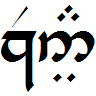|
Plants In Middle-earth
The plants in Middle-earth, the fictional world devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, are a mixture of real plant species with List of fictional plants#In J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth, fictional ones. Middle-earth was intended to represent the real world in an imagined past, and in many respects its natural history is realistic. The botany and ecology of Middle-earth are described in sufficient detail for botanists to have identified its plant communities, ranging from Arctic tundra to hot deserts, with many named plant species, both wild and cultivated. Scholars such as Walter S. Judd, Dinah Hazell, Tom Shippey, and Matthew T. Dickerson have noted that Tolkien described fictional plants for reasons including his own interest in plants and scenery, to enrich his descriptions of an area with beauty and emotion, to fulfil specific plot needs, to characterise the peoples of Middle-earth, and to establish tangible symbols in his mythology. Context J. R. R. Tolkien intended Middle-ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterbur
''Petasites'' is a genus of flowering plants in the sunflower family, Asteraceae, that are commonly referred to as butterburs and coltsfoots.''Petasites''. Flora of North America. Volume 20, Page 635. efloras.org. They are perennial plants with thick, creeping underground s and large -like leaves during the growing season. Most species are native to Asia or southern Europe. Characteristics The short spikes of s are produced just before the leaves in lat ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcreation
Mythopoeia ( grc, , , myth-making), or mythopoesis, is a narrative genre in modern literature and film where an artificial or fictionalized mythology is created by the writer of prose, poetry, or other literary forms. This meaning of the word follows its use by J. R. R. Tolkien in the 1930s. The authors in this genre integrate traditional mythological themes and archetypes into fiction. Mythopoeia is also the act of creating a mythology. Genre The term ''mythopoeia'' comes from Hellenistic Greek (), meaning 'myth-making'; an alternative is ''mythopoesis'' () of similar meaning. The definition of ''mythopoeia'' as "a creating of myth" is first recorded from 1846. In early use, it meant the making of myths in ancient times. It was adopted by J. R. R. Tolkien as the title of one of his poems, written in 1931 and published in ''Tree and Leaf''. While many literary works carry mythic themes, only a few approach the dense self-referentiality and purpose of mythopoesis. Myth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern Style (British Art Nouveau style), Modern Style in English. It was popular between 1890 and 1910 during the Belle Époque period, and was a reaction against the academic art, eclecticism and historicism of 19th century architecture and decoration. It was often inspired by natural forms such as the sinuous curves of plants and flowers. Other characteristics of Art Nouveau were a sense of dynamism and movement, often given by asymmetry or whiplash lines, and the use of modern materials, particularly iron, glass, ceramics and later concrete, to create unusual forms and larger open spaces.Sembach, Klaus-Jürgen, ''L'Art Nouveau'' (2013), pp. 8–30 One major objective of Art Nouveau was to break down the traditional distinction between fine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elvish Languages
Elvish languages are constructed languages used by Elves in a fantasy setting. The philologist and fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien created the first of these languages, including Quenya and Sindarin. Tolkien's Elvish languages The philologist and high fantasy author J. R. R. Tolkien created many languages for his Elves, leading him to create the mythology of his Middle-earth books, complete with multiple divisions of the Elves, to speak the languages he had constructed. The languages have quickly spread in modern-day use. His interest was primarily philological, and he stated that his stories grew out of his languages. The languages were the first thing Tolkien created for his mythos, starting with what he originally called "Qenya", the first primitive form of Elvish. This was later called Quenya (High-elven) and is one of the two most complete of Tolkien's languages (the other being Sindarin, or Grey-elven). The phonology and grammar of Quenya are influenced by Finnish, while Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quenya
Quenya ()Tolkien wrote in his "Outline of Phonology" (in ''Parma Eldalamberon'' 19, p. 74) dedicated to the phonology of Quenya: is "a sound as in English ''new''". In Quenya is a combination of consonants, ibidem., p. 81. is a constructed language, one of those devised by J. R. R. Tolkien for the Elves in his Middle-earth fiction. Tolkien began devising the language around 1910, and restructured its grammar several times until it reached its final state. The vocabulary remained relatively stable throughout the creation process. He successively changed the language's name from ''Elfin'' and ''Qenya'' to the eventual ''Quenya''. Finnish had been a major source of inspiration, but Tolkien was also fluent in Latin and Old English, and was familiar with Greek, Welsh (the latter being the primary inspiration for Sindarin, Tolkien's other major Elvish language), and other ancient Germanic languages, particularly Gothic, during his development of Quenya. A notable feature of Tolki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolkien's Artwork
Tolkien's artwork was a key element of his creativity from the time when he began to write fiction. The philologist and author J. R. R. Tolkien prepared illustrations for his Middle-earth fantasy books, facsimile artefacts, Tolkien's maps, more or less "picturesque" maps, calligraphy, and sketches and paintings from life. Some of his artworks combined several of these elements to support his fiction. In his lifetime, some of his artworks were included in his novels ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''; others were used on the covers of different editions of these books. Posthumously, collections of his artworks have been published, and academics have begun to evaluate him as an artist as well as an author. Influences Influences on Tolkien's artwork identified by scholars include Japonisme, Art Nouveau, Viking art, Viking design, and William Morris. Japonisme is seen in stylised features like Tolkien's mountains, waves, and Dragon (Middle-earth), dragons. Morris's book ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society For Promoting Christian Knowledge
The Society for Promoting Christian Knowledge (SPCK) is a UK-based Christian charity. Founded in 1698 by Thomas Bray, it has worked for over 300 years to increase awareness of the Christian faith in the UK and across the world. The SPCK is the oldest Anglican mission organisation in the world, though it is now more ecumenical in outlook and publishes books for a wide range of Christian denominations. It is currently the leading publisher of Christian books in the United Kingdom and the third oldest independent publisher in the UK. Mission The SPCK has a vision of a world in which everyone is transformed by Christian knowledge. Its mission is to lead the way in creating books and resources that help everyone to make sense of faith. Education has always been a core part of SPCK's mission. History Foundation On 8 March 1698, Rev. Thomas Bray met a small group of friends, including Sir Humphrey Mackworth, Colonel Maynard Colchester, Lord Guilford and John Hooke at Lincoln's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isles, and over six thousand smaller islands."British Isles", ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. They have a total area of and a combined population of almost 72 million, and include two sovereign states, the Republic of Ireland (which covers roughly five-sixths of Ireland), and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland. The Channel Islands, off the north coast of France, are normally taken to be part of the British Isles, even though they do not form part of the archipelago. The oldest rocks are 2.7 billion years old and are found in Ireland, Wales and the northwest of Scotland. During the Silurian period, the north-western regions collided with the south-east, which had been part of a separate continental landmass. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flora (publication)
A Flora is a book or other work which describes the plant species occurring in an area or time period, often with the aim of allowing identification. The term is usually capitalized to distinguish it from the use of "flora" to mean the plants rather than their descriptions. Some classic and modern Floras are listed below. Traditionally Floras are books, but some are now published on CD-ROM or websites. The area that a Flora covers can be either geographically or politically defined. Floras usually require some specialist botanical knowledge to use with any effectiveness. A Flora often contains diagnostic keys. Often these are ''dichotomous'' keys, which require the user to repeatedly examine a plant, and decide which one of two alternatives given in the Flora best applies to the plant. Floras produced at a local or regional level rarely contain identification keys. Instead they aim to impart more detailed understanding of the local status and distribution of that area's plants. M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Alexander Johns
Charles Alexander Johns (1811–1874) was a 19th-century British botanist and educator who was the author of a long series of popular books on natural history. Early years Charles Alexander Johns was born on 31 December 1811 in Plymouth, England, one of eight surviving children of Henry Incledon Johns, a banker and poet, and Maria (Boone) Johns. Two of his sisters, Emily and Julia, would prove to be exceptionally talented botanical artists. An economic crisis in 1825 forced the closure of the bank where Johns's father Henry was a working partner, throwing him out of a job and causing hardship for the family. Henry Johns then went to work as a teacher at Plymouth New Grammar School. Johns's father had encouraged his interest in natural history from an early age, and Charles had aimed for a career in the church, following an established pattern in Britain of "parson naturalists." One of his early teachers was a local silversmith and amateur botanist, George Banks, who published ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)