|
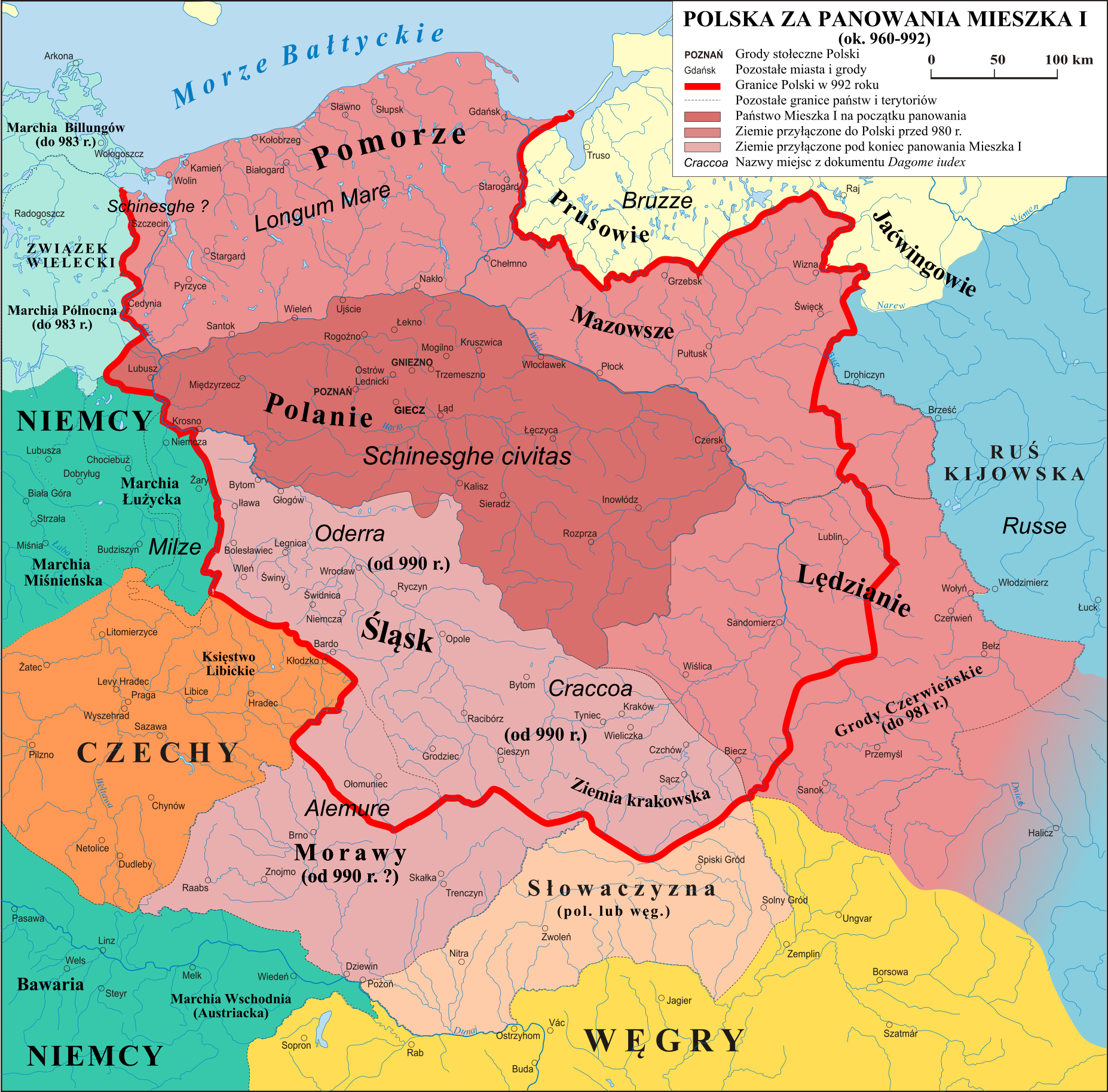
Poborzans
Poborzans, also spelled as Pobożans, is an ethnographic group of Polish people, that are part of the ethnographic subgroup of Masovians. They originate from the north west Masovia, located within the region of Poborze and Zawkrze, to the north of Mława river. The group is descendant of the Polish nobility that had inhabit the area in the Late Middle Ages The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Eur .... They are culturally separate from the neighbouring groups.''Obrazy regionalnego zróżnicowania ludu i jego kultury''. In: Stanisław Węglarz (editor): ''Łódzkie Studia Etnograficzne. T. XXXVI: Tutejsi i inni – O etnograficznym zróżnicowaniu kultury ludowej''. Łódź: Polskie Towarzystwo Ludoznawcze, 1997, p. 80. ISSN 0076-0382. Notes References Lechites Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masovians
Masovians, also spelled as Mazovians, and historically known as Masurians, is an ethnographic group of Polish people that originate from the region of Masovia, located mostly within borders of the Masovian Voivodeship, Poland. They speak the Masovian dialect dialect of Polish.G. Odoj, A. Peć: ''Dziedzictwo kulturowe – edukacja regionalna''. Dzierżoniów: Wydawnictwo Alex, 2000, p. 74, ISBN 83-85589-35-X, OCLC 749376082. The group originate from the Lechitic tribe of Masovians, first referenced in the historical records by Nestor the Chronicler in the 11th century. Name The name Masovian, in Polish, ''Mazowszanin'', comes from the name of the region of Masovia, in Polish known as ''Mazowsze''. The name of the region, comes from its Old Polish names ''Mazow'', and ''Mazosze'', and most likely came from word ''maz'' (ancestory word of modern ''maź'' and ''mazać''), which was used to either describe a "''muddy region''" or a "''person covered in mud''". Historically, prior t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Language
Polish (Polish: ''język polski'', , ''polszczyzna'' or simply ''polski'', ) is a West Slavic language of the Lechitic group written in the Latin script. It is spoken primarily in Poland and serves as the native language of the Poles. In addition to being the official language of Poland, it is also used by the Polish diaspora. There are over 50 million Polish speakers around the world. It ranks as the sixth most-spoken among languages of the European Union. Polish is subdivided into regional dialects and maintains strict T–V distinction pronouns, honorifics, and various forms of formalities when addressing individuals. The traditional 32-letter Polish alphabet has nine additions (''ą'', ''ć'', ''ę'', ''ł'', ''ń'', ''ó'', ''ś'', ''ź'', ''ż'') to the letters of the basic 26-letter Latin alphabet, while removing three (x, q, v). Those three letters are at times included in an extended 35-letter alphabet, although they are not used in native words. The traditional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zawkrze
Zawkrze, also Zawkrze Land ( pl, ziemia zawkrzańska), is a small historic region of Poland (ziemia), located in northern Mazovia, along the border with Masuria. Its approximate area is , and the population is about 114,000. Currently, Zawkrze has three towns, and more than 200 villages. Its name comes from the Wkra river – Zawkrze means ''the land behind the Wkra'', from the perspective of Płock, the historic capital of Mazovia. The largest town of the region is Mława, while the historic capital of Zawkrze is Szreńsk. Zawkrze lies between the Wkra (in the south), Dzialdowka (in the west), Orzyca and Łydynia (in the east) rivers, and the former border with Prussia in the north. The northern border was established by the Treaty of Kalisz in 1343. From east to west, Zawkrze is some , while from north to south – some . Currently, Zawkrze is divided between five counties and two voivodeships - Mława, Żuromin, Ciechanów, Nidzica and Działdowo. It has three towns, Mława ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavic Ethnic Groups
Slavic, Slav or Slavonic may refer to: Peoples * Slavic peoples, an ethno-linguistic group living in Europe and Asia ** East Slavic peoples, eastern group of Slavic peoples ** South Slavic peoples, southern group of Slavic peoples ** West Slavic peoples, western group of Slavic peoples ** Slavic Americans, Americans of Slavic descent * Anti-Slavic sentiment, negative attitude towards Slavic peoples * Pan-Slavic movement, movement in favor of Slavic cooperation and unity * Slavic studies, a multidisciplinary field of studies focused on history and culture of Slavic peoples Languages, alphabets, and names * Slavic languages, a group of closely related Indo-European languages ** Proto-Slavic language, reconstructed proto-language of all Slavic languages ** Old Church Slavonic, 9th century Slavic literary language, used for the purpose of evangelizing the Slavic peoples ** Church Slavonic, a written and spoken variant of Old Church Slavonic, standardized and widely adopted by Sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lechites
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and the Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians. History According to Polish legend, Mieszko I inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder (Polans, Masovians, Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians) into a single country of Poland. His son, Bolesław I the Brave, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław, Kołobrzeg, and Kraków, and an archbishopric at Gniezno. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemia, Moravia, Kievan Rus' and Lusatia, and forced the western Pomeranians to pay Poland a tribute. Shortly before his death Bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the Periodization, period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renaissance). Around 1300, centuries of prosperity and growth in Europe came to a halt. A series of famines and Plague (disease), plagues, including the Great Famine of 1315–1317 and the Black Death, reduced the population to around half of what it had been before the calamities. Along with depopulation came social unrest and endemic warfare. France and England experienced serious peasant uprisings, such as the Jacquerie and the Peasants' Revolt, as well as over a century of intermittent conflict, the Hundred Years' War. To add to the many problems of the period, the unity of the Catholic Church was temporarily shattered by the Western Schism. Collectively, those events are sometimes called the Crisis of the Late Middle Ages. D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Szlachta
The ''szlachta'' (Polish: endonym, Lithuanian: šlėkta) were the noble estate of the realm in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth who, as a class, had the dominating position in the state, exercising extensive political rights and power. Szlachta as a class differed significantly from the feudal nobility of Western Europe. The estate was officially abolished in 1921 by the March Constitution."Szlachta. Szlachta w Polsce" ''Encyklopedia PWN'' The origins of the ''szlachta'' are obscure and the subject of several theories. Traditionally, its members owned land (allods), [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mława
Mława (; yi, מלאווע ''Mlave'') is a town in north-east Poland with 30,403 inhabitants in 2020. It is the capital of Mława County. It is situated in the Masovian Voivodeship. During the invasion of Poland in 1939, the battle of Mława was fought to the north of the city. History The first mention of Mława comes from July 2, 1426, when three princes of Mazovia - Siemowit V, Trojden II and Władysław I came here to a session of a local court. It is not known if Mława had already been an urban center, as there are no sources which would prove it. Three years later, Mława was incorporated as a town It was a royal town, located in the Płock Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province. In 1521 during the Polish-Teutonic War, the town was captured and looted by the Teutonic Knights. In 1659 the town was burned by the Swedish troops, and in 1795, following the Third Partition of Poland, Mława became part of the Kingdom of Prussia. In 1807 it was included in the short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Masovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centuries, Mazovia developed a separate sub-culture featuring diverse folk songs, architecture, dress and traditions different from those of other Poles. Historical Mazovia existed from the Middle Ages until the partitions of Poland and consisted of three voivodeships with the capitals in Warsaw, Płock and Rawa. The main city of the region was Płock, which was even capital of Poland from 1079 to 1138; however, in Early Modern Times Płock lost its importance to Warsaw, which became the capital of Poland. From 1138, Mazovia was governed by a separate branch of the Piast dynasty and when the last ruler of the independent Duchy of Mazovia died, it was fully incorporated to the Polish Crown in 1526. During the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnographic Group
An ethnographic group is a group that has cultural traits that make it stand out from the larger ethnic group it is a part of. In other words, members of an ethnographic group will also consider themselves to be members of a larger ethnic group, both sharing a collective consciousness with it, and possessing their own distinct one.Wojciech JanickiThe distribution and significance of Tatar ethnic group in Poland/ref> Ethnographic groups are presumed to be significantly assimilated with the larger ethnic group they are part of, though they retain distinctive, differentiating characteristics related to cultural values such as speech, religion, costume, or other cultural aspects. The concept of an ethnographic group is rarely found in Western works, and has been attributed to late 20th-century ethnographic studies in the countries of the former Soviet Union and its Eastern Bloc. This term has been used for example in works of Bulgarian, Georgian, Hungarian and Polish ethnographers. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |