|
Poincaré Map
In mathematics, particularly in dynamical systems, a first recurrence map or Poincaré map, named after Henri Poincaré, is the intersection of a periodic orbit in the state space of a continuous dynamical system with a certain lower-dimensional subspace, called the Poincaré section, transversal to the flow of the system. More precisely, one considers a periodic orbit with initial conditions within a section of the space, which leaves that section afterwards, and observes the point at which this orbit first returns to the section. One then creates a map to send the first point to the second, hence the name ''first recurrence map''. The transversality of the Poincaré section means that periodic orbits starting on the subspace flow through it and not parallel to it. A Poincaré map can be interpreted as a discrete dynamical system with a state space that is one dimension smaller than the original continuous dynamical system. Because it preserves many properties of periodic and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
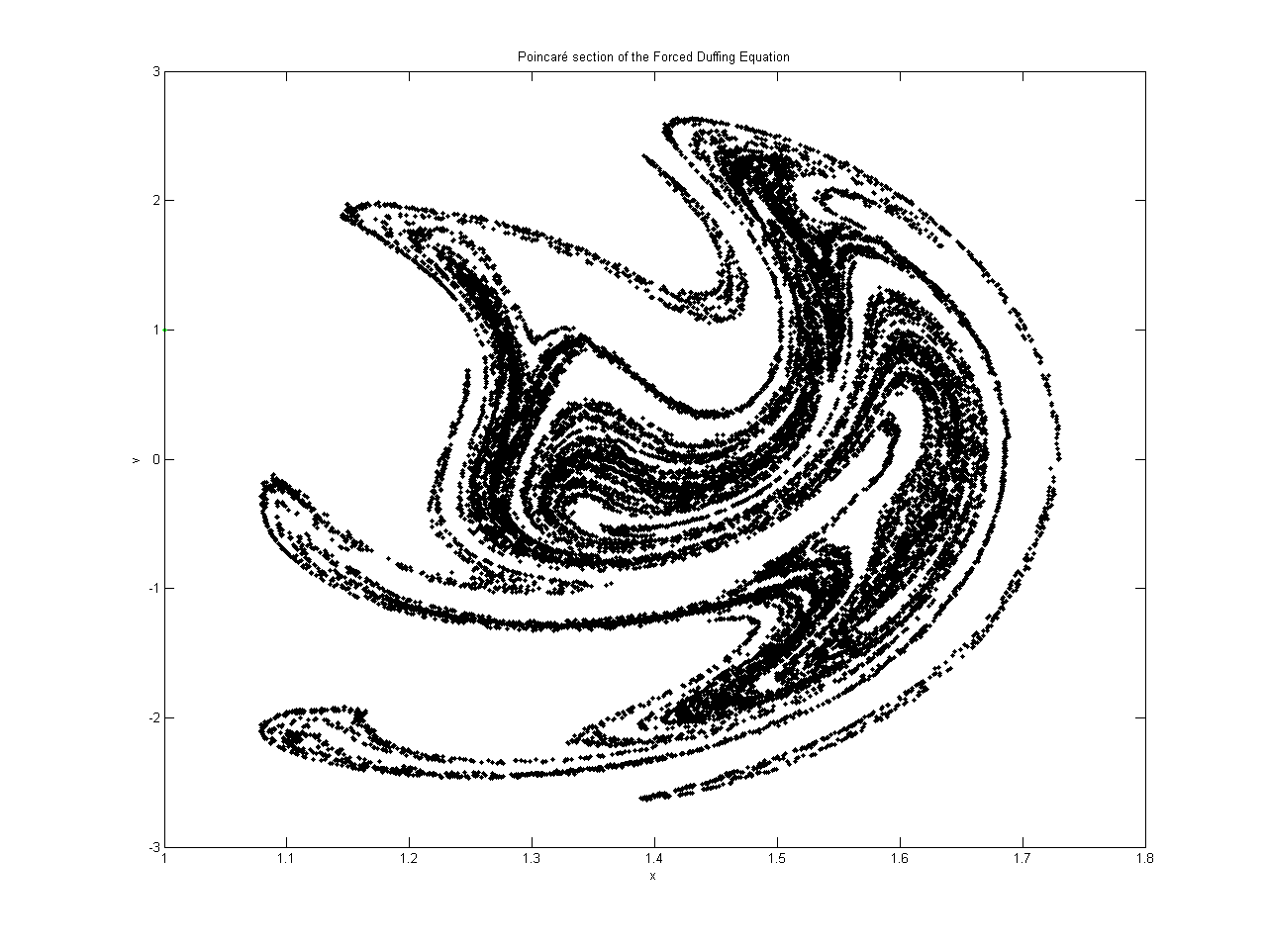
Forced Duffing Equation Poincaré Section
''Forced'' is a single-player and co-op action role-playing game developed by BetaDwarf, released in October 2013 for Windows, OS X and Linux through the Steam platform as well as Wii U. It is about gladiators fighting for their freedom in a fantasy arena where they are assisted by a spirit-like character called Balfus. Gameplay consists of selecting a weapon class and abilities to combat the various enemies of each arena, while solving puzzles using the help of Balfus. BetaDwarf was formed by a small group of students in 2011, who began developing the game in an unused classroom in Aalborg University – Copenhagen, Denmark. They were removed months later and launched a successful Kickstarter campaign involving an Imgur picture which documented their progress. ''Forced'' received moderate to favorable reviews with most critics praising its competitive gameplay and puzzle-system. The game's weak plot, technical glitches and excess difficulty were the negative highlights. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. The set of real numbers is denoted or \mathbb and is sometimes called "the reals". The adjective ''real'' in this context was introduced in the 17th century by René Descartes to distinguish real numbers, associated with physical reality, from imaginary numbers (such as the square roots of ), which seemed like a theoretical contrivance unrelated to physical reality. The real numbers include the rational numbers, such as the integer and the fraction . The rest of the real ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hénon Map
The Hénon map, sometimes called Hénon–Pomeau attractor/map, is a discrete-time dynamical system. It is one of the most studied examples of dynamical systems that exhibit chaotic behavior. The Hénon map takes a point (''xn'', ''yn'') in the plane and maps it to a new point :\beginx_ = 1 - a x_n^2 + y_n\\y_ = b x_n.\end The map depends on two parameters, ''a'' and ''b'', which for the classical Hénon map have values of ''a'' = 1.4 and ''b'' = 0.3. For the classical values the Hénon map is chaotic. For other values of ''a'' and ''b'' the map may be chaotic, intermittent, or converge to a periodic orbit. An overview of the type of behavior of the map at different parameter values may be obtained from its orbit diagram. The map was introduced by Michel Hénon as a simplified model of the Poincaré section of the Lorenz model. For the classical map, an initial point of the plane will either approach a set of points known as the Hénon strange ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroboscopic Map , high-intensity and short-duration stroboscopic device
{{disambig ...
Stroboscopic may refer to: * Stroboscopic effect, visual temporal aliasing * Stroboscopic effect (lighting), a temporal light artefact visible if a moving object is lit with modulated light with specific modulation frequencies and amplitudes * Stroboscope, any of various stroboscopic devices * Strobe light A strobe light or stroboscopic lamp, commonly called a strobe, is a device used to produce regular flashes of light. It is one of a number of devices that can be used as a stroboscope. The word originated from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poincaré Recurrence
Poincaré is a French surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Henri Poincaré (1854–1912), French physicist, mathematician and philosopher of science * Henriette Poincaré (1858-1943), wife of Prime Minister Raymond Poincaré * Lucien Poincaré (1862–1920), physicist, brother of Raymond and cousin of Henri * Raymond Poincaré (1860–1934), French Prime Minister or President ''inter alia'' from 1913 to 1920, cousin of Henri See also *List of things named after Henri Poincaré In physics and mathematics, a number of ideas are named after Henri Poincaré: * Euler–Poincaré characteristic * Hilbert–Poincaré series * Poincaré–Bendixson theorem * Poincaré–Birkhoff theorem * Poincaré–Birkhoff–Witt theorem, us .... * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Poincare French-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
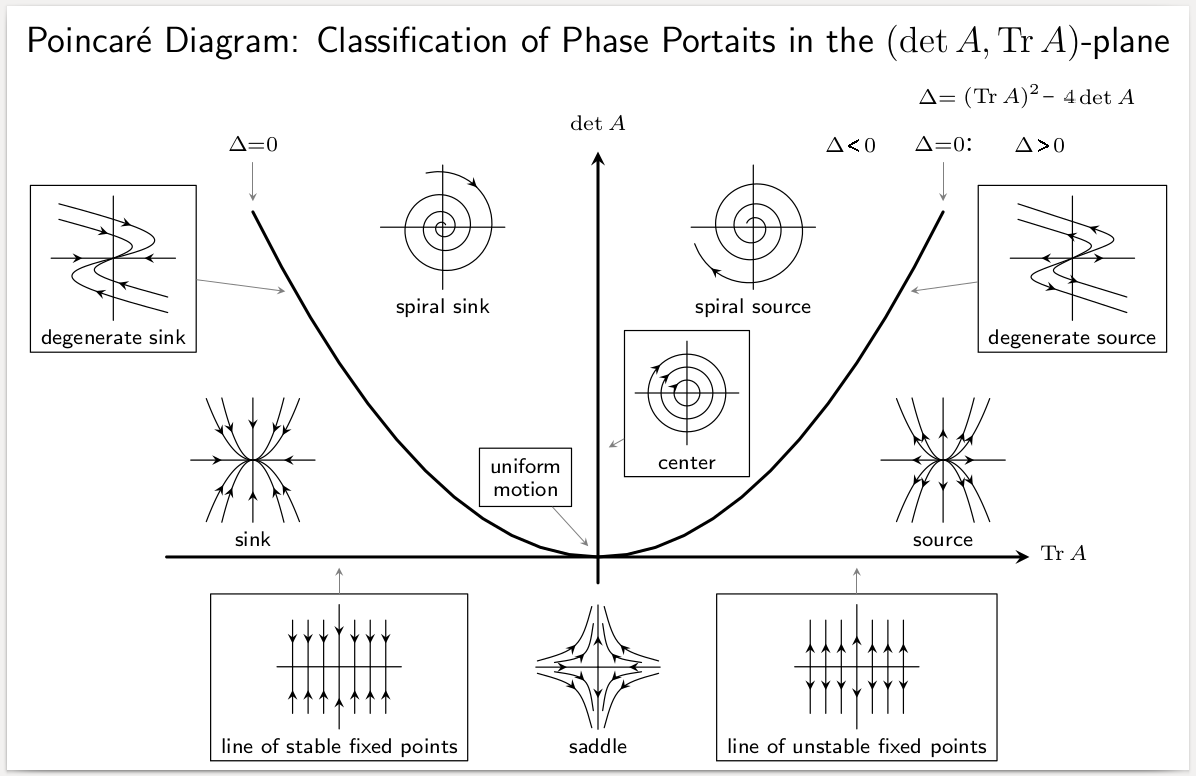
Asymptotically Stable
Various types of stability may be discussed for the solutions of differential equations or difference equations describing dynamical systems. The most important type is that concerning the stability of solutions near to a point of equilibrium. This may be discussed by the theory of Aleksandr Lyapunov. In simple terms, if the solutions that start out near an equilibrium point x_e stay near x_e forever, then x_e is Lyapunov stable. More strongly, if x_e is Lyapunov stable and all solutions that start out near x_e converge to x_e, then x_e is asymptotically stable. The notion of exponential stability guarantees a minimal rate of decay, i.e., an estimate of how quickly the solutions converge. The idea of Lyapunov stability can be extended to infinite-dimensional manifolds, where it is known as structural stability, which concerns the behavior of different but "nearby" solutions to differential equations. Input-to-state stability (ISS) applies Lyapunov notions to systems with input ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stability Theory
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions. The heat equation, for example, is a stable partial differential equation because small perturbations of initial data lead to small variations in temperature at a later time as a result of the maximum principle. In partial differential equations one may measure the distances between functions using Lp norms or the sup norm, while in differential geometry one may measure the distance between spaces using the Gromov–Hausdorff distance. In dynamical systems, an orbit is called '' Lyapunov stable'' if the forward orbit of any point is in a small enough neighborhood or it stays in a small (but perhaps, larger) neighborhood. Various criteria have been developed to prove stability or instability of an orbit. Under favorable circumstances, the question may be reduced to a well-studied problem invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Differentiable Dynamical System
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a pipe, the random motion of particles in the air, and the number of fish each springtime in a lake. The most general definition unifies several concepts in mathematics such as ordinary differential equations and ergodic theory by allowing different choices of the space and how time is measured. Time can be measured by integers, by real or complex numbers or can be a more general algebraic object, losing the memory of its physical origin, and the space may be a manifold or simply a set, without the need of a smooth space-time structure defined on it. At any given time, a dynamical system has a state representing a point in an appropriate state space. This state is often given by a tuple of real numbers or by a vector in a geometrical man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stability Theory
In mathematics, stability theory addresses the stability of solutions of differential equations and of trajectories of dynamical systems under small perturbations of initial conditions. The heat equation, for example, is a stable partial differential equation because small perturbations of initial data lead to small variations in temperature at a later time as a result of the maximum principle. In partial differential equations one may measure the distances between functions using Lp norms or the sup norm, while in differential geometry one may measure the distance between spaces using the Gromov–Hausdorff distance. In dynamical systems, an orbit is called '' Lyapunov stable'' if the forward orbit of any point is in a small enough neighborhood or it stays in a small (but perhaps, larger) neighborhood. Various criteria have been developed to prove stability or instability of an orbit. Under favorable circumstances, the question may be reduced to a well-studied problem invol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Positive Semi-orbit
In mathematics, specifically in the study of dynamical systems, an orbit is a collection of points related by the evolution function of the dynamical system. It can be understood as the subset of phase space covered by the trajectory of the dynamical system under a particular set of initial conditions, as the system evolves. As a phase space trajectory is uniquely determined for any given set of phase space coordinates, it is not possible for different orbits to intersect in phase space, therefore the set of all orbits of a dynamical system is a partition of the phase space. Understanding the properties of orbits by using topological methods is one of the objectives of the modern theory of dynamical systems. For discrete-time dynamical systems, the orbits are sequences; for real dynamical systems, the orbits are curves; and for holomorphic dynamical systems, the orbits are Riemann surfaces. Definition Given a dynamical system (''T'', ''M'', Φ) with ''T'' a group, ''M'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffeomorphism
In mathematics, a diffeomorphism is an isomorphism of smooth manifolds. It is an invertible function that maps one differentiable manifold to another such that both the function and its inverse are differentiable. Definition Given two manifolds M and N, a differentiable map f \colon M \rightarrow N is called a diffeomorphism if it is a bijection and its inverse f^ \colon N \rightarrow M is differentiable as well. If these functions are r times continuously differentiable, f is called a C^r-diffeomorphism. Two manifolds M and N are diffeomorphic (usually denoted M \simeq N) if there is a diffeomorphism f from M to N. They are C^r-diffeomorphic if there is an r times continuously differentiable bijective map between them whose inverse is also r times continuously differentiable. Diffeomorphisms of subsets of manifolds Given a subset X of a manifold M and a subset Y of a manifold N, a function f:X\to Y is said to be smooth if for all p in X there is a neighbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Function (mathematics)
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words map, mapping, transformation, correspondence, and operator are often used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function.Codomain ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics'Codomain. ''Encyclopedia of Mathematics''/ref> The earliest known approach to the notion of function can be traced back to works of Persian mathematicians Al-Biruni and Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |