|
Plasmonic Nanolithography
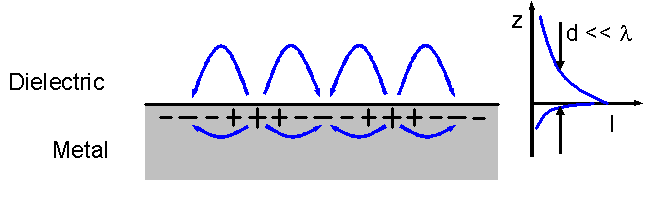
Plasmonic nanolithography (also known as plasmonic lithography or plasmonic photolithography) is a nanolithographic process that utilizes surface plasmon excitations such as surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs) to fabricate nanoscale structures. SPPs, which are surface waves that propagate in between planar dielectric-metal layers in the optical regime, can bypass the diffraction limit on the optical resolution that acts as a bottleneck for conventional photolithography. Theory Surface plasmon polaritons are surface electromagnetic waves that propagate in between two surfaces with sign-changing permittivities. They originate from coupling of photons to plasma oscillations, quantized as plasmons. SPPs result in evanescent fields that decay perpendicularly to the interface where the propagation occurs. The dispersion relation for SPPs permits the excitation of wavelengths shorter than the free-space wavelength of the inbound light, additionally ensuring subwavelength field confin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanolithography
Nanolithography (NL) is a growing field of techniques within nanotechnology dealing with the engineering (patterning e.g. etching, depositing, writing, printing etc) of nanometer-scale structures on various materials. The modern term reflects on a design of structures built in range of 10−9 to 10−6 meters, i.e. nanometer scale. Essentially, the field is a derivative of lithography, only covering very small structures. All NL methods can be categorized into four groups: photo lithography, scanning lithography, soft lithography and other miscellaneous techniques. History The NL has evolved from the need to increase the number of sub-micrometer features (e.g. transistors, capacitors etc.) in an integrated circuit in order to keep up with Moore's Law. While lithographic techniques have been around since the late 18th century, none were applied to nanoscale structures until the mid-1950s. With evolution of the semiconductor industry, demand for techniques capable of producing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fiber Bragg Grating
A fiber Bragg grating (FBG) is a type of distributed Bragg reflector constructed in a short segment of optical fiber that reflects particular wavelengths of light and transmits all others. This is achieved by creating a periodic variation in the refractive index of the fiber core, which generates a wavelength-specific dielectric mirror. Hence a fiber Bragg grating can be used as an inline optical fiber to block certain wavelengths, can be used for sensing applications, or it can be used as wavelength-specific reflector. History The first in-fiber Bragg grating was demonstrated by Ken Hill in 1978. Initially, the gratings were fabricated using a visible laser propagating along the fiber core. In 1989, Gerald Meltz and colleagues demonstrated the much more flexible transverse holographic inscription technique where the laser illumination came from the side of the fiber. This technique uses the interference pattern of ultraviolet laser light to create the periodic structure of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Negative-index Metamaterial
Negative-index metamaterial or negative-index material (NIM) is a metamaterial whose refractive index for an electromagnetic wave has a negative value over some frequency range. NIMs are constructed of periodic basic parts called unit cells, which are usually significantly smaller than the wavelength of the externally applied electromagnetic radiation. The unit cells of the first experimentally investigated NIMs were constructed from circuit board material, or in other words, wires and dielectrics. In general, these artificially constructed cells are stacked or planar and configured in a particular repeated pattern to compose the individual NIM. For instance, the unit cells of the first NIMs were stacked horizontally and vertically, resulting in a pattern that was repeated and intended (see below images). Specifications for the response of each unit cell are predetermined prior to construction and are based on the intended response of the entire, newly constructed, material. In o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasmonic Lens
In nano-optics, a plasmonic lens generally refers to a lens (optics), lens for surface plasmon polaritons (SPPs), i.e. a device that redirects SPPs to converge towards a single Focus (optics), focal point. Because SPPs can have very small wavelength, they can converge into a very small and very intense spot, much smaller than the vacuum, free space wavelength and the diffraction limit. A simple example of a plasmonic lens is a series of concentric, concentric rings on a metal, metal film. Any light that hits the film from free space at a 90 degree angle, known as Angle of incidence (optics), the normal, will get coupled into a SPP (this part works like a diffraction grating, diffraction grating coupler), and that SPP will be heading towards the center of the circles, which is the focal point. See alsPress release: Denser computer chips possible with plasmonic lenses UC Berkeley News. 2008-10-22 Another example is a tapered "dimple". In 2007, a novel, or technologically new, plasmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wave Interference
In physics, interference is a phenomenon in which two waves combine by adding their displacement together at every single point in space and time, to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude. Constructive and destructive interference result from the interaction of waves that are correlated or coherent with each other, either because they come from the same source or because they have the same or nearly the same frequency. Interference effects can be observed with all types of waves, for example, light, radio, acoustic, surface water waves, gravity waves, or matter waves. Etymology The word ''interference'' is derived from the Latin words ''inter'' which means "between" and ''fere'' which means "hit or strike", and was coined by Thomas Young in 1801. Mechanisms The principle of superposition of waves states that when two or more propagating waves of the same type are incident on the same point, the resultant amplitude at that point is equal to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanostructure
A nanostructure is a structure of intermediate size between microscopic and molecular structures. Nanostructural detail is microstructure at nanoscale. In describing nanostructures, it is necessary to differentiate between the number of dimensions in the volume of an object which are on the nanoscale. Nanotextured surfaces have ''one dimension'' on the nanoscale, i.e., only the thickness of the surface of an object is between 0.1 and 100 nm. Nanotubes have ''two dimensions'' on the nanoscale, i.e., the diameter of the tube is between 0.1 and 100 nm; its length can be far more. Finally, spherical nanoparticles have ''three dimensions'' on the nanoscale, i.e., the particle is between 0.1 and 100 nm in each spatial dimension. The terms nanoparticles and ultrafine particles (UFP) are often used synonymously although UFP can reach into the micrometre range. The term ''nanostructure'' is often used when referring to magnetic technology. Nanoscale structure in biology i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biconical Antenna
In radio systems, a biconical antenna is a broad-bandwidth antenna made of two roughly conical conductive objects, nearly touching at their points.Zhuohui Zhang,''Analysis and design of a broadband antenna for software defined radio'', ProQuest, 2007 , page 6 Biconical antennas are broadband dipole antennas, typically exhibiting a bandwidth of three octaves or more. A common subtype is the bowtie antenna, essentially a two-dimensional version of the biconial design which is often used for short-range UHF television reception. These are also sometimes referred to as butterfly antennas. Properties The biconical antenna has a broad bandwidth because it is an example of a traveling wave structure; the analysis for a theoretical infinite antenna resembles that of a transmission line. For an infinite antenna, the characteristic impedance at the point of connection is a function of the cone angle only and is independent of the frequency. Practical antennas have finite length and a def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer (monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many applications. A familiar example is the household mirror, which typically has a thin metal coating on the back of a sheet of glass to form a reflective interface. The process of silvering was once commonly used to produce mirrors, while more recently the metal layer is deposited using techniques such as sputtering. Advances in thin film deposition techniques during the 20th century have enabled a wide range of technological breakthroughs in areas such as magnetic recording media, electronic semiconductor devices, integrated passive devices, LEDs, optical coatings (such as antireflective coatings), hard coatings on cutting tools, and for both energy generation (e.g. thin-film solar cells) and storage ( thin-film batteries). It is also being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aperture
In optics, an aperture is a hole or an opening through which light travels. More specifically, the aperture and focal length of an optical system determine the cone angle of a bundle of rays that come to a focus in the image plane. An optical system typically has many openings or structures that limit the ray bundles (ray bundles are also known as ''pencils'' of light). These structures may be the edge of a lens or mirror, or a ring or other fixture that holds an optical element in place, or may be a special element such as a diaphragm placed in the optical path to limit the light admitted by the system. In general, these structures are called stops, and the aperture stop is the stop that primarily determines the ray cone angle and brightness at the image point. In some contexts, especially in photography and astronomy, ''aperture'' refers to the diameter of the aperture stop rather than the physical stop or the opening itself. For example, in a telescope, the aperture ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silver
Silver is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₂erǵ-, ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and reflectivity of any metal. The metal is found in the Earth's crust in the pure, free elemental form ("native silver"), as an alloy with gold and other metals, and in minerals such as argentite and chlorargyrite. Most silver is produced as a byproduct of copper, gold, lead, and zinc Refining (metallurgy), refining. Silver has long been valued as a precious metal. Silver metal is used in many bullion coins, sometimes bimetallism, alongside gold: while it is more abundant than gold, it is much less abundant as a native metal. Its purity is typically measured on a per-mille basis; a 94%-pure alloy is described as "0.940 fine". As one of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoresist
A photoresist (also known simply as a resist) is a light-sensitive material used in several processes, such as photolithography and photoengraving, to form a patterned coating on a surface. This process is crucial in the electronic industry. The process begins by coating a substrate with a light-sensitive organic material. A patterned mask is then applied to the surface to block light, so that only unmasked regions of the material will be exposed to light. A solvent, called a developer, is then applied to the surface. In the case of a positive photoresist, the photo-sensitive material is degraded by light and the developer will dissolve away the regions that were exposed to light, leaving behind a coating where the mask was placed. In the case of a negative photoresist, the photosensitive material is strengthened (either polymerized or cross-linked) by light, and the developer will dissolve away only the regions that were not exposed to light, leaving behind a coating in areas w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_250_nm_by_250_nm_image_of_one-atom-thick_silver_islands_grown_on_palladium_(111)_surface.png)


