|
Political Prisoners In Poland
Political prisoners in Poland and Polish territories (under the administration of other states) have existed throughout much of the 19th and 20th centuries. In the 19th century, some Polish political prisoners started using their situation of imprisonment to act politically. This phenomenon became visible as early as in the aftermath of the Greater Poland Uprising of 1848. The Russian Empire's first socialist party, the Polish Proletariat (party), Proletariat, established a political prisoner culture and tradition in Congress Poland, and used their imprisonment as a terrain of struggle. Political prisoners also existed under the interwar Second Polish Republic, under the Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), Nazi occupation in World War II, and in the post-war People's Republic of Poland periods. Until the elimination of the compulsory draft in Poland in 2009, contentious objectors to the mandatory military in Poland service continued to be imprisoned for one year, and were recognized ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Revolutions Of 1848
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in European history to date. The revolutions were essentially Democracy, democratic and Liberalism, liberal in nature, with the aim of removing the old Monarchy, monarchical structures and creating independent nation-states, as envisioned by romantic nationalism. The revolutions spread across Europe after an initial revolution began in French Revolution of 1848, France in February. Over 50 countries were affected, but with no significant coordination or cooperation among their respective revolutionaries. Some of the major contributing factors were widespread dissatisfaction with political leadership, demands for more participation (decision making), participation in government and democracy, demands for freedom of the press, other demands made by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
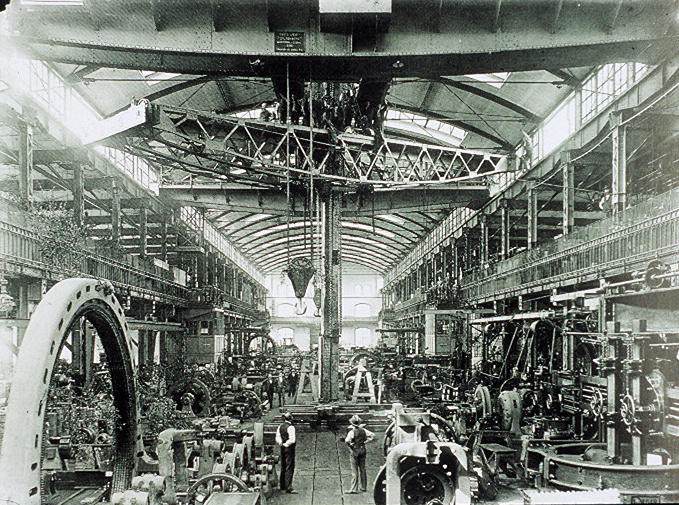
Ludwik Waryński
Ludwik Tadeusz Waryński (24 September 1856 at Martynówka – 2 March 1889 in Shlisselburg) was an activist and theoretician of the socialist movement in Poland. Biography Waryński was born at Martynówka, Kiev Governorate (Мартинівка in present-day Kaniv Raion, Cherkasy Oblast, Ukraine), the son of a January Uprising insurrectionist. In 1865, he began his education at the gymnasium in Bila Tserkva. Beginning in 1874 he studied in Saint Petersburg at the Technological Institute, where he met other socialists, and joined the Polish Socialist Youth. Student disturbances at the Institute in 1875 led to Waryński being forced to leave. He returned to his father's residence under police surveillance, and spent the next year educating himself. Early in 1877, he arrived in Warsaw and dedicated himself to furthering socialism in Polish. He founded the first socialist magazine in the lands of the Russian-occupied Poland. He then joined the Agronomical School in Puławy whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
January Uprising
The January Uprising ( pl, powstanie styczniowe; lt, 1863 metų sukilimas; ua, Січневе повстання; russian: Польское восстание; ) was an insurrection principally in Russia's Kingdom of Poland that was aimed at the restoration of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. It began on 22 January 1863 and continued until the last insurgents were captured by the Russian forces in 1864. It was the longest-lasting insurgency in partitioned Poland. The conflict engaged all levels of society and arguably had profound repercussions on contemporary international relations and ultimately provoked a social and ideological paradigm shift in national events that went on to have a decisive influence on the subsequent development of Polish society. A confluence of factors rendered the uprising inevitable in early 1863. The Polish nobility and urban bourgeois circles longed for the semi-autonomous status they had enjoyed in Congress Poland before the previous insur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black-Red-Gold
The national colours of the Federal Republic of Germany are officially black, red, and gold, defined with the adoption of the West German flag as a tricolour with these colours in 1949. As Germany was divided into West Germany and East Germany beginning in 1949 and continuing through 1990, both Germanies retained the black, red, and gold colors on each respective flag. After German reunification in 1990, West and East Germany adopted the West German flag as the flag of the reunited Germany, therefore maintaining black, red, and gold as Germany's colors. The colours ultimately hark back to the tricolour adopted by the ''Urburschenschaft'' of Jena in 1815, representing an early phase in the development of German nationalism and the idea of a unified German state. Since the 1860s, there has been a competing tradition of national colours as black, white, and red, based on the Hanseatic flags, used as the flag of the North German Confederation and the German Empire. The Weimar R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeughaus
The Zeughaus (English: Arsenal) is a listed building and the oldest structure on Unter den Linden boulevard in the historic centre of Berlin. Erected from 1695 to 1706 according to plans by Johann Arnold Nering, Martin Grünberg, Andreas Schlüter and Jean de Bodt in Baroque style, it was later converted into a Prussian Hall of Fame. Damaged during the Allied bombing in World War II, it was rebuilt from 1949 to 1967 as part of the Forum Fridericianum. Since 2003, it has been home to the Deutsches Historisches Museum (German Historic Museum). Since June 2021 it is closed for necessary renovations and for the renewal of the Permanent Exhibition probably until the end of 2025. History The Zeughaus is the oldest structure at Unter den Linden. It was built by Frederick III, Elector of Brandenburg between 1695 and 1730 in the Baroque style, to be used as an artillery arsenal for the display of cannons from Brandenburg and Prussia. The first building master was Johann Arnold Nering. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
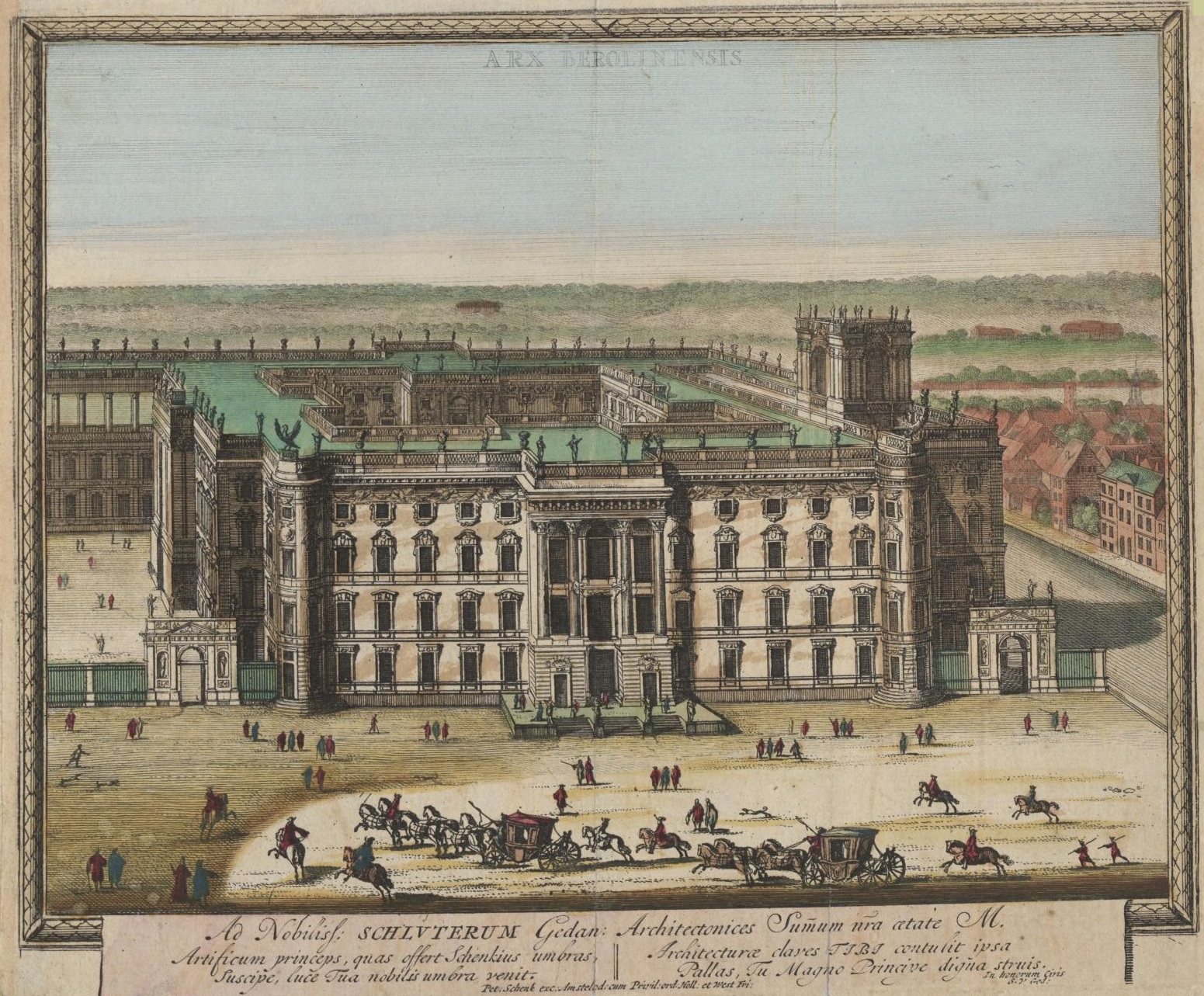
Berliner Schloss
The Berlin Palace (german: Berliner Schloss), formally the Royal Palace (german: Königliches Schloss), on the Museum Island in the Mitte area of Berlin, was the main residence of the House of Hohenzollern from 1443 to 1918. Expanded by order of King Frederick I of Prussia according to plans by Andreas Schlüter from 1689 to 1713, it was thereafter considered a major work of Prussian Baroque architecture. The former royal palace was one of Berlin’s largest buildings and shaped the cityscape with its dome. Used for various government functions after the fall of the monarchy in 1918, it was damaged during the Allied bombing in World War II, and was demolished by the East German authorities in 1950. In the 1970s, it became the location of the modernist East German Palace of the Republic (the central government building of East Germany). After German reunification and several years of debate and discussion, particularly regarding the fraught historical legacy of both building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick William IV Of Prussia
Frederick William IV (german: Friedrich Wilhelm IV.; 15 October 17952 January 1861), the eldest son and successor of Frederick William III of Prussia, reigned as King of Prussia from 7 June 1840 to his death on 2 January 1861. Also referred to as the "romanticist on the throne", he is best remembered for the many buildings he had constructed in Berlin and Potsdam as well as for the completion of the Gothic Cologne Cathedral. In politics, he was a conservative, who initially pursued a moderate policy of easing press censorship and reconciling with the Catholic population of the kingdom. During the German revolutions of 1848–1849, he at first accommodated the revolutionaries but rejected the title of Emperor of the Germans offered by the Frankfurt Parliament in 1849, believing that Parliament did not have the right to make such an offer. He used military force to crush the revolutionaries throughout the German Confederation. From 1849 onward he converted Prussia into a constit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spring Of Nations
The Revolutions of 1848, known in some countries as the Springtime of the Peoples or the Springtime of Nations, were a series of political upheavals throughout Europe starting in 1848. It remains the most widespread revolutionary wave in European history to date. The revolutions were essentially democratic and liberal in nature, with the aim of removing the old monarchical structures and creating independent nation-states, as envisioned by romantic nationalism. The revolutions spread across Europe after an initial revolution began in France in February. Over 50 countries were affected, but with no significant coordination or cooperation among their respective revolutionaries. Some of the major contributing factors were widespread dissatisfaction with political leadership, demands for more participation in government and democracy, demands for freedom of the press, other demands made by the working class for economic rights, the upsurge of nationalism, the regrouping of establis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moabit
Moabit () is an inner city locality in the borough of Mitte, Berlin, Germany. As of 2016, around 77,000 people lived in Moabit. First inhabited in 1685 and incorporated into Berlin in 1861, the former industrial and working-class neighbourhood is fully surrounded by three watercourses, which define its present-day border. Between 1945 and 1990, Moabit was part of the British sector of West Berlin and directly bordered East Berlin. Until the administrative reform in 2001, Moabit was a part of the district of Tiergarten. Colloquially, the name ''Moabit'' also refers to the Central Criminal Court (''Strafgericht'') and detention centre, which deals with all criminal cases in Berlin and is based in Moabit. Name The origin of the name ''Moabit'' is disputed. According to one account, it can be traced back to the Huguenots, in the time of King Frederick William I of Prussia. These French refugees are said to have named their new residence in reference to the Biblical description ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constituent states, Berlin is surrounded by the State of Brandenburg and contiguous with Potsdam, Brandenburg's capital. Berlin's urban area, which has a population of around 4.5 million, is the second most populous urban area in Germany after the Ruhr. The Berlin-Brandenburg capital region has around 6.2 million inhabitants and is Germany's third-largest metropolitan region after the Rhine-Ruhr and Rhine-Main regions. Berlin straddles the banks of the Spree, which flows into the Havel (a tributary of the Elbe) in the western borough of Spandau. Among the city's main topographical features are the many lakes in the western and southeastern boroughs formed by the Spree, Havel and Dahme, the largest of which is Lake Müggelsee. Due to its l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwik Mierosławski
Ludwik Adam Mierosławski (; January 17, 1814 in Nemours, Seine-et-Marne – November 22, 1878 in Paris) was a Polish general, writer, poet, historian and political activist. Took part in the November Uprising of the 1830s, after its fall he emigrated to France, where he taught Slavic history and military theory. Chosen as a commander for the Greater Poland Uprising of 1846, he was taken prisoner early but amnestied during the Spring of Nations. In 1848 and 1849 he fought for the insurgents in Baden and in the Electorate of the Palatinate. Afterwards he returned to France; he also had contacts with Italian activists like Giuseppe Garibaldi. He also took part in the January Uprising in the 1860s, as the first of four dictators of the Uprising. Biography Mierosławski was born on 17 January 1814 in Nemours, France, as a son of Colonel Adam Kasper Mierosławski (1785–1837), an officer of the Duchy of Warsaw and Polish Legions of the Napoleonic period) and aide to French general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)