|
Possessive Antecedent
In English grammar, a pronoun has a possessive antecedent if its antecedent (the noun that it refers to) appears in the possessive case; for example, in the following sentence, ''Winston Churchill'' is a possessive antecedent, serving as it does as the antecedent for the pronoun ''him'': :Winston Churchill's history shows him to have been a good writer. In the 1960s, some usage guides started to reject the use of possessive antecedents. These guides argue that a pronoun's antecedent cannot be a noun in a possessive construct; in this case, they contend that ''Winston Churchill'', embedded as it is in the construct ''Winston Churchill's'', cannot serve as the antecedent for the pronoun ''him''. The basis for this contention is that a pronoun's antecedent must be a noun, so that if ''Winston Churchill's'' is an adjective, then a pronoun cannot refer back to it. This rule does not reflect ordinary English usage, and it is commonly ignored (intentionally or otherwise) even by those who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8th and 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar
In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraints, a field that includes domains such as phonology, morphology (linguistics), morphology, and syntax, often complemented by phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are currently two different approaches to the study of grammar: traditional grammar and Grammar#Theoretical frameworks, theoretical grammar. Fluency, Fluent speakers of a variety (linguistics), language variety or ''lect'' have effectively internalized these constraints, the vast majority of which – at least in the case of one's First language, native language(s) – are language acquisition, acquired not by conscious study or language teaching, instruction but by hearing other speakers. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antecedent (grammar)
In grammar, an antecedent is an expression (word, phrase, clause, sentence, etc.) that gives its meaning to a proform (pronoun, pro-verb, pro-adverb, etc.). A proform takes its meaning from its antecedent; e.g., "John arrived late because traffic held him up." The pronoun ''him'' refers to and takes its meaning from ''John'', so ''John'' is the antecedent of ''him''. Proforms usually follow their antecedents, but sometimes they precede them, in which case one is, technically, dealing with postcedents instead of antecedents. The prefix ''ante-'' means "before" or "in front of", and ''post-'' means "after" or "behind". The term ''antecedent'' stems from traditional grammar. The linguistic term that is closely related to ''antecedent'' and ''proform'' is '' anaphora''. Theories of syntax explore the distinction between antecedents and postcedents in terms of binding. Examples Almost any syntactic category can serve as the antecedent to a proform. The following examples illustrate a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possessive Case
A possessive or ktetic form (abbreviated or ; from la, possessivus; grc, κτητικός, translit=ktētikós) is a word or grammatical construction used to indicate a relationship of possession in a broad sense. This can include strict ownership, or a number of other types of relation to a greater or lesser degree analogous to it. Most European languages feature possessive forms associated with personal pronouns, like the English ''my'', ''mine'', ''your'', ''yours'', ''his'' and so on. There are two main ways in which these can be used (and a variety of terminologies for each): * Together with a noun, as in ''my car'', ''your sisters'', ''his boss''. Here the possessive form serves as a '' possessive determiner''. * Without an accompanying noun, as in ''mine is red'', ''I prefer yours'', ''this book is his''. A possessive used in this way is called a ''substantive possessive pronoun'', a possessive pronoun or an ''absolute pronoun''. Some languages, including English, als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Origo (pragmatics)
In pragmatics, the origo is the reference point on which deictic relationships are based. In most deictic systems, the origo identifies with the current speaker (or some property thereof). For instance, if the speaker, John, were to say "This is now my fish", then John would be the origo, and the deictic word "my" would be dependent on that fact. Likewise, his use of the word "this" and "now" communicate his properties, namely his location and point in time. The word origo comes from Latin ''origo'', which means "origin" (pl. ''origines''). ''Origo'' is also the origin of the English word "origin". This word also occurs in the term phrase ''fons et origo'', meaning "source and origin" (''fons'', "source", ''et'', "and", ''origo'', "origin"). See also * Referent A referent () is a person or thing to which a name – a linguistic expression or other symbol – refers. For example, in the sentence ''Mary saw me'', the referent of the word ''Mary'' is the particular person cal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
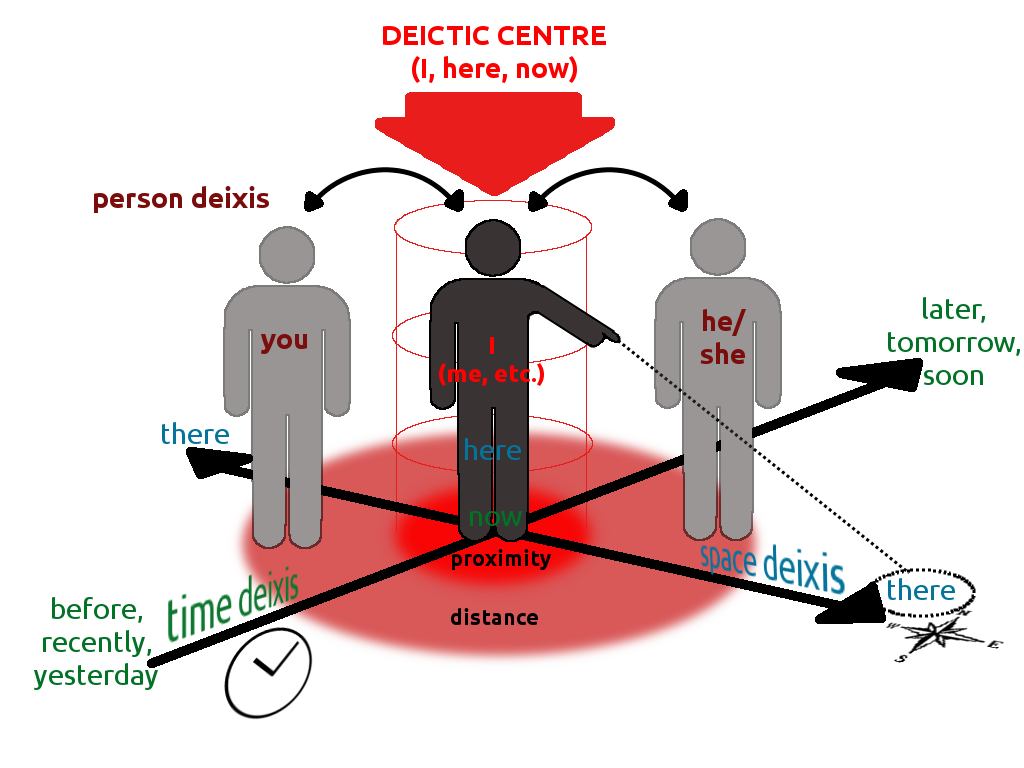
Deixis
In linguistics, deixis (, ) is the use of general words and phrases to refer to a specific time, place, or person in context, e.g., the words ''tomorrow'', ''there'', and ''they''. Words are deictic if their semantic meaning is fixed but their denoted meaning varies depending on time and/or place. Words or phrases that require contextual information to be fully understood—for example, English pronouns—are deictic. Deixis is closely related to anaphora. Although this article deals primarily with deixis in spoken language, the concept is sometimes applied to written language, gestures, and communication media as well. In linguistic anthropology, deixis is treated as a particular subclass of the more general semiotic phenomenon of indexicality, a sign "pointing to" some aspect of its context of occurrence. Although this article draws examples primarily from English, deixis is believed to be a feature (to some degree) of all natural languages.Lyons, John (1977) "Deixis, space an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Grammar
English grammar is the set of structural rules of the English language. This includes the structure of words, phrases, clauses, Sentence (linguistics), sentences, and whole texts. This article describes a generalized, present-day Standard English – a form of speech and writing used in public discourse, including broadcasting, education, entertainment, government, and news, over a range of Register (sociolinguistics), registers, from formal to informal. Divergences from the grammar described here occur in some historical, social, cultural, and regional List of dialects of the English language, varieties of English, although these are more minor than differences in English phonology, pronunciation and lexicon, vocabulary. Modern English has largely abandoned the inflectional grammatical case, case system of Indo-European in favor of analytic language, analytic constructions. The personal pronouns retain morphological case more strongly than any other word class (a remnant of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |