|
Pneumatic Trail
Pneumatic trail or trail of the tire is a trail-like effect generated by compliant tires rolling on a hard surface and subject to side loads, as in a turn. More technically, it is the distance that the resultant force of side-slip occurs behind the geometric center of the contact patch. Causes Pneumatic trail is caused by the progressive build-up of lateral force along the length of the contact patch, such that lateral forces are greater towards the rear of the contact patch (though less so when the rear of the contact patch begins sliding) and this creates a torque on the tire called the self aligning torque. Because the direction of the side-slip is towards the outside of a turn, the force on the tire is towards the center of the turn. Therefore, this torque tends to turn the front wheel in the direction of the side-slip, away from the direction of the turn. Variation Pneumatic trail is at its maximum when the slip angle is zero and decreases as slip angle increases. Pneumatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tire Pneumatic Trail
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tread and a body. The tread provides traction while the body provides containment for a quantity of compresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicycle And Motorcycle Geometry
Bicycle and motorcycle geometry is the collection of key measurements (lengths and angles) that define a particular bike configuration. Primary among these are wheelbase, steering axis angle, fork offset, and trail. These parameters have a major influence on how a bike handles. Wheelbase Wheelbase is the ''horizontal'' distance between the centers (or the ground contact points) of the front and rear wheels. Wheelbase is a function of rear frame length, steering axis angle, and fork offset. It is similar to the term wheelbase used for automobiles and trains. Wheelbase has a major influence on the longitudinal stability of a bike, along with the height of the center of mass of the combined bike and rider. Short bikes are much more suitable for performing wheelies and stoppies. Steering axis angle The steering axis angle is called caster angle when measured from vertical axis or head angle when measured from horizontal axis. The steering axis is the axis about which the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tire
A tire (American English) or tyre (British English) is a ring-shaped component that surrounds a wheel's rim to transfer a vehicle's load from the axle through the wheel to the ground and to provide traction on the surface over which the wheel travels. Most tires, such as those for automobiles and bicycles, are pneumatically inflated structures, which also provide a flexible cushion that absorbs shock as the tire rolls over rough features on the surface. Tires provide a footprint, called a contact patch, that is designed to match the weight of the vehicle with the bearing strength of the surface that it rolls over by providing a bearing pressure that will not deform the surface excessively. The materials of modern pneumatic tires are synthetic rubber, natural rubber, fabric, and wire, along with carbon black and other chemical compounds. They consist of a tread and a body. The tread provides traction while the body provides containment for a quantity of compressed a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cornering Force
Cornering force or side force is the lateral (i.e., parallel to wheel axis) force produced by a vehicle tire during cornering. Cornering force is generated by tire slip and is proportional to slip angle at low slip angles. The rate at which cornering force builds up is described by relaxation length. Slip angle describes the deformation of the tire contact patch, and this deflection of the contact patch deforms the tire in a fashion akin to a spring. As with deformation of a spring, deformation of the tire contact patch generates a reaction force in the tire; the cornering force. Integrating the force generated by every tread element along the contact patch length gives the total cornering force. Although the term, "tread element" is used, the compliance in the tire that leads to this effect is actually a combination of sidewall deflection and deflection of the rubber within the contact patch. The exact ratio of sidewall compliance to tread compliance is a factor in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
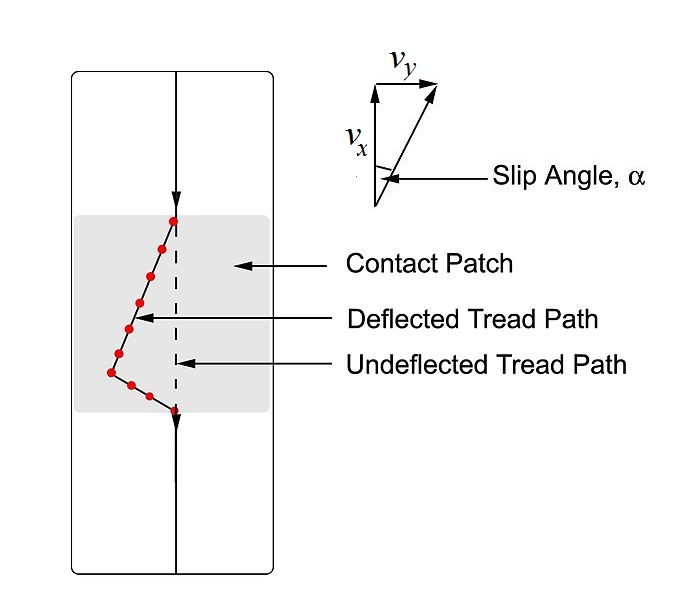
Slip Angle
In vehicle dynamics, slip angle or sideslip angle is the angle between the direction in which a wheel is pointing and the direction in which it is actually traveling (i.e., the angle between the forward velocity vector v_x and the vector sum of wheel forward velocity v_x and lateral velocity v_y, as defined in the image to the right). This slip angle results in a force, the cornering force, which is in the plane of the contact patch and perpendicular to the intersection of the contact patch and the midplane of the wheel. This cornering force increases approximately linearly for the first few degrees of slip angle, then increases non-linearly to a maximum before beginning to decrease. The slip angle, \alpha is defined as \alpha \triangleq -\arctan\left(\frac\right) Causes A non-zero slip angle arises because of deformation in the tire carcass and tread. As the tire rotates, the friction between the contact patch and the road results in individual tread 'elements' (finite s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contact Patch
Contact patch is the portion of a vehicle's tire that is in actual contact with the road surface. It is commonly used in the discussion of pneumatic (i.e. pressurized) tires, where the term is used strictly to describe the portion of the tire’s tread that touches the road surface. The term “footprint” is used almost synonymously. Solid wheels also exhibit a contact patch which is generally smaller than the pneumatic “footprint”. Contact patch size The contact patch is the only connection between the road and the vehicle. Pneumatic rubber tires The size and shape of the contact patch, as well as the pressure distribution within the contact patch, are important to the ride qualities and handling characteristics of a vehicle. Since the wear characteristics of tires is a highly competitive area between tire manufacturers, a lot of the research done concerning the contact patch is considered highly proprietary and, therefore, very little is published on the subject. Beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torque
In physics and mechanics, torque is the rotational equivalent of linear force. It is also referred to as the moment of force (also abbreviated to moment). It represents the capability of a force to produce change in the rotational motion of the body. The concept originated with the studies by Archimedes of the usage of levers, which is reflected in his famous quote: "''Give me a lever and a place to stand and I will move the Earth''". Just as a linear force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist to an object around a specific axis. Torque is defined as the product of the magnitude of the perpendicular component of the force and the distance of the line of action of a force from the point around which it is being determined. The law of conservation of energy can also be used to understand torque. The symbol for torque is typically \boldsymbol\tau, the lowercase Greek letter ''tau''. When being referred to as moment of force, it is commonly denoted by . I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Aligning Torque
Self aligning torque, also known as aligning torque, aligning moment, SAT, or Mz, is the torque that a tire creates as it rolls along, which tends to steer it, i.e. rotate it around its vertical axis. In the presence of a non-zero slip angle, this torque tends to steer the tire toward the direction in which it is traveling, hence its name. The magnitude of this torque can be calculated as the product of the lateral force generated at the contact patch and the distance behind the wheel centre at which that force acts. This distance is known as the pneumatic trail. The steering torque around a non-vertical steer axis with non-zero mechanical trail is given by : (trail + pneumatic trail) · cos( caster angle) · ''F''''y''. Even if the slip angle and camber angle are zero, and the road is flat, this torque will still be generated due to asymmetries in the tire's construction and the asymmetrical shape and pressure distribution o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bike Physics
Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics is the science of the motion of bicycles and motorcycles and their components, due to the forces acting on them. Dynamics falls under a branch of physics known as classical mechanics. Bike motions of interest include balancing, steering, braking, accelerating, suspension activation, and vibration. The study of these motions began in the late 19th century and continues today. Bicycles and motorcycles are both single-track vehicles and so their motions have many fundamental attributes in common and are fundamentally different from and more difficult to study than other wheeled vehicles such as dicycles, tricycles, and quadracycles. As with unicycles, bikes lack lateral stability when stationary, and under most circumstances can only remain upright when moving forward. Experimentation and mathematical analysis have shown that a bike stays upright when it is steered to keep its center of mass over its wheels. This steering is usually supplied b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camber Thrust
Camber thrust and camber force are terms used to describe the force generated perpendicular to the direction of travel of a rolling tire due to its camber angle and finite contact patch. Camber thrust is generated when a point on the outer surface of a leaned and rotating tire, that would normally follow a path that is elliptical when projected onto the ground, is forced to follow a straight path while coming in contact with the ground, due to friction. This deviation towards the direction of the lean causes a deformation in the tire tread and carcass that is transmitted to the vehicle as a force in the direction of the lean. Camber thrust is approximately linearly proportional to camber angle for small angles, reaches its steady-state value nearly instantaneously after a change in camber angle, and so does not have an associated relaxation length. Bias-ply tires have been found to generate more camber thrust than radial tires. Camber stiffness is a parameter used to describe the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caster Angle
250px, θ is the caster angle, the red line is the pivot line, and the grey area is the tire. 250px, Front suspension of a race car, the caster angle is formed by the line between upper and lower ball joint. The caster angle or castor angle is the angular displacement of the steering axis from the vertical axis of a steered wheel in a car, motorcycle, bicycle, other vehicle or a vessel, as seen from the side of the vehicle. The steering axis in a car with dual ball joint suspension is an imaginary line that runs through the center of the upper ball joint to the center of the lower ball joint, or through the center of the kingpin for vehicles having a kingpin. Caster causes a wheel to align with the direction of travel, and can be accomplished either by caster displacement or caster angle. Caster displacement moves the steering axis ahead of the axis of wheel rotation, as with the front wheels of a shopping cart. Caster angle moves the steering axis from vertical. In automob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relaxation Length
Relaxation length is a property of pneumatic tires that describes the delay between when a slip angle is introduced and when the cornering force reaches its steady-state value. It is also described as the distance that a tire rolls before the lateral force builds up to 63% of its steady-state value. It can be calculated as the ratio of ''cornering stiffness'' over the ''lateral stiffness'', where cornering stiffness is the ratio of cornering force over slip angle, and lateral stiffness is the ratio of lateral force over lateral displacement. Values Pacejka gives a rule of thumb that "at nominal vertical load the relaxation length is of the order of magnitude of the wheel radius". Relaxations lengths have been found to be between 0.12 and 0.45 meters, with higher values corresponding to higher velocities and heavier loads. Tests on motorcycle tires have found that the ratio of cornering stiffness over lateral stiffness produces values 20-25% higher than those calculated as 63% o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |