|
Polyamine
A polyamine is an organic compound having more than two amino groups. Alkyl polyamines occur naturally, but some are synthetic. Alkylpolyamines are colorless, hygroscopic, and water soluble. Near neutral pH, they exist as the ammonium derivatives. Most aromatic polyamines are crystalline solids at room temperature. Natural polyamines Low-molecular-weight linear polyamines are found in all forms of life. The principal examples are the triamine spermidine and the tetraamine spermine. They are structurally and biosynthetically related to the diamines putrescine and cadaverine. Polyamine metabolism is regulated by the activity of the enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (ODC). Polyamines are found in high concentrations in the mammalian brain. File:Spermidine-2D-skeletal.svg, spermidine File:Spermine.svg, spermine Synthetic polyamines Several synthetic polyamines are used in chemical industry and the research laboratory. They are mainly of interest as additives to motor oil and as co-rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermidine
Spermidine is a polyamine compound () found in ribosomes and living tissues and having various metabolic functions within organisms. It was originally isolated from semen. Function Spermidine is an aliphatic polyamine. Spermidine synthase (SPDS) catalyzes its formation from putrescine. It is a precursor to other polyamines, such as spermine and its structural isomer thermospermine. Spermidine synchronizes an array of biological processes, (such as Ca2+, Na+, K+ -ATPase) thus maintaining membrane potential and controlling intracellular pH and volume. Spermidine regulates biological processes, such as Ca2+ influx by glutamatergic N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor (NMDA receptor), which has been associated with nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and cGMP/PKG pathway activation and a decrease of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in cerebral cortex synaptosomes. Spermidine is a longevity agent in mammals due to various mechanisms of action, which are just beginning to be understood. Autophagy is the main m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermine
Spermine is a polyamine involved in cellular metabolism that is found in all Eukaryote, eukaryotic cells. The precursor for synthesis of spermine is the amino acid ornithine. It is an essential growth factor in some Bacterium, bacteria as well. It is found as a polycation at physiological pH. Spermine is associated with nucleic acids and is thought to stabilize helical structure, particularly in viruses. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek first described crystals of spermine phosphate in human semen in 1678. The name ''spermin'' was first used by the German chemists Albert Ladenburg, Ladenburg and Abel in 1888, and the correct structure of spermine was not finally established until 1926, simultaneously in England (by Dudley, Rosenheim, and Starling) and Germany (by Wrede et al.). Spermine is the chemical primarily responsible for the characteristic odor of semen. Derivative A derivative (chemistry), derivative of spermine, N1, N12-bis(ethyl)spermine (also known as BESm) was investig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ornithine Decarboxylase
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis. In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer. Reaction mechanism Lysine 69 on ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) binds the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate to form a Schiff base. Ornithine displaces the lysine to form a Schiff base attached to orthonine, which decarboxylates to form a quinoid intermediate. This intermediate rearranges to form a Schiff base attached to putrescine, which is attacked by lysine to release putrescine product and reform PLP-bound ODC. This is the first step and the rate-limiting step in humans for the production of polyamines, compounds required for cell division. Structure image:Ornithine Decarboxylase Publication View.png, 270px, 3D crystal structure of ornithine decarboxylase.; ; rendered viPyMOL The active form of ornithine decarboxyla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
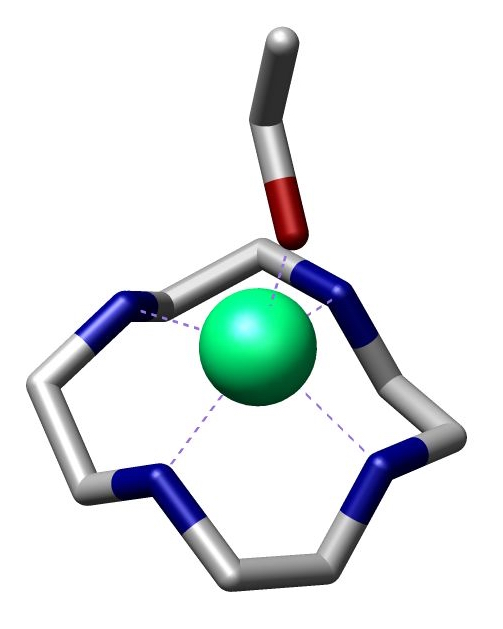
Cyclam
Cyclam (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) is an organic compound with the formula (NHCH2CH2NHCH2CH2CH2)2. Classified as an aza-crown ether, it is a white solid that is soluble in water. As a macrocyclic ligand, it binds strongly to many transition metal cations. The compound was first prepared by the reaction of 1,3-dibromopropane and ethylenediamine. The compound features four secondary amines. Its complexes therefore can exist as several diastereomers, depending on the relative orientation of the N–H centres. Its complexes feature alternating five- and six-membered chelate rings. The closely related ligand cyclen ((CH2CH2NH)4) forms only five-membered C2N2M chelate rings and tends not to form square-planar complexes. ''N''-Alkyl derivatives Metal-cyclam complexes are prone to oxidative degradation, which is initiated by deprotonation of the secondary amine. This flaw led to the development of cyclam derivatives wherein the NH centres are replaced by tertiary amines. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylenimine
Polyethylenimine (PEI) or polyaziridine is a polymer with repeating units composed of the amine group and two carbon aliphatic ''CHCH'' spacers. Linear polyethyleneimines contain all secondary amines, in contrast to branched PEIs which contain primary, secondary and tertiary amino groups. Totally branched, dendrimeric forms were also reported. PEI is produced on an industrial scale and finds many applications usually derived from its polycationic character. Properties The linear PEI is a semi-crystalline solid at room temperature while branched PEI is a fully amorphous polymer existing as a liquid at all molecular weights. Linear polyethyleneimine is soluble in hot water, at low pH, in methanol, ethanol, or chloroform. It is insoluble in cold water, benzene, ethyl ether, and acetone. Linear polyethyleneimine has a melting point of around 67 °C. Both linear and branched polyethyleneimine can be stored at room temperature. Linear polyethyleneimine is able to form cryogels up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,1,1-Tris(aminomethyl)ethane
1,1,1-Tris(aminomethyl)ethane (TAME) is an organic compound with the formula CHC(CHNH). It is a colorless liquid. It is classified as a polyamine tripodal ligand, i.e., capable of binding to metal ions through three sites and hence is a tridentate chelating ligand, occupying a face of the coordination polyhedron. Preparation TAME is synthesized by the Pd/C-catalyzed hydrogenation of 1,1,1-tris(azidomethyl)ethane. Although azides are potentially explosive, they are excellent and practical source of primary amines. The required tris(azidomethyl)ethane is obtained from the tritosylate by salt metathesis using sodium azide. These two steps are: :3 NaN + CHC(CHOTs) → CHC(CHN) + 3 NaOTs :3 H + CHC(CHN) → CHC(CHNH) + 3 N Complexes of TAME The tripodal TAME ligand coordinates facially to metal ions. This stereochemical feature has been exploited in the preparation of platinum(IV) cage complexes, e.g., t(tame) which is a six coordinate Pt(IV) complex. Platinum in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pentamethyldiethylenetriamine
PMDTA (''N'',''N'',''N′'',''N′′'',''N′′''-pentamethyldiethylenetriamine) is an organic compound with the formula CH3)2NCH2CH2sub>2NCH3. PMDTA is a basic, bulky, and flexible, tridentate ligand that is a used in organolithium chemistry. It is a colorless liquid, although impure samples appear yellowish. Synthesis PMDTA is prepared from diethylenetriamine by the Eschweiler-Clarke reaction, involving the use of formaldehyde and formic acid Formic acid (), systematically named methanoic acid, is the simplest carboxylic acid, and has the chemical formula HCOOH and structure . It is an important intermediate in chemical synthesis and occurs naturally, most notably in some ants. Es .... :(H2N H2sub>2)2NH + 5 CH2O + 5 HCO2H → (Me2N H2sub>2)2NMe + 5 CO2 + 5 H2O Comparison with diethylenetriamine Unlike diethylenetriamine, all three amines in PMDTA are tertiary. Both PMDTA and diethylenetriamine are tridentate ligands that form two five-membered ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Putrescine
Putrescine is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4(NH2)2. It is a colorless solid that melts near room temperature. It is classified as a diamine. Together with cadaverine, it is largely responsible for the foul odor of putrefying flesh, but also contributes to other unpleasant odors. Production Putrescine is produced on an industrial scale by the hydrogenation of succinonitrile. Biotechnological production of putrescine from renewable feedstock has been investigated. A metabolically engineered strain of ''Escherichia coli'' that produces putrescine at high concentrations in glucose mineral salts medium has been described. Biochemistry Spermidine synthase uses putrescine and ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine (decarboxylated ''S''-adenosyl methionine) to produce spermidine. Spermidine in turn is combined with another ''S''-adenosylmethioninamine and gets converted to spermine. Putrescine is synthesized in small quantities by healthy living cells by the action of ornithine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyethylenimine
Polyethylenimine (PEI) or polyaziridine is a polymer with repeating units composed of the amine group and two carbon aliphatic ''CHCH'' spacers. Linear polyethyleneimines contain all secondary amines, in contrast to branched PEIs which contain primary, secondary and tertiary amino groups. Totally branched, dendrimeric forms were also reported. PEI is produced on an industrial scale and finds many applications usually derived from its polycationic character. Properties The linear PEI is a semi-crystalline solid at room temperature while branched PEI is a fully amorphous polymer existing as a liquid at all molecular weights. Linear polyethyleneimine is soluble in hot water, at low pH, in methanol, ethanol, or chloroform. It is insoluble in cold water, benzene, ethyl ether, and acetone. Linear polyethyleneimine has a melting point of around 67 °C. Both linear and branched polyethyleneimine can be stored at room temperature. Linear polyethyleneimine is able to form cryogels up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triazinane
Triazinanes are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is . They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazinanes being common. The triazinanes have six-membered cyclohexane-like ring but with three carbons replaced by nitrogens. Most commonly, the amines are tertiary. References * ''Heterocyclic Chemistry'' T.L. Gilchrist 1985 (1997, ) See also * 6-membered rings with one nitrogen atom: Piperidine * 6-membered rings with two nitrogen atoms: Diazinane ** Hexahydropyrimidine ** Hexahydropyridazine * Triazine Triazines are a class of nitrogen-containing heterocycles. The parent molecules' molecular formula is . They exist in three isomeric forms, 1,3,5-triazines being common. Structure The triazines have planar six-membered benzene-like ring but ... {{Authority control Heterocyclic compounds with 1 ring Nitrogen heterocycles Six-membered rings Polyamines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclen
Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Synthesis Some syntheses exploit the Thorpe-Ingold effect to facilitate ring-formation. Illustrative is the reaction of the deprotonated tosylamides with ditosylates: :TsN(CH2CH2NTsNa)2 + TsN(CH2CH2OTs)2 → (TsNCH2CH2)4 The resulting macrocycle can be deprotected with strong acid. Base gives the tetramine. High dilution conditions result in a low reaction rate penalty and this disadvantage is removed in an alternative procedure starting from triethylenetetraamine and dithiooxamide to a bisamidine – also a bis(imidazoline) – followed by reduction and ring expansion with DIBAL. : In one study cyclen is covalently bonded through a propylene molecular spacer to adenine and chelated with zinc diperchlorate. This complex is able to selectively bind uracil and uridine in a 1:2 ratio both through the adenine part and cyclen part of the molecule as evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocycle
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry. Synthesis The formation of macrocycles by ring-closure is called macrocylization. Pioneering work was reported for studies on terpenoid macrocycles. The central challenge to macrocyclization is that ring-closing reactions do not favor the formation of large rings. Instead, small rings or polymers tend to form. This kinetic problem can be addressed by using high-dilution reactions, whereby intramolecular processes are favored relative to polymerizations. Some macrocyclizations are favored using template reactions. Templates are ions, molecules, surfaces etc. that bind and pre-organize compounds, guiding them toward formation of a particular ring size. The crown ethers are often generated in the presence of an alkali metal cation, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cl2.png)