|
Politics Of Kosovo
The politics of Kosovo takes place in a framework of a multi-party parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the President ''(Presidenti)'' is the head of state and the Prime Minister ''(Kryeministri)'' the head of government. Parliamentary elections are held every four years, the most recent in 2021. The executive power is exercised by the government ''(Qeveria)'', presided over by the Prime Minister. Legislative power is vested in both the executive and the parliament ''(Kuvendi)''. The Judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. Government Executive The Executive of Kosovo is the collection of Kosovo institutions that exercises executive authority in Kosovo. It is headed by the Prime Minister of Kosovo, and also includes the prime minister, the deputy prime ministers, and various ministers. The President of Kosovo also plays a role. Albin Kurti is the Prime Minister of Kosovo and head of government. Vjosa Osmani is the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coat Of Arms Of Kosovo
The coat of arms of the Republic of Kosovo was introduced following the unilateral declaration of independence on 17 February 2008. It shows six white stars in an arc above a solid golden shape of Kosovo as seen on a standard projection map, placed on a rounded triangular shield with a blue field and a golden border. Its central figures, the stars and the shape, are also the content of the new blue flag of Kosovo, already adopted at the same time. Government emblems Some of the institutions of Kosovo have adopted their own distinct emblems to represent themselves. File:Seal of the President of Kosovo.svg, Emblem used by the President of Kosovo File:Emblem of the Constitutional Court of the Republic of Kosovo (black and white).svg, Emblem of the Constitutional Court of Kosovo History Symbols used during United Nations administration The Constitutional Charter for Provisional Self-Government in Kosovo, promulgated by United Nations Mission in Kosovo (UNMIK) in May 2001, st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary Of Kosovo
The Judiciary of Kosovo is the collection of the central Kosovo institutions that exercises judicial authority in Kosovo. According to the 2008 Constitution of Kosovo, the judicial system is composed of the Supreme Court and subordinate courts, a Constitutional Court, and an independent prosecutorial institution. The courts are administered by the Kosovo Judicial Council. History Until 2010, when the Law on Courts was approved by the Parliament of the Republic of Kosovo, the 1978 Law on Courts was in force. Under this law there was a regular system of courts consisting of the Municipal Court, District Court, the Court for Minor Offences, the High Court for Minor Offences and the Supreme Court. After the Constitution was enacted, another Court was added to the judicial system: Constitutional Court. But, as explained below, with the new law in force, the system of the Courts and Prosecution Offices had started to change. In 1999, UNMIK was deployed to provide an interim adminis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic League Of Kosovo
The Democratic League of Kosovo ( sq, Lidhja Demokratike e Kosovës, LDK) is the oldest and one of the largest political parties in Kosovo. At the legislative elections held on 24 October 2004 the party won 45.4% of the popular vote and 47 out of 120 seats, seven of which have defected to the Nexhat Daci-led Democratic League of Dardania. One of the founding members, Ibrahim Rugova was the president of the party as the president of Kosovo until his death, on 21 January 2006. At the last legislative elections held on 17 November 2007, the party won only 22.6% and 25 seats but went on to form a Coalition government with Hashim Thaçi's Democratic Party of Kosovo (PDK). In October 2010, the LDK withdrew from the coalition. History During the late 1980s, nationalism was on the rise throughout the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. Since 1974 the province of Kosovo, although part of the Socialist Republic of Serbia, was a self-governed entity over which the Serbian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vetëvendosje
Lëvizja Vetëvendosje (, en, Self-determination Movement; LVV) is a centre-left to left-wing political party in Kosovo. It is orientated towards principles of social democracy, populism, and Albanian nationalism. Vetëvendosje was founded in 2005 as a grassroots, anti-establishment movement and as a successor of the Kosova Action Network (KAN) and participated in elections for the first time in 2010. The movement widely bases its ideology on the works of Ukshin Hoti. Vetëvendosje campaigns for social and political change based on the principles of equality, democracy, political freedom and social justice for every citizen. The program of Vetëvendosje focuses on three main axes: meritocracy, developmental state, and welfare state. Vetëvendosje is the largest political movement in Kosovo, having won 58 seats in the 2021 Kosovan parliamentary election together with Vjosa Osmani's Guxo! list, which ran inside Vetëvendosje's list. It is in government in coalition with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary
The judiciary (also known as the judicial system, judicature, judicial branch, judiciative branch, and court or judiciary system) is the system of courts that adjudicates legal disputes/disagreements and interprets, defends, and applies the law in legal cases. Definition The judiciary is the system of courts that interprets, defends, and applies the law in the name of the state. The judiciary can also be thought of as the mechanism for the resolution of disputes. Under the doctrine of the separation of powers, the judiciary generally does not make statutory law (which is the responsibility of the legislature) or enforce law (which is the responsibility of the executive), but rather interprets, defends, and applies the law to the facts of each case. However, in some countries the judiciary does make common law. In many jurisdictions the judicial branch has the power to change laws through the process of judicial review. Courts with judicial review power may annul the laws ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legislative Power
A legislature is an deliberative assembly, assembly with the authority to make laws for a Polity, political entity such as a Sovereign state, country or city. They are often contrasted with the Executive (government), executive and Judiciary, judicial powers of government. Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as primary legislation. In addition, legislatures may observe and steer governing actions, with authority to amend the budget involved. The members of a legislature are called legislators. In a democracy, legislators are most commonly popularly Election, elected, although indirect election and appointment by the executive are also used, particularly for bicameralism, bicameral legislatures featuring an upper chamber. Terminology The name used to refer to a legislative body varies by country. Common names include: * Assembly (from ''to assemble'') * Congress (from ''to congregate'') * Council (from Latin 'meeting') * Diet (from old German 'people') * Estate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Executive Power
The Executive, also referred as the Executive branch or Executive power, is the term commonly used to describe that part of government which enforces the law, and has overall responsibility for the governance of a state. In political systems based on the separation of powers, such as the USA, government authority is distributed between several branches in order to prevent power being concentrated in the hands of a single person or group. To achieve this, each branch is subject to checks by the other two; in general, the role of the Legislature is to pass laws, which are then enforced by the Executive, and interpreted by the Judiciary. The Executive can be also be the source of certain types of law, such as a decree or executive order. In those that use fusion of powers, typically Parliamentary systems, the Executive forms the government and its members generally belong to the political party that controls the legislature or "Parliament". Since the Executive requires the supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
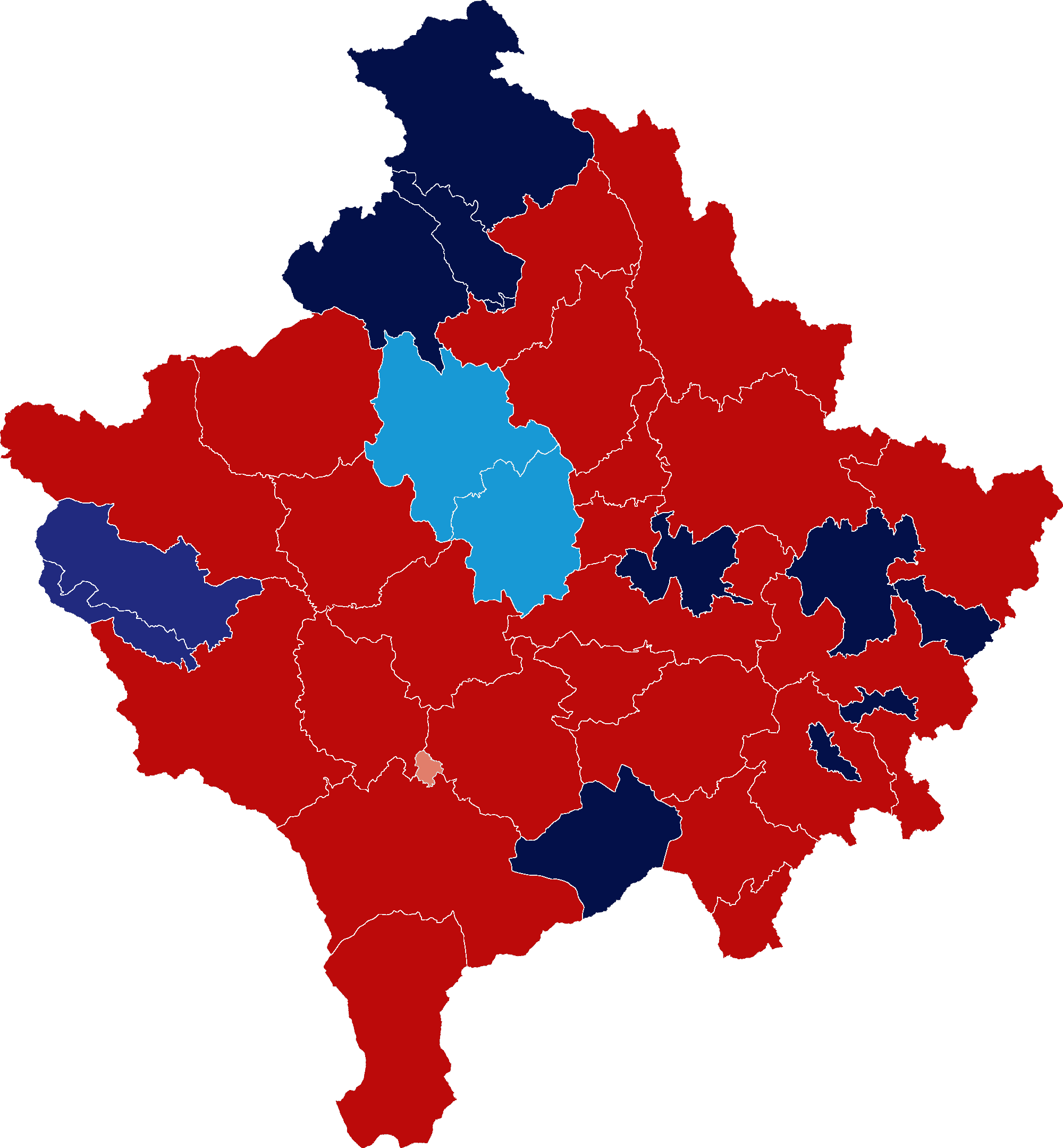
2021 Kosovan Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Kosovo on 14 February 2021. The results were a landslide victory for Vetëvendosje led by Albin Kurti and its coalition partner, Vjosa Osmani, former speaker of the parliament of Kosovo. The alliance won more than 50% of the total votes, the highest share since the first elections held in 2001, while their nearest rivals, the Democratic Party, finished in second place, trailing by more than 33%. Background The October 2019 parliamentary elections saw opposition party Vetëvendosje emerge as the largest faction in parliament, finishing just ahead of the Democratic League of Kosovo (LDK). The two parties formed a new government on 3 February 2020, with Vetëvendosje leader Albin Kurti as the Prime Minister. Kurti was elected Prime Minister with 66 votes and ten abstentions. The 34 opposition MPs boycotted the vote and left the Assembly building. The coalition soon collapsed as the LDK filed a no-confidence motion on 25 March 2020 due to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Of Government
The head of government is the highest or the second-highest official in the executive branch of a sovereign state, a federated state, or a self-governing colony, autonomous region, or other government who often presides over a cabinet, a group of ministers or secretaries who lead executive departments. In diplomacy, "head of government" is differentiated from " head of state"HEADS OF STATE, HEADS OF GOVERNMENT, MINISTERS FOR FOREIGN AFFAIRS , Protocol and Liaison Service, United Nations (19 October 2012). Retrieved 29 July 2013. although in some countries, for example the United States, they are the same person. The authority of a head of government, such as a president, chancellor, or prime minister and the relationship between that position and other state instit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Of State
A head of state (or chief of state) is the public persona who officially embodies a state (polity), state#Foakes, Foakes, pp. 110–11 "[The head of state] being an embodiment of the State itself or representatitve of its international persona." in its unity and legitimacy. Depending on the country's form of government and separation of powers, the head of state may be a ceremonial figurehead or concurrently the head of government and more (such as the president of the United States, who is also commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces). In a parliamentary system, such as the Politics of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom or Politics of India, India, the head of state usually has mostly ceremonial powers, with a separate head of government. However, in some parliamentary systems, like Politics of South Africa, South Africa, there is an executive president that is both head of state and head of government. Likewise, in some parliamentary systems the head of sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Representative Democracy
Representative democracy, also known as indirect democracy, is a type of democracy where elected people represent a group of people, in contrast to direct democracy. Nearly all modern Western-style democracies function as some type of representative democracy: for example, the United Kingdom (a unitary parliamentary constitutional monarchy), India (a federal parliamentary republic), France (a unitary semi-presidential republic), and the United States (a federal presidential republic). Representative democracy can function as an element of both the parliamentary and the presidential systems of government. It typically manifests in a lower chamber such as the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, and the Lok Sabha of India, but may be curtailed by constitutional constraints such as an upper chamber and judicial review of legislation. Some political theorists (including Robert Dahl, Gregory Houston, and Ian Liebenberg) have described representative democracy as pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parliamentary System
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democratic governance Governance is the process of interactions through the laws, norms, power or language of an organized society over a social system ( family, tribe, formal or informal organization, a territory or across territories). It is done by the ... of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy from its ability to command the support ("confidence") of the legislature, typically a parliament, to which it is accountable. In a parliamentary system, the head of state is usually a person distinct from the head of government. This is in contrast to a presidential system, where the head of state often is also the head of government and, most importantly, where the executive does not derive its democratic legitimacy from the legislature. Countries with parliamentary systems may be Constitutional monarchy, cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)