|
Plethysmography
A plethysmograph is an instrument for measuring changes in volume within an organ or whole body (usually resulting from fluctuations in the amount of blood or air it contains). The word is derived from the Greek "plethysmos" (increasing, enlarging, becoming full), and "graphein" (to write). Organs studied Lungs Pulmonary plethysmographs are commonly used to measure the functional residual capacity (FRC) of the lungs—the volume in the lungs when the muscles of respiration are relaxed—and total lung capacity. In a traditional plethysmograph (or "body box"), the test subject, or patient, is placed inside a sealed chamber the size of a small telephone booth with a single mouthpiece. At the end of normal expiration, the mouthpiece is closed. The patient is then asked to make an inspiratory effort. As the patient tries to inhale (a maneuver which looks and feels like panting), the lungs expand, decreasing pressure within the lungs and increasing lung volume. This, in turn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penile Plethysmograph
Penile plethysmography (PPG) or phallometry is measurement of blood flow to the penis, typically used as a proxy for measurement of sexual arousal. The most commonly reported methods of conducting penile plethysmography involve the measurement of the circumference of the penis with a mercury-in-rubber or electromechanical strain gauge, or the volume of the penis with an airtight cylinder and inflatable cuff at the base of the penis. Corpora cavernosa nerve penile plethysmographs measure changes in response to inter-operative electric stimulation during surgery. The volumetric procedure was invented by Kurt Freund and is considered to be particularly sensitive at low arousal levels. The easier to use circumferential measures are more widely used, however, and more common in studies using erotic film stimuli. A corresponding device in women is the vaginal photoplethysmograph. For sexual offenders it is typically used to determine the level of sexual arousal as the subject is expose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
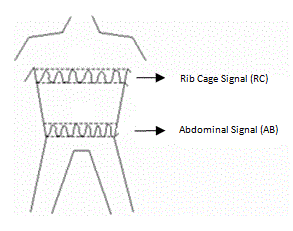
Respiratory Inductance Plethysmography
Respiratory inductance plethysmography (RIP) is a method of evaluating pulmonary ventilation by measuring the movement of the chest and abdominal wall. Accurate measurement of pulmonary ventilation or breathing often requires the use of devices such as masks or mouthpieces coupled to the airway opening. These devices are often both encumbering and invasive, and thus ill suited for continuous or ambulatory measurements. As an alternative RIP devices that sense respiratory excursions at the body surface can be used to measure pulmonary ventilation. According to a paper by Konno and Mead "the chest can be looked upon as a system of two compartments with only one degree of freedom each". Therefore, any volume change of the abdomen must be equal and opposite to that of the rib cage. The paper suggests that the volume change is close to being linearly related to changes in antero-posterior (front to back of body) diameter. When a known air volume is inhaled and measured with a spiromet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spirometry
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is helpful in assessing breathing patterns that identify conditions such as asthma, pulmonary fibrosis, cystic fibrosis, and COPD. It is also helpful as part of a system of health surveillance, in which breathing patterns are measured over time. Spirometry generates pneumotachographs, which are charts that plot the volume and flow of air coming in and out of the lungs from one inhalation and one exhalation. Indications Spirometry is indicated for the following reasons: * to diagnose or manage asthma * to detect respiratory disease in patients presenting with symptoms of breathlessness, and to distinguish respiratory from cardiac disease as the cause * to measure bronchial responsiveness in patients suspected of having asthma * to diagnose and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulmonary Function Testing
Pulmonary function testing (PFT) is a complete evaluation of the respiratory system including patient history, physical examinations, and tests of pulmonary function. The primary purpose of pulmonary function testing is to identify the severity of pulmonary impairment. Pulmonary function testing has diagnostic and therapeutic roles and helps clinicians answer some general questions about patients with lung disease. PFTs are normally performed by a pulmonary function technician, respiratory therapist, respiratory physiologist, physiotherapist, pulmonologist, or general practitioner. Indications Pulmonary function testing is a diagnostic and management tool used for a variety of reasons, such as: * Diagnose lung disease. * Monitor the effect of chronic diseases like asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, or cystic fibrosis. * Detect early changes in lung function. * Identify narrowing in the airways. * Evaluate airway bronchodilator reactivity. * Show if environmental facto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoplethysmograph
A photoplethysmogram (PPG) is an optically obtained plethysmogram that can be used to detect blood volume changes in the microvascular bed of tissue. A PPG is often obtained by using a pulse oximeter which illuminates the skin and measures changes in light absorption. A conventional pulse oximeter monitors the perfusion of blood to the dermis and subcutaneous tissue of the skin. With each cardiac cycle the heart pumps blood to the periphery. Even though this pressure pulse is somewhat damped by the time it reaches the skin, it is enough to distend the arteries and arterioles in the subcutaneous tissue. If the pulse oximeter is attached without compressing the skin, a pressure pulse can also be seen from the venous plexus, as a small secondary peak. The change in volume caused by the pressure pulse is detected by illuminating the skin with the light from a light-emitting diode (LED) and then measuring the amount of light either transmitted or reflected to a photodiode. Each c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
COPD
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a type of progressive lung disease characterized by long-term respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. The main symptoms include shortness of breath and a cough, which may or may not produce mucus. COPD progressively worsens, with everyday activities such as walking or dressing becoming difficult. While COPD is incurable, it is preventable and treatable. The two most common conditions of COPD are emphysema and chronic bronchitis and they have been the two classic COPD phenotypes. Emphysema is defined as enlarged airspaces (alveoli) whose walls have broken down resulting in permanent damage to the lung tissue. Chronic bronchitis is defined as a productive cough that is present for at least three months each year for two years. Both of these conditions can exist without airflow limitation when they are not classed as COPD. Emphysema is just one of the structural abnormalities that can limit airflow and can exist without airflow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impedance Plethysmography
Impedance cardiography (ICG) is a non-invasive technology measuring total electrical conductivity of the thorax and its changes in time to process continuously a number of cardiodynamic parameters, such as stroke volume (SV), heart rate (HR), cardiac output (CO), ventricular ejection time (VET), pre-ejection period and used to detect the impedance changes caused by a high-frequency, low magnitude current flowing through the thorax between additional two pairs of electrodes located outside of the measured segment. The sensing electrodes also detect the ECG signal, which is used as a timing clock of the system. Introduction Impedance cardiography (ICG), also referred to as electrical impedance plethysmography (EIP) or Thoracic Electrical Bioimpedance (TEB) has been researched since the 1940s. NASA helped develop the technology in the 1960s. The use of impedance cardiography in psychophysiological research was pioneered by the publication of an article by Miller and Horvath in 1978 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pre-clinical Development
In drug development, preclinical development, also termed preclinical studies or nonclinical studies, is a stage of research that begins before clinical trials (testing in humans) and during which important feasibility, iterative testing and drug safety data are collected, typically in laboratory animals. The main goals of preclinical studies are to determine a starting, safe dose for first-in-human study and assess potential toxicity of the product, which typically include new medical devices, prescription drugs, and diagnostics. Companies use stylized statistics to illustrate the risks in preclinical research, such as that on average, only one in every 5,000 compounds that enters drug discovery to the stage of preclinical development becomes an approved drug. Types of preclinical research Each class of product may undergo different types of preclinical research. For instance, drugs may undergo pharmacodynamics (what the drug does to the body) (PD), pharmacokinetics (wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Respiratory Therapy
A respiratory therapist is a specialized healthcare professional, healthcare practitioner trained in Intensive care medicine, critical care and cardio-pulmonary medicine in order to work therapeutically with people who have acute critical conditions, Cardiovascular disease, cardiac and Respiratory disease, pulmonary disease. Respiratory therapists graduate from a college or university with a degree in respiratory therapy and have passed a national board certifying examination. The NBRC (National Board for Respiratory Care) is responsible for credentialing as a CRT (Certified Respiratory Therapist, certified respiratory therapist), or RRT (Registered Respiratory Therapist, registered respiratory therapist), The specialty certifications of respiratory therapy include: CPFT and RPFT (Certified or Registered Pulmonary Function Technologist), ACCS (Adult Critical Care Specialist), NPS (Neonatal/Pediatric Specialist), and SDS (Sleep disorder specialist, Sleep Disorder Specialist). Re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measuring Instruments
A measuring instrument is a device to measure a physical quantity. In the physical sciences, quality assurance, and engineering, measurement is the activity of obtaining and comparing physical quantities of real-world objects and events. Established standard objects and events are used as units, and the process of measurement gives a number relating the item under study and the referenced unit of measurement. Measuring instruments, and formal test methods which define the instrument's use, are the means by which these relations of numbers are obtained. All measuring instruments are subject to varying degrees of instrument error and measurement uncertainty. These instruments may range from simple objects such as rulers and stopwatches to electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Virtual instrumentation is widely used in the development of modern measuring instruments. Time In the past, a common time measuring instrument was the sundial. Today, the usual measuring instru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Equipment
A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase. Discovery of what would be considered a medical device by modern standards dates as far back as c. 7000 BC in Baluchistan where Neolithic dentists used flint-tipped drills and bowstrings. Study of archeology and Roman medical literature also indicate that many types of medical devices were in widespread use during the time of ancient Rome. In the United States it wasn't until the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optoelectronic Plethysmography
Optoelectronic plethysmography is a method to evaluate ventilation through an external measurement of the chest wall surface motion. A number of small reflective markers are placed on the thoraco-abdominal surface by hypoallergenic adhesive tape. A system for human motion analysis measures the three-dimensional coordinates of these markers and the enclosed volume is computed by connecting the points to form triangles. From optoelectronic plethysmography it is thus possible to obtain volume variations of the entire chest wall and its different compartments. The chest wall can be modeled as being composed of three different compartments: pulmonary rib cage, abdominal rib cage, and the abdomen. This model is the most appropriate for the study of chest wall kinematics in the majority of conditions, including exercise. It takes into consideration the fact that the lung- and diaphragm-apposed parts of the rib cage are exposed to substantially different pressures on their inner surface d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |