|
Pierre Waldeck-Rousseau
Pierre Marie René Ernest Waldeck-Rousseau (; 2 December 184610 August 1904) was a French Republican politician who served as the Prime Minister of France. Early life Pierre Waldeck-Rousseau was born in Nantes, Brittany. His father, René Waldeck-Rousseau, a barrister at the Nantes bar and a leader of the local republican party, figured in the revolution of 1848 as one of the deputies elected to the Constituent Assembly for Loire Inférieure. The son was a delicate child whose eyesight made reading difficult, and his early education was therefore entirely oral. He studied law at Poitiers and in Paris, where he took his licentiate in January 1869. His father's record ensured his reception in high republican circles. Jules Grévy stood sponsor for him at the Parisian bar. After six months of waiting for briefs in Paris, he decided to return home and to join the bar of St Nazaire early in 1870. In September he became, in spite of his youth, secretary to the municipal commissi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nadar (artist)
Gaspard-Félix Tournachon (5 April 1820 – 20 March 1910), known by the pseudonym Nadar, was a French photographer, caricaturist, journalist, novelist, balloonist, and proponent of heavier-than-air flight. In 1858, he became the first person to take aerial photographs. Photographic portraits by Nadar are held by many of the great national collections of photographs. His son, Paul Nadar (1856–1939), continued the studio after his death. Life Gaspard-Félix Tournachon (also known as Nadar) was born in early April 1820 in Paris, though some sources state he was born in Lyon. His father, Victor Tournachon, was a printer and bookseller. Nadar began to study medicine but quit for economic reasons after his father's death. Nadar started working as a caricaturist and novelist for various newspapers. He fell in with the Parisian bohemian group of Gérard de Nerval, Charles Baudelaire, and Théodore de Banville. His friends picked a nickname for him, perhaps by a playful habit of ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Grévy
François Judith Paul Grévy (15 August 1807 – 9 September 1891), known as Jules Grévy (), was a French people, French lawyer and politician who served as President of France from 1879 to 1887. He was a leader of the Opportunist Republicans, Moderate Republicans, and given that his predecessors were Monarchism in France, monarchists who tried without success to restore the French monarchy, Grévy is considered the first real Republicanism, republican president of France. Born in a small town in the Jura (department), Jura department, Grévy moved to Paris where he initially followed a career in law before becoming a republican activist. He began his political career after the French Revolution of 1848, as a member of the National Assembly (France), National Assembly of the French Second Republic, where he became known for his opposition to Napoleon III, Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte and as a supporter of lesser authority for the executive branch. During the 1851 French coup d'éta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labor Laws
Labour laws (also known as labor laws or employment laws) are those that mediate the relationship between workers, employing entities, trade unions, and the government. Collective labour law relates to the tripartite relationship between employee, employer, and union. Individual labour law concerns employees' rights at work also through the contract for work. are social norms (in some cases also technical standards) for the minimum socially acceptable conditions under which employees or contractors are allowed to work. Government agencies (such as the former US Employment Standards Administration) enforclabour law(legislature, regulatory, or judicial). History Following the unification of the city-states in Assyria and Sumer by Sargon of Akkad into a single empire ruled from his home city circa 2334 BC, common Mesopotamian standards for length, area, volume, weight, and time used by artisan guilds in each city was promulgated by Naram-Sin of Akkad (c. 2254–2218 BC), Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Judicial System
In France, career judges are considered civil servants exercising one of the sovereign powers of the state, so French citizens are eligible for judgeship, but not citizens of the other EU countries. France's independent court system enjoys special statutory protection from the executive branch. Procedures for the appointment, promotion, and removal of judges vary depending on whether it is for the ordinary ("") or administrative stream. Judicial appointments in the judicial stream must be approved by a special panel, the High Council of the Judiciary. Once appointed, career judges serve for life and cannot be removed without specific disciplinary proceedings conducted before the Council with due process. The Ministry of Justice handles the administration of courts and the judiciary, including paying salaries or constructing new courthouses. The Ministry also funds and administers the prison system. Lastly, it receives and processes applications for presidential pardons and propose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minister Of The Interior (France)
Minister of the Interior (french: Ministre de l'Intérieur; ) is a prominent position in the Government of France. The position is equivalent to the interior minister in other countries, like the Home Secretary in the United Kingdom, the Minister of Public Safety in Canada, or similar to a combination of the Attorney General and the Secretary of Homeland Security in the United States. Responsibilities The Minister of the Interior is responsible for the following: * The general interior security of the country, with respect to criminal acts or natural catastrophes ** including the major law-enforcement forces *** the National Police *** the National Gendarmerie for its police operations since 2009; as a part of the French Armed Forces, the Gendarmerie is administratively under the purview of the Ministry of Armed Forces ** General directorate for civil defence and crisis management (Sécurité Civile) *** the directorate of Firefighters (Sapeurs-Pompiers) * the granting of id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Ferry Laws On Public, Laic And Mandatory Education
The Jules Ferry Laws are a set of French laws which established free education in 1881, then mandatory and ''laic'' (secular) education in 1882. Jules Ferry, a lawyer holding the office of Minister of Public Instruction in the 1880s, is widely credited for creating the modern Republican school (''l'école républicaine''). The dual system of state and church schools that were largely staffed by religious officials was replaced by state schools and lay school teachers. The educational reforms enacted by Jules Ferry are often attributed to a broader anti-clerical campaign in France. History French education during the 19th century was marked by two distinct and segregated systems, the first being a secondary school system and the second a primary school system. However, in each of these systems, the Catholic Church provided an alternative to secular schooling that was often the only option for families in economically depressed regions of France. Although the Republican party is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolution and the development of modern political, economic, and educational thought. His ''Discourse on Inequality'' and ''The Social Contract'' are cornerstones in modern political and social thought. Rousseau's sentimental novel ''Julie, or the New Heloise'' (1761) was important to the development of preromanticism and romanticism in fiction. His '' Emile, or On Education'' (1762) is an educational treatise on the place of the individual in society. Rousseau's autobiographical writings—the posthumously published '' Confessions'' (composed in 1769), which initiated the modern autobiography, and the unfinished '' Reveries of the Solitary Walker'' (composed 1776–1778)—exemplified the late 18th-century " Age of Sensibility", and featured a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Léon Gambetta
Léon Gambetta (; 2 April 1838 – 31 December 1882) was a French lawyer and republican politician who proclaimed the French Third Republic in 1870 and played a prominent role in its early government. Early life and education Born in Cahors, Gambetta is said to have inherited his vigour and eloquence from his father, a Genoese grocer who had married a Frenchwoman named Massabie. At the age of fifteen, Gambetta lost the sight of his right eye in an accident, and it eventually had to be removed. Despite this handicap, he distinguished himself at school in Cahors. He then worked at his father's grocery shop in Cahors, the ''Bazar génois'' ("Genoese bazaar"), and in 1857 went to study at the Faculty of Law of Paris. His temperament gave him great influence among the students of the ''Quartier latin'', and he was soon known as an inveterate enemy of the imperial government. Career Gambetta was called to the bar in 1859. He was admitted to the Conférence Molé in 1861 and wrote ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Republican Union (France)
The Republican Union (french: Union républicaine, UR), later known as the Progressive Union (french: Union progressiste, UP), was a French parliamentary group founded in 1871 as a heterogeneous alliance of moderate Radicalism (historical), radicals, former Communards and opponents of the Treaty of Versailles (1871), French-Prussian Treaty. History Formed in the early years of the French Third Republic, the Republican Union led by Léon Gambetta was strongly opposed to the Treaty of Frankfurt as much understanding to the Paris Commune, repressed by the moderate Adolphe Thiers. The party's electoral lists also included notable activists and intellectuals like Louis Blanc (elected with 216,000 votes), Victor Hugo, Giuseppe Garibaldi, Edgar Quinet, Pierre Waldeck-Rousseau, Émile Littré, Charles Floquet, Georges Clemenceau, Arthur Ranc and Gustave Courbet. Initially on the far-left politics, extreme left of the Parliament of France, the group became close to the Opportunist Republ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
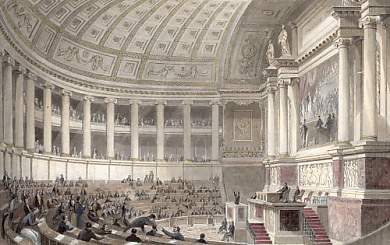
Chamber Of Deputies Of France
Chamber of Deputies (french: Chambre des députés) was a parliamentary body in France in the nineteenth and twentieth centuries: * 1814–1848 during the Bourbon Restoration and the July Monarchy, the Chamber of Deputies was the lower house of the French Parliament, elected by census suffrage. * 1875–1940 during the French Third Republic, the Chamber of Deputies was the legislative assembly of the French Parliament, elected by universal suffrage. When reunited with the Senate in Versailles, the French Parliament was called the National Assembly (''Assemblée nationale'') and carried out the election of the president of the French Republic. During the Bourbon Restoration Created by the Charter of 1814 and replacing the Corps législatif, which existed under the First French Empire, the Chamber of Deputies was composed of individuals elected by census suffrage. Its role was to discuss laws and, most importantly, to vote taxes. According to the Charter, deputies were elected f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rennes
Rennes (; br, Roazhon ; Gallo: ''Resnn''; ) is a city in the east of Brittany in northwestern France at the confluence of the Ille and the Vilaine. Rennes is the prefecture of the region of Brittany, as well as the Ille-et-Vilaine department. In 2017, the urban area had a population of 357,327 inhabitants, and the larger metropolitan area had 739,974 inhabitants.Comparateur de territoire Unité urbaine 2020 de Rennes (35701), Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Rennes (013) INSEE The inhabitants of Rennes are called Rennais/Rennaises in French. Rennes's history goes back more than 2,000 years, at a time when it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Security
National security, or national defence, is the security and defence of a sovereign state, including its citizens, economy, and institutions, which is regarded as a duty of government. Originally conceived as protection against military attack, national security is widely understood to include also non-military dimensions, including the security from terrorism, minimization of crime, economic security, energy security, environmental security, food security, and cyber-security. Similarly, national security risks include, in addition to the actions of other nation states, action by violent non-state actors, by narcotic cartels, and by multinational corporations, and also the effects of natural disasters. Governments rely on a range of measures, including political, economic, and military power, as well as diplomacy, to safeguard the security of a nation state. They may also act to build the conditions of security regionally and internationally by reducing transnational caus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)