|
Cyclen
Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Synthesis Some syntheses exploit the Thorpe-Ingold effect to facilitate ring-formation. Illustrative is the reaction of the deprotonated tosylamides with ditosylates: :TsN(CH2CH2NTsNa)2 + TsN(CH2CH2OTs)2 → (TsNCH2CH2)4 The resulting macrocycle can be deprotected with strong acid. Base gives the tetramine. High dilution conditions result in a low reaction rate penalty and this disadvantage is removed in an alternative procedure starting from triethylenetetraamine and dithiooxamide to a bisamidine – also a bis(imidazoline) – followed by reduction and ring expansion with DIBAL. : In one study cyclen is covalently bonded through a propylene molecular spacer to adenine and chelated with zinc diperchlorate. This complex is able to selectively bind uracil and uridine in a 1:2 ratio both through the adenine part and cyclen part of the molecule as evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclen Synthesis Dithiooxamide Method
Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Synthesis Some syntheses exploit the Thorpe-Ingold effect to facilitate ring-formation. Illustrative is the reaction of the deprotonated tosylamides with ditosylates: :TsN(CH2CH2NTsNa)2 + TsN(CH2CH2OTs)2 → (TsNCH2CH2)4 The resulting macrocycle can be deprotected with strong acid. Base gives the tetramine. High dilution conditions result in a low reaction rate penalty and this disadvantage is removed in an alternative procedure starting from triethylenetetraamine and dithiooxamide to a amidine, bisamidine – also a bis(2-Imidazoline, imidazoline) – followed by organic reduction, reduction and ring expansion with DIBAL. : In one study cyclen is covalent bond, covalently bonded through a propylene molecular spacer to adenine and chelation, chelated with zinc perchlorate, diperchlorate. This complex is able to selectively bind uracil and uridine in a 1:2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
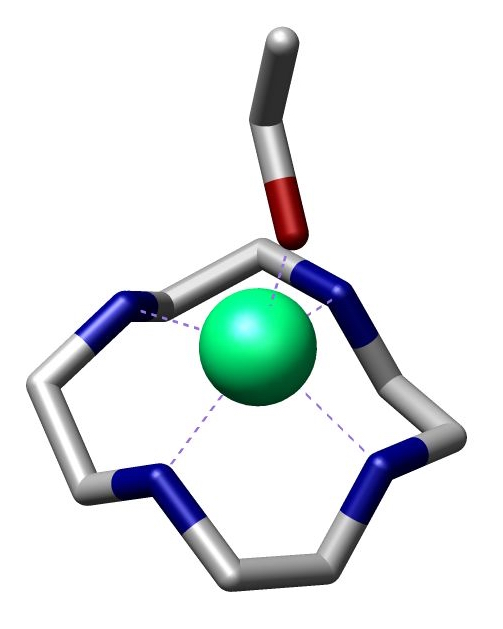
Cyclen Zinc InorgChem 1997 4579 Commons
Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Synthesis Some syntheses exploit the Thorpe-Ingold effect to facilitate ring-formation. Illustrative is the reaction of the deprotonated tosylamides with ditosylates: :TsN(CH2CH2NTsNa)2 + TsN(CH2CH2OTs)2 → (TsNCH2CH2)4 The resulting macrocycle can be deprotected with strong acid. Base gives the tetramine. High dilution conditions result in a low reaction rate penalty and this disadvantage is removed in an alternative procedure starting from triethylenetetraamine and dithiooxamide to a bisamidine – also a bis(imidazoline) – followed by reduction and ring expansion with DIBAL. : In one study cyclen is covalently bonded through a propylene molecular spacer to adenine and chelated with zinc diperchlorate. This complex is able to selectively bind uracil and uridine in a 1:2 ratio both through the adenine part and cyclen part of the molecule as evid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dithiooxamide
Dithiooxamide, also known as rubeanic acid is an organic compound. It is the sulfur analog of oxamide. It acts as a chelating agent, e.g. in the detection or determination of copper. It has also been used as a building block in the synthesis of cyclen Cyclen (1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane) is a aza-crown ether with the formula (CH2CH2NH)4. It is a white solid. Synthesis Some syntheses exploit the Thorpe-Ingold effect to facilitate ring-formation. Illustrative is the reaction of the depro ....{{OrgSynth , title = 1,4,7,10-Tetraazacyclododecane , author = David P. Reed and Gary R. Weisman , collvol = 10 , collvolpages = 667 , year = 2004 , prep = v78p0073 References Thioamides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclam
Cyclam (1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane) is an organic compound with the formula (NHCH2CH2NHCH2CH2CH2)2. Classified as an aza-crown ether, it is a white solid that is soluble in water. As a macrocyclic ligand, it binds strongly to many transition metal cations. The compound was first prepared by the reaction of 1,3-dibromopropane and ethylenediamine. The compound features four secondary amines. Its complexes therefore can exist as several diastereomers, depending on the relative orientation of the N–H centres. Its complexes feature alternating five- and six-membered chelate rings. The closely related ligand cyclen ((CH2CH2NH)4) forms only five-membered C2N2M chelate rings and tends not to form square-planar complexes. ''N''-Alkyl derivatives Metal-cyclam complexes are prone to oxidative degradation, which is initiated by deprotonation of the secondary amine. This flaw led to the development of cyclam derivatives wherein the NH centres are replaced by tertiary amines. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aza-crown Ether
In organic chemistry, an aza-crown ether is an aza analogue of a crown ether (cyclic polyether). That is, it has a nitrogen atom (amine linkage, or ) in place of each oxygen atom (ether linkage, ) around the ring. While the parent crown ethers have the formulae , the parent ''aza''-crown ethers have the formulae , where n = 3, 4, 5, 6. Well-studied aza crowns include triazacyclononane (n = 3), cyclen (n = 4), and hexaaza-18-crown-6 (n = 6). File:Me3TACN.png, 1,4,7-Trimethyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane, a tridentate ligand used in coordination chemistry. File:Cyclam.png, Cyclam is a tetraaza crown ether with alternating and linkers between amine centers. File:Plerixafor.svg, Plerixafor, a derivative of cyclam, is used to treat lymphoma and multiple myeloma. File:Cryptand.svg, 2.2.2-Cryptand is an aza-crown of the mixed ether-amine variety. Synthesis The synthesis of aza crown ethers are subject to the challenges associated with the preparation of macrocycles. The 18-membered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelation
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a Denticity, polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast medium, contrast agents in MRI, MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chelating Agents
Chelation is a type of bonding of ions and molecules to metal ions. It involves the formation or presence of two or more separate coordinate bonds between a polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand and a single central metal atom. These ligands are called chelants, chelators, chelating agents, or sequestering agents. They are usually organic compounds, but this is not a necessity, as in the case of zinc and its use as a maintenance therapy to prevent the absorption of copper in people with Wilson's disease. Chelation is useful in applications such as providing nutritional supplements, in chelation therapy to remove toxic metals from the body, as contrast agents in MRI scanning, in manufacturing using homogeneous catalysts, in chemical water treatment to assist in the removal of metals, and in fertilizers. Chelate effect The chelate effect is the greater affinity of chelating ligands for a metal ion than that of similar nonchelating (monodentate) ligands for the same metal. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macrocycles
Macrocycles are often described as molecules and ions containing a ring of twelve or more atoms. Classical examples include the crown ethers, calixarenes, porphyrins, and cyclodextrins. Macrocycles describe a large, mature area of chemistry. Synthesis The formation of macrocycles by ring-closure is called macrocylization. Pioneering work was reported for studies on terpenoid macrocycles. The central challenge to macrocyclization is that ring-closing reactions do not favor the formation of large rings. Instead, small rings or polymers tend to form. This kinetic problem can be addressed by using high-dilution reactions, whereby intramolecular processes are favored relative to polymerizations. Some macrocyclizations are favored using template reactions. Templates are ions, molecules, surfaces etc. that bind and pre-organize compounds, guiding them toward formation of a particular ring size. The crown ethers are often generated in the presence of an alkali metal cation, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethyleneamines
Ethyleneamines are a class of amine compounds containing ethylene (-CH2CH2-) linkages between amine groups. These compounds are generally colorless, low-viscosity liquids with a fishy amine odor. They are primarily used as building block chemicals and in epoxy resin curing agent chemistry. Production There are two main routes for the production of ethyleneamines, the reaction between ethylene dichloride and ammonia, and the reductive amination of monethanolamine. World capacity of ethyleneamines for the year 2001 was estimated to be 385,000 tonnes/year, with the majority comprising the ethylene dichloride route. In the ethylene dichloride route, the initial product of this reaction is ethylenediamine. In the presence of excess ethylene dichloride, the initial ethyleneamine is extended by one ethylene unit. The terminal alkyl chloride reacts with ammonia to give the amine, and the polyamine chain can be extended further in this fashion. Addition of a polyamine to the initial react ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. A mass spectrum is a type of plot of the ion signal as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. These spectra are used to determine the elemental or isotopic signature of a sample, the masses of particles and of molecules, and to elucidate the chemical identity or structure of molecules and other chemical compounds. In a typical MS procedure, a sample, which may be solid, liquid, or gaseous, is ionized, for example by bombarding it with a beam of electrons. This may cause some of the sample's molecules to break up into positively charged fragments or simply become positively charged without fragmenting. These ions (fragments) are then separated accordin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uridine
Uridine (symbol U or Urd) is a glycosylated pyrimidine analog containing uracil attached to a ribose ring (or more specifically, a ribofuranose) via a β-N1-glycosidic bond. The analog is one of the five standard nucleosides which make up nucleic acids, the others being adenosine, thymidine, cytidine and guanosine. The five nucleosides are commonly abbreviated to their symbols, U, A, dT, C, and G, respectively. However, thymidine is more commonly written as 'dT' ('d' represents 'deoxy') as it contains a 2'-deoxyribofuranose moiety rather than the ribofuranose ring found in uridine. This is because thymidine is found in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and usually not in ribonucleic acid (RNA). Conversely, uridine is found in RNA and not DNA. The remaining three nucleosides may be found in both RNA and DNA. In RNA, they would be represented as A, C and G whereas in DNA they would be represented as dA, dC and dG. Biosynthesis Uridine is widely produced in nature as uridine monophosp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uracil
Uracil () (symbol U or Ura) is one of the four nucleobases in the nucleic acid RNA. The others are adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). In RNA, uracil binds to adenine via two hydrogen bonds. In DNA, the uracil nucleobase is replaced by thymine (T). Uracil is a demethylated form of thymine. Uracil is a common and naturally occurring pyrimidine derivative. The name "uracil" was coined in 1885 by the German chemist Robert Behrend, who was attempting to synthesize derivatives of uric acid. Originally discovered in 1900 by Alberto Ascoli, it was isolated by hydrolysis of yeast nuclein; it was also found in bovine thymus and spleen, herring sperm, and wheat germ. It is a planar, unsaturated compound that has the ability to absorb light. Based on 12C/13C isotopic ratios of organic compounds found in the Murchison meteorite, it is believed that uracil, xanthine, and related molecules can also be formed extraterrestrially. Data from the Cassini mission, orbiting in the Saturn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cl2.png)
6) (BIGNOU01).png)

.jpg)