|
Pomegranate (firm)
The pomegranate (''Punica granatum'') is a fruit-bearing deciduous shrub in the family Lythraceae, subfamily Punicoideae, that grows between tall. The pomegranate is rich in symbolic and mythological associations in many cultures. The pomegranate was thought to have originated from Afghanistan and Iran before being introduced and exported to other parts of Asia, Africa, and Europe. It was introduced into Spanish America in the late 16th century and into California by Spanish settlers in 1769. They are widely cultivated throughout West Asia and Caucasus region, South Asia, Central Asia, north and tropical Africa, the drier parts of Southeast Asia, and the Mediterranean Basin. The fruit is typically in season in the Southern Hemisphere from March to May, and in the Northern Hemisphere from September to February. As intact sarcotestas or as juice, pomegranates are used in baking, cooking, juice blends, meal garnishes, smoothies, and alcoholic beverages, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (; 23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after his ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné Blunt (2004), p. 171. (), was a Swedish botanist, zoologist, taxonomist, and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was born in Råshult, the countryside of Småland, in southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he continued to collect an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
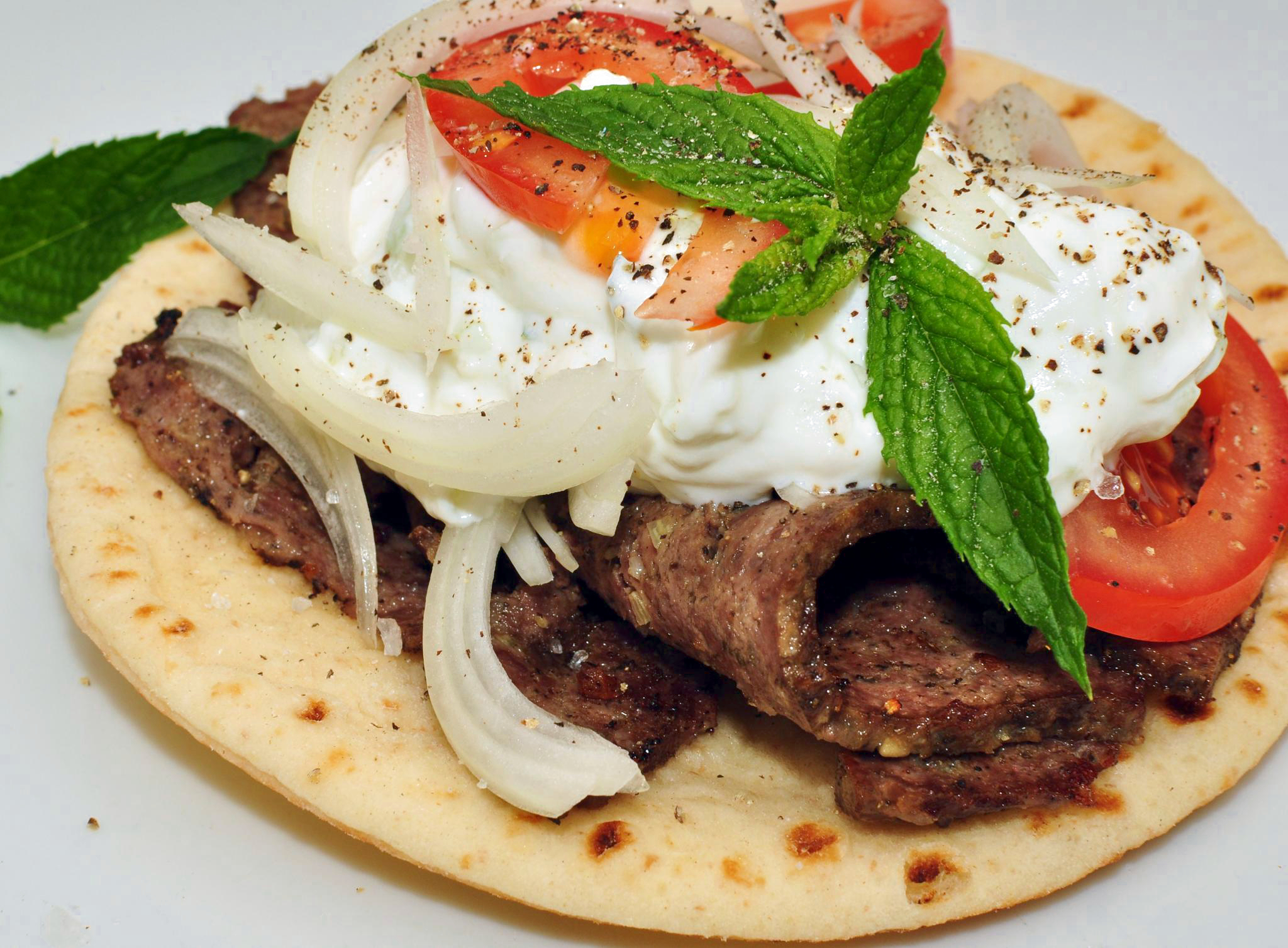
Garnish (food)
A garnish is an item or substance used as a decoration or embellishment accompanying a prepared food dish or drink. In many cases, it may give added or contrasting flavor. Some garnishes are selected mainly to augment the visual impact of the plate, while others are selected specifically for the flavor they may impart. This is in contrast to a condiment, a prepared sauce added to another food item primarily for its flavor. A food item which is served with garnish may be described as being garni, the French term for "garnished." Many garnishes are not intended to be eaten, though for some it is fine to do so. Parsley is an example of a traditional garnish; this pungent green herb has small distinctly shaped leaves, firm stems, and is easy to trim into a garnish. Overview A garnish makes food or drink items more visually appealing. They may, for example, enhance their color, such as when paprika is sprinkled on a salmon salad. They may provide a color contrast, for example whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cochineal
The cochineal ( , ; ''Dactylopius coccus'') is a scale insect in the suborder Sternorrhyncha, from which the natural dye carmine is derived. A primarily sessility (motility), sessile parasitism, parasite native to tropical and subtropical South America through North America (Mexico and the Southwest United States), this insect lives on Cactus, cacti in the genus ''Opuntia'', feeding on plant moisture and nutrients. The insects are found on the pads of prickly pear cacti, collected by brushing them off the plants, and dried. The insect produces carminic acid that deters predation by other insects. Carminic acid, typically 17–24% of dried insects' weight, can be extracted from the body and eggs, then mixed with aluminium or calcium salts to make carmine dye, also known as cochineal. Today, carmine is primarily used as a Food coloring, colorant in food and in lipstick (Carmine, E120 or Carminic acid, Natural Red 4). Carmine dye was used in the Americas for coloring fabrics and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metathesis (linguistics)
Metathesis (; from Greek , from "I put in a different order"; Latin: ''transpositio'') is the transposition of sounds or syllables in a word or of words in a sentence. Most commonly, it refers to the interchange of two or more contiguous segments or syllables, known as adjacent metathesis or local metathesis: * ''foliage'' > ''**foilage'' (adjacent segments) * ''anemone'' > ''**anenome'' (adjacent syllables) * ''cavalry'' > ''**calvary'' (codas of adjacent syllables) Metathesis may also involve interchanging non-contiguous sounds, known as nonadjacent metathesis, long-distance metathesis, or hyperthesis, as shown in these examples of metathesis sound change from Latin to Spanish: * Latin > Spanish "word" * Latin > Spanish "miracle" * Latin > Spanish "danger, peril" * Latin > Spanish "crocodile" Many languages have words that show this phenomenon, and some even use it as a regular part of their grammar, such as Hebrew and Fur. The process of metathesis has altered the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet (name)
Garnet is a name of Middle English origin, derived from the dark red gemstone, which was in turn named for the pomegranate that the garnet crystals resemble. The surname Garnett comes from an Old English occupational surname referring to a seller of hinges. It is both a surname and a given name. The name came into occasional use along with other gem names during the late Victorian era. Garnet was among the top 1,000 names for girls in the United States between 1884 and 1944. It was most popular in 1911, when it was the 376th most popular given name for American girls. It was in occasional use for boys in the United States between 1882 and 1925. It was most popular in 1904, when it was 593rd most popular name for American boys. The name has not appeared among the top 1,000 names for boys or girls since 1944 in the United States. People Surname * Eldon Garnet (born 1946), Canadian artist * Henry Garnet (1555–1606), English Jesuit * Henry Highland Garnet (1815–1882), African-Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Language
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is the language of literature, official documents, and formal written m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granada
Granada (,, DIN 31635, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada (Spain), Sierra Nevada mountains, at the confluence of four rivers, the Darro (river), Darro, the Genil, the Monachil (river), Monachil and the Beiro. Ascribed to the Vega de Granada ''comarca'', the city sits at an average elevation of Above mean sea level, above sea level, yet is only one hour by car from the Mediterranean coast, the Costa Tropical. Nearby is the Sierra Nevada Ski Station, where the FIS Alpine World Ski Championships 1996 were held. In the 2021 national census, the population of the city of Granada proper was 227,383, and the population of the entire municipal area was estimated to be 231,775, ranking as the Ranked lists of Spanish municipalities, 20th-largest urban area of Spain. About 3.3% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folk Etymology
Folk etymology (also known as popular etymology, analogical reformation, reanalysis, morphological reanalysis or etymological reinterpretation) is a change in a word or phrase resulting from the replacement of an unfamiliar form by a more familiar one. The form or the meaning of an archaic, foreign, or otherwise unfamiliar word is reinterpreted as resembling more familiar words or morphemes. The term ''folk etymology'' is a loan translation from German language, German ''Volksetymologie'', coined by Ernst Förstemann in 1852. Folk etymology is a Productivity (linguistics), productive process in historical linguistics, language change, and social relation, social interaction. Reanalysis of a word's history or original form can affect its spelling, pronunciation, or meaning. This is frequently seen in relation to loanwords or words that have become archaic or obsolete. Examples of words created or changed through folk etymology include the English dialectal form wikt:sparrowgrass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blazon
In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct the appropriate image. The verb ''to blazon'' means to create such a description. The visual depiction of a coat of arms or flag has traditionally had considerable latitude in design, but a verbal blazon specifies the essentially distinctive elements. A coat of arms or flag is therefore primarily defined not by a picture but rather by the wording of its blazon (though in modern usage flags are often additionally and more precisely defined using geometrical specifications). ''Blazon'' is also the specialized language in which a blazon is written, and, as a verb, the act of writing such a description. ''Blazonry'' is the art, craft or practice of creating a blazon. The language employed in ''blazonry'' has its own vocabulary, grammar and syntax, which becomes essential for comprehension when blazoning a complex coat of arms. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned as the main medium of scholarly exchange, as the liturgical language of the Church, and as the working language of science, literature, law, and administration. Medieval Latin represented a continuation of Classical Latin and Late Latin, with enhancements for new concepts as well as for the increasing integration of Christianity. Despite some meaningful differences from Classical Latin, Medieval writers did not regard it as a fundamentally different language. There is no real consensus on the exact boundary where Late Latin ends and Medieval Latin begins. Some scholarly surveys begin with the rise of early Ecclesiastical Latin in the middle of the 4th century, others around 500, and still others with the replacement of written Late Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are major factors in different styles of wine. These differences result from the complex interactions between the biochemical development of the grape, the reactions involved in fermentation, the grape's growing environment (terroir), and the wine production process. Many countries enact legal appellations intended to define styles and qualities of wine. These typically restrict the geographical origin and permitted varieties of grapes, as well as other aspects of wine production. Wines not made from grapes involve fermentation of other crops including rice wine and other fruit wines such as plum, cherry, pomegranate, currant and elderberry. Wine has been produced for thousands of years. The earliest evidence of wine is from the Caucasus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



.jpg)

