|
Pihani
Pihani is a town and nagar palika parishad (municipal board) in Hardoi district of Uttar Pradesh, India. Historically, the city was a centre of sword production, leading to at least one British writer calling it "the Damascus of Oudh". Today, important industries in Pihani include jaggery and woven carpets. As of 2011, the town's population is 36,014, in 5,626 households. Pihani also serves as the headquarters of a community development block in Shahabad tehsil. Geography Pihani is located at . It has an average elevation of 141 metres (462 feet). Demographics India census, Pihani had a population of 27,535. Males constitute 52% of the population and females 48%. Pihani has an average literacy rate of 46%, lower than the national average of 59.5%: male literacy is 53%, and female literacy is 38%. In Pihani, 19% of the population is under 6 years of age. Transport Pihani is well connected with Hardoi City . Government and private buses are available for H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
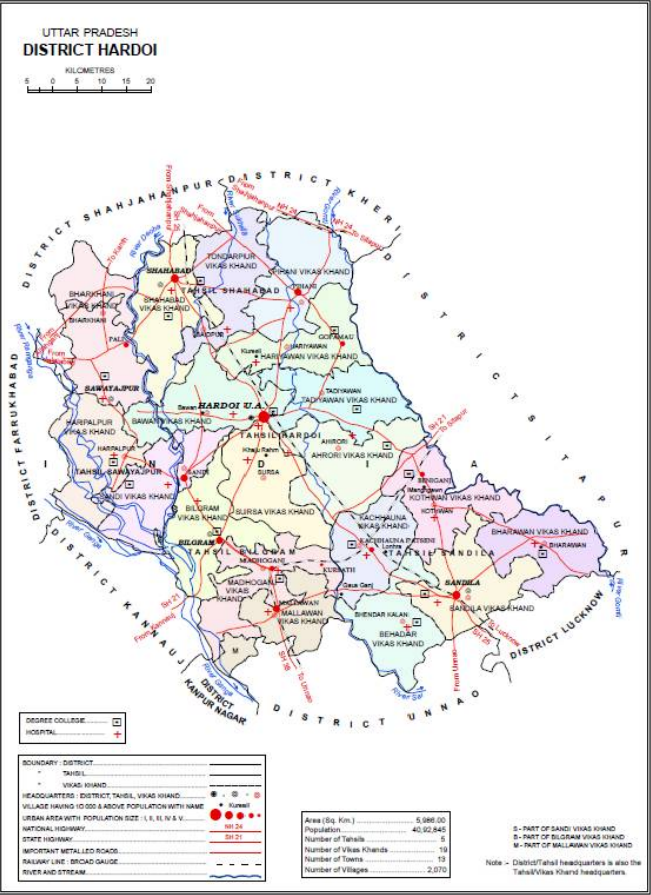
Hardoi District
Hardoi district is a district situated in the center of Uttar Pradesh, India. The district headquarters is in the city of Hardoi. Hardoi is the third largest district of Uttar Pradesh. It falls under Lucknow division in the history region of Awadh As of the 2011 census, the total population of Hardoi district is 4,092,845 people, in 730,442 households. It is the 13th-most populous district in Uttar Pradesh. History The present-day Hardoi district was created by the British after their takeover of Awadh in 1856. At the time of Akbar in the 1500s, the area of the modern district was divided between the sarkars of Lucknow and Khairabad. Five ''mahal''s were in Lucknow sarkar: Sandila, Mallanwan, Kachhandao, "Garanda" (probably a miscopying of Gundwa), and Bilgram. The Ain-i-Akbari does list a mahal of Hardoi in Lucknow district, but this was referring to the Hardoi in modern Rae Bareli district instead of the one in Hardoi district. As for the sarkar of Khairabad, the mahals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardoi
Hardoi is a city and municipal board in Hardoi district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the administrative headquarters of Hardoi district. History The early history of Hardoi is obscure. The name suggests a Bhar, a Dalit caste of pasi origin, but tradition either attributes it to a Thathera ruler named Raja Harnakas or to a religious devotee named Hardeo Babar who supposedly lived here around 1000 CE. In any case, the site was inhabited from an early date; below the old town is an ancient '' khera'' that covers 16 acres. Around 1300, a group of Chamar Gaurs led by one Sale Singh are said to have conquered the place from the Thatheras, destroyed their fortress, and re-founded the city. At the turn of the 20th century, Hardoi consisted of two distinct parts: "old" Hardoi, occupying the original site of the village, and "new" Hardoi, which was developed after the establishment of the British civil station in the late 1850s. "New" Hardoi had wide streets, well-shaded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahabad, Hardoi
Shahabad is a town nearby Hardoi city and a municipal board in Hardoi district in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. At one point of time it was counted among the few biggest cities of Oudh, but declined rapidly in later period and now reduced to a town. It is the site of the Tomb of Diler Khan, a governor in the time of Shah Jahahan and Aurangzeb.There is a renowned coaching center named Al-Amaan Study center. As of 2011, the population of Shahabad is 80,226, in 13,958 households. It is the seat of a tehsil and a community development block. Important local industries include carpet weaving, building materials, and dairy products. History According to a tradition recorded by Joseph Tiefenthaler in the 1700s, Shahabad occupied the site of a former village called Angadpur, after its founder Angad, the nephew of Rama. Modern Shahabad was founded in 1677 by one Nawab Diler Khan, a Pathan officer in the Mughal army, who had been sent to quell an uprising in Shahjahanpur. He overt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Indian Cities
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording and calculating information about the members of a given population. This term is used mostly in connection with national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications and other useful information to co-ordinate international practices. The UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), in turn, defines the census of agriculture as "a statistical operation for collecting, processing and disseminating data on the structure of agriculture, covering th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamarind
Tamarind (''Tamarindus indica'') is a Legume, leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is probably indigenous to tropical Africa. The genus ''Tamarindus'' is monotypic taxon, monotypic, meaning that it contains only this species. It belongs to the family Fabaceae. The tamarind tree produces brown, pod-like fruits that contain a sweet, tangy pulp, which is used in cuisines around the world. The pulp is also used in traditional medicine and as a metal polish. The tree's wood can be used for woodworking and Tamarind#Tamarind seed oil and kernel powder, tamarind seed oil can be extracted from the seeds. Tamarind's tender young leaves are used in Indian cuisine, Indian and Filipino cuisine. Because tamarind has multiple uses, it is cultivated around the world in Tropical zone, tropical and Subtropics, subtropical zones. Description The tamarind is a long-lived, medium-growth tree, which attains a maximum crown (botany), crown height of . The crown has an irregular, vase-shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in India. A strong personality and a successful general, Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent. His power and influence, however, extended over the entire subcontinent because of Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration throughout his empire and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his non-Muslim subjects. Eschewing t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nawab Sadr Jahan
Nawab ( Balochi: نواب; ar, نواب; bn, নবাব/নওয়াব; hi, नवाब; Punjabi : ਨਵਾਬ; Persian, Punjabi , Sindhi, Urdu: ), also spelled Nawaab, Navaab, Navab, Nowab, Nabob, Nawaabshah, Nawabshah or Nobab, is a Royal title indicating a sovereign ruler, often of a South Asian state, in many ways comparable to the western title of Prince. The relationship of a Nawab to the Emperor of India has been compared to that of the Kings of Saxony to the German Emperor. In earlier times the title was ratified and bestowed by the reigning Mughal emperor to semi-autonomous Muslim rulers of subdivisions or princely states in the Indian subcontinent loyal to the Mughal Empire, for example the Nawabs of Bengal. The title is common among Muslim rulers of South Asia as an equivalent to the title Maharaja. "Nawab" usually refers to males and literally means ''Viceroy''; the female equivalent is "Begum" or "''Nawab Begum''". The primary duty of a Nawab was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری) (1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان) , was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin to the weight of 178 grams and named the currency as rupee based on the ancient Sanskrit term for silver. An ethnic Pashtun ruler, Sher Shah took control of the Mughal Empire in 1540 CE. After his accidental death in 1545 CE, his son Islam Shah became his successor. He first served as a private before rising to become a commander in the Mughal army under Babur and then the governor of Bihar. In 1537, when Babur's son Humayun was elsewhere on an expedition, Sher Shah overran the state of Bengal and established the Suri dynasty. A brilliant strategist, Sher Shah proved himself as a gifted administrator as well as a capable general. His reorganization of the empire laid the foundations for the later Mughal emperors, notably Akbar, son of Hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northern India, and Bangladesh from 1530 to 1540 and again from 1555 to 1556. Like his father, Babur, he lost his empire early but regained it with the aid of the Safavid dynasty of Persia, with additional territory. At the time of his death in 1556, the Mughal Empire spanned almost one million square kilometres. In December 1530, Humayun succeeded his father to the throne of Delhi as ruler of the Mughal territories in the Indian subcontinent. Humayun was an inexperienced ruler when he came to power, at the age of 22. His half-brother Kamran Mirza inherited Kabul and Kandahar, the northernmost parts of their father's empire. The two half-brothers would become bitter rivals. Humayun lost Mughal territories to Sher Shah Suri, but regained them 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thathera
The Thathera is a Hindu and Sikh artisan caste in India, who traditional occupation is the making of brass and copper utensils. In 2014, the craft of the Thathera community of Jandiala Guru were included in UNESCO’s List of Intangible Cultural Heritage. Present circumstances The Thathera community are divided into 47 clans. The main ones are Chauhan, Parmar, Gohil, Mahecha Rathod, Vadher, Solanki, Bhatti, khasi, Kagda and Puvar . In Uttar Pradesh, they are found mainly in Lalitpur, Jalaun, Banda, Kanpur, Lucknow, Mirzapur and Indore M.p also In Bihar, they are found in the districts of Patna, Nalanda, Gaya, Nawada, Bhagalpur, Muzaffarpur, Munger, Purnea, Begusarai, Katihar, Khagaria, and Madhubani. The Bihar Thathera are divided into a number of exogamous clans such as the Chandrahar, Chaswar, Mirdang, Amarpallo, and Peswa. The Thathera are basically a community of artisans. Metal work, business and repair of utensils are their traditional occupations. Many of them ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |