytoma, subependymal giant cell astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma), that often are clearly outlined on diagnostic images * Diffuse zones of infiltration (e.g., high-grade astrocytoma, anaplastic astrocytoma, glioblastoma), that share various features, including the ability to arise at any location in the central nervous system, but with a preference for the cerebral hemispheres; they occur usually in adults, and have an intrins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabes Dorsalis
Tabes dorsalis is a late consequence of neurosyphilis, characterized by the slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the neural tracts primarily in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord (nerve root). These patients have lancinating nerve root pain which is aggravated by coughing, and features of sensory ataxia with ocular involvement. Signs and symptoms Signs and symptoms may not appear for decades after the initial infection and include weakness, diminished reflexes, paresthesias (shooting and burning pains, pricking sensations, and formication), hypoesthesias (abnormally diminished sense of touch), tabetic gait (locomotor ataxia), progressive degeneration of the joints, loss of coordination, episodes of intense pain and disturbed sensation (including glossodynia), personality changes, urinary incontinence, dementia, deafness, visual impairment, positive Romberg's test, and impaired response to light (Argyll Robertson pupil). The skeletal musculature is hypotonic d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locomotor Ataxia
Locomotor ataxia is the inability to precisely control one's own bodily movements. __TOC__ Disease People afflicted with this disease may walk in a jerky, non-fluid manner. They will not know where their arms and legs are without looking (i.e. a failure of proprioception), but can, for instance, feel and locate a hot object placed against their feet. It is often a symptom of tabes dorsalis, which is a key finding in tertiary syphilis. It is caused by degeneration of the posterior (dorsal) white column of the spinal cord. In popular culture The chilling effects of this condition and its connection to venereal disease are dramatized in the story "Love O' Women" by Rudyard Kipling. Bram Stoker's death certificate A death certificate is either a legal document issued by a medical practitioner which states when a person died, or a document issued by a government civil registration office, that declares the date, location and cause of a person's death, as ... named the cause of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treponema Pallidum
''Treponema pallidum'', formerly known as ''Spirochaeta pallida'', is a spirochaete bacterium with various subspecies that cause the diseases syphilis, bejel (also known as endemic syphilis), and yaws. It is transmitted only among humans. It is a helically coiled microorganism usually 6–15 μm long and 0.1–0.2 μm wide. ''T. pallidum'''s lack of either a tricarboxylic acid cycle or oxidative phosphorylation results in minimal metabolic activity. The treponemes have a cytoplasmic and an outer membrane. Using light microscopy, treponemes are visible only by using dark field illumination. ''Treponema pallidum'' consists of three subspecies, ''T. p. pallidum, T. p. endemicum,'' and ''T. p. pertenue,'' each of which has a distinct associated disease. Subspecies Three subspecies of ''T. pallidum'' are known: * ''Treponema pallidum pallidum'', which causes syphilis * ''T. p. endemicum'', which causes bejel or endemic syphilis * ''T. p. pertenue'', which causes yaws The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerve Roots
A nerve root (Latin: ''radix nervi'') is the initial segment of a nerve leaving the central nervous system. Nerve roots can be classified as: *Cranial nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the twelve pairs of cranial nerves leaving the central nervous system from the brain stem or the highest levels of the spinal cord. *Spinal nerve roots: the initial or proximal segment of one of the thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves leaving the central nervous system from the spinal cord. Each spinal nerve is formed by the union of a sensory dorsal root and a motor ventral root, meaning that there are sixty-two dorsal/ventral root pairs, and therefore one hundred and twenty-four nerve roots in total, each of which stems from a bundle of nerve rootlets (or root filaments). Cranial nerve roots Cranial nerves originate directly from the brain's surface: two from the cerebrum and the ten others from the brain stem. Cranial roots differ from spinal roots: some of these roots do not se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
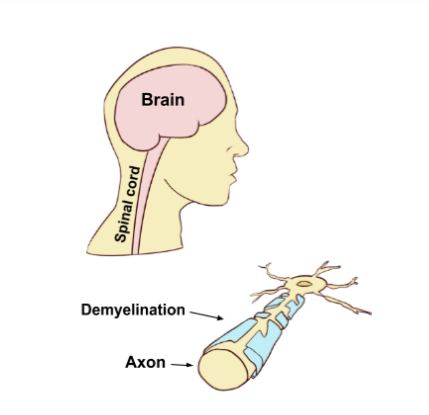
Demyelination
A demyelinating disease is any disease of the nervous system in which the myelin sheath of neurons is damaged. This damage impairs the conduction of signals in the affected nerves. In turn, the reduction in conduction ability causes deficiency in sensation, movement, cognition, or other functions depending on which nerves are involved. Demyelinating diseases can be caused by genetics, infectious agents, autoimmune reactions, and other unknown factors. Proposed causes for demyelination include genetics and environmental factors such as being triggered by a viral infection or chemical exposure. Organophosphate poisoning by commercial insecticides such as sheep dip, weed killers, and flea treatment preparations for pets, can also result in nerve demyelination. Chronic neuroleptic exposure may cause demyelination. Vitamin B12 deficiency may also result in dysmyelination. Demyelinating diseases are traditionally classified in two kinds: demyelinating myelinoclastic diseases and dem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myelin
Myelin is a lipid-rich material that surrounds nerve cell axons (the nervous system's "wires") to insulate them and increase the rate at which electrical impulses (called action potentials) are passed along the axon. The myelinated axon can be likened to an electrical wire (the axon) with insulating material (myelin) around it. However, unlike the plastic covering on an electrical wire, myelin does not form a single long sheath over the entire length of the axon. Rather, myelin sheaths the nerve in segments: in general, each axon is encased with multiple long myelinated sections with short gaps in between called nodes of Ranvier. Myelin is formed in the central nervous system (CNS; brain, spinal cord and optic nerve) by glial cells called oligodendrocytes and in the peripheral nervous system (PNS) by glial cells called Schwann cells. In the CNS, axons carry electrical signals from one nerve cell body to another. In the PNS, axons carry signals to muscles and glands or from senso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobalamin
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in metabolism. It is one of eight B vitamins. It is required by animals, which use it as a cofactor in DNA synthesis, in both fatty acid and amino acid metabolism. It is important in the normal functioning of the nervous system via its role in the synthesis of myelin, and in the circulatory system in the maturation of red blood cells in the bone marrow. Plants do not need cobalamin and carry out the reactions with enzymes that are not dependent on it. Vitamin B12 is the most chemically complex of all vitamins, and for humans, the only vitamin that must be sourced from animal-derived foods or from supplements. Only some archaea and bacteria can synthesize vitamin B12. Most people in developed countries get enough B12 from the consumption of meat or foods with animal sources. Foods containing vitamin B12 include meat, clams, liver, fish, poultry, eggs, and dairy products. Many breakfast cereals are for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals dissolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schwannoma
A schwannoma (or neurilemmoma) is a usually benign nerve sheath tumor composed of Schwann cells, which normally produce the insulating myelin sheath covering peripheral nerves. Schwannomas are homogeneous tumors, consisting only of Schwann cells. The tumor cells always stay on the outside of the nerve, but the tumor itself may either push the nerve aside and/or up against a bony structure (thereby possibly causing damage). Schwannomas are relatively slow-growing. For reasons not yet understood, schwannomas are mostly benign and less than 1% become malignant, degenerating into a form of cancer known as neurofibrosarcoma. These masses are generally contained within a capsule, so surgical removal is often successful. Schwannomas can be associated with neurofibromatosis type II, which may be due to a loss-of-function mutation in the protein merlin. They are universally S-100 positive, which is a marker for cells of neural crest cell origin. Schwannomas of the head and neck are a fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoma
A sarcoma is a malignant tumor, a type of cancer that arises from transformed cells of mesenchymal (connective tissue) origin. Connective tissue is a broad term that includes bone, cartilage, fat, vascular, or hematopoietic tissues, and sarcomas can arise in any of these types of tissues. As a result, there are many subtypes of sarcoma, which are classified based on the specific tissue and type of cell from which the tumor originates. Sarcomas are ''primary'' connective tissue tumors, meaning that they arise in connective tissues. This is in contrast to ''secondary'' (or "metastatic") connective tissue tumors, which occur when a cancer from elsewhere in the body (such as the lungs, breast tissue or prostate) spreads to the connective tissue. The word ''sarcoma'' is derived from the Greek σάρκωμα ''sarkōma'' "fleshy excrescence or substance", itself from σάρξ ''sarx'' meaning "flesh". Classification Sarcomas are typically divided into two major groups: bone sarcom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


