|
Piazza San Pietro
Saint Peter's Square ( la, Forum Sancti Petri, it, Piazza San Pietro ,) is a large plaza located directly in front of St. Peter's Basilica in Vatican City, the papal enclave inside Rome, directly west of the neighborhood (rione) of Borgo. Both the square and the basilica are named after Saint Peter, an apostle of Jesus whom Catholics consider to be the first Pope. At the centre of the square is an ancient Egyptian obelisk, erected at the current site in 1586. Gian Lorenzo Bernini designed the square almost 100 years later, including the massive Doric colonnades, four columns deep, which embrace visitors in "the maternal arms of Mother Church". A granite fountain constructed by Bernini in 1675 matches another fountain designed by Carlo Maderno in 1613. History The open space which lies before the basilica was redesigned by Gian Lorenzo Bernini from 1656 to 1667, under the direction of Pope Alexander VII, as an appropriate forecourt, designed "so that the greatest number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—' * german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ') * pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—' * pt, Cidade do Vaticano—' * es, Ciudad del Vaticano—' is an independent city-state, microstate and enclave and exclave, enclave within Rome, Italy. Also known as The Vatican, the state became independent from Italy in 1929 with the Lateran Treaty, and it is a distinct territory under "full ownership, exclusive dominion, and sovereign authority and jurisdiction" of the Holy See, itself a Sovereignty, sovereign entity of international law, which maintains the city state's Temporal power of the Holy See, temporal, Foreign relations of the Holy See, diplomatic, and spiritual Legal status of the Holy See, independence. With an area of and a 2019 population of about 453, it is the smallest state in the world both by area and List of countries and dependencies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by Ancient Egyptians and called ''tekhenu'', the Greeks used the Greek term to describe them, and this word passed into Latin and ultimately English. Ancient obelisks are monolithic; they consist of a single stone. Most modern obelisks are made of several stones. Ancient obelisks Egyptian Obelisks were prominent in the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, and played a vital role in their religion placing them in pairs at the entrance of the temples. The word "obelisk" as used in English today is of Greek rather than Egyptian origin because Herodotus, the Greek traveler, was one of the first classical writers to describe the objects. A number of ancient Egyptian obelisks are known to have survived, plus the " Unfinished Obelisk" found part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chigi-Albani Family
The House of Chigi () is an Italy, Italian princely family of Siena, Sienese origin descended from the counts of Ardenghesca, which possessed castles in the Maremma, southern Tuscany. Later, the family settled in Rome. The earliest authentic mention of them is in the 13th century, with one Alemanno, counsellor of the Republic of Siena. History Origins The first very prominent member was Mariano Chigi, Mariano (1439–1504), a banker and two time ambassador of Siena to the Popes Pope Alexander VI, Alexander VI and Pope Julius II, Julius II. He founded the Roman branch of the family, the other branch was started by his brother, Benedetto. Notable members Agostino Chigi (1465–1520) was the most famous member of the family during the Renaissance. He became an immensely rich banker, and built the palace and gardens afterwards known as the Villa Farnesina, Farnesina, decorated by Raphael, Sebastiano del Piombo, Giulio Romano, and Il Sodoma, and was noted for the splendour of his ente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by Ancient Egyptians and called ''tekhenu'', the Greeks used the Greek term to describe them, and this word passed into Latin and ultimately English. Ancient obelisks are monolithic; they consist of a single stone. Most modern obelisks are made of several stones. Ancient obelisks Egyptian Obelisks were prominent in the architecture of the ancient Egyptians, and played a vital role in their religion placing them in pairs at the entrance of the temples. The word "obelisk" as used in English today is of Greek rather than Egyptian origin because Herodotus, the Greek traveler, was one of the first classical writers to describe the objects. A number of ancient Egyptian obelisks are known to have survived, plus the " Unfinished Obelisk" found part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vatican Obelisk
The city of Rome harbours thirteen ancient obelisks, the most in the world. There are eight ancient Egyptian and five Ancient Rome, ancient Roman obelisks in Rome, together with a number of more modern obelisks; there was also until 2005 an Kingdom of Aksum, ancient Ethiopian obelisk in Rome. The Romans used special heavy cargo carriers called obelisk ships to transport the monuments down the Nile to Alexandria and from there across the Mediterranean Sea to Rome. On site, large Crane (machine)#History, Roman cranes were employed to erect the monoliths. Ancient Egyptian obelisks At least eight obelisks created in antiquity by the Egyptians were taken from Egypt after the Roman conquest of Egypt, Roman conquest and brought to Rome. Ancient Roman obelisks At least five obelisks were manufactured in Roman Egypt, Egypt in the Roman period at the request of the wealthy Romans, or made in Rome as copies of ancient Egyptian originals. Obelisk of Axum There was also an Ethio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Di San Pietro 1450
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name to the architectural form of the basilica. Originally, a basilica was an ancient Roman public building, where courts were held, as well as serving other official and public functions. Basilicas are typically rectangular buildings with a central nave flanked by two or more longitudinal aisles, with the roof at two levels, being higher in the centre over the nave to admit a clerestory and lower over the side-aisles. An apse at one end, or less frequently at both ends or on the side, usually contained the raised tribunal occupied by the Roman magistrates. The basilica was centrally located in every Roman town, usually adjacent to the forum and often opposite a temple in imperial-era forums. Basilicas were also built in private residences and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander VII
Pope Alexander VII ( it, Alessandro VII; 13 February 159922 May 1667), born Fabio Chigi, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 7 April 1655 to his death in May 1667. He began his career as a vice- papal legate, and he held various diplomatic positions in the Holy See. He was ordained as a priest in 1634, and he became bishop of Nardo in 1635. He was later transferred in 1652, and he became bishop of Imola. Pope Innocent X made him secretary of state in 1651, and in 1652, he was appointed a cardinal. Early in his papacy, Alexander, who was seen as an anti-nepotist at the time of his election, lived simply; later, however, he gave jobs to his relatives, who eventually took over his administration. His administration worked to support the Jesuits. However, his administration's relations with France were strained due to his frictions with French diplomats. Alexander was interested in architecture and supported various urban projects in Rome. He als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateran Treaty
The Lateran Treaty ( it, Patti Lateranensi; la, Pacta Lateranensia) was one component of the Lateran Pacts of 1929, agreements between the Kingdom of Italy under King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy and the Holy See under Pope Pius XI to settle the long-standing Roman Question. The treaty and associated pacts were named after the Lateran Palace where they were signed on 11 February 1929, and the Italian parliament ratified them on 7 June 1929. The treaty recognized Vatican City as an independent state under the sovereignty of the Holy See. The Italian government also agreed to give the Roman Catholic Church financial compensation for the loss of the Papal States. In 1948, the Lateran Treaty was recognized in the Constitution of Italy as regulating the relations between the state and the Catholic Church. Constitution of Italy, article 7. The treaty was significantly revised in 1984, ending the status of Catholicism as the sole state religion. Content The Lateran Pacts are often p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque
The Baroque (, ; ) is a style of architecture, music, dance, painting, sculpture, poetry, and other arts that flourished in Europe from the early 17th century until the 1750s. In the territories of the Spanish and Portuguese empires including the Iberian Peninsula it continued, together with new styles, until the first decade of the 19th century. It followed Renaissance art and Mannerism and preceded the Rococo (in the past often referred to as "late Baroque") and Neoclassical styles. It was encouraged by the Catholic Church as a means to counter the simplicity and austerity of Protestant architecture, art, and music, though Lutheran Baroque art developed in parts of Europe as well. The Baroque style used contrast, movement, exuberant detail, deep colour, grandeur, and surprise to achieve a sense of awe. The style began at the start of the 17th century in Rome, then spread rapidly to France, northern Italy, Spain, and Portugal, then to Austria, southern Germany, and Russia. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
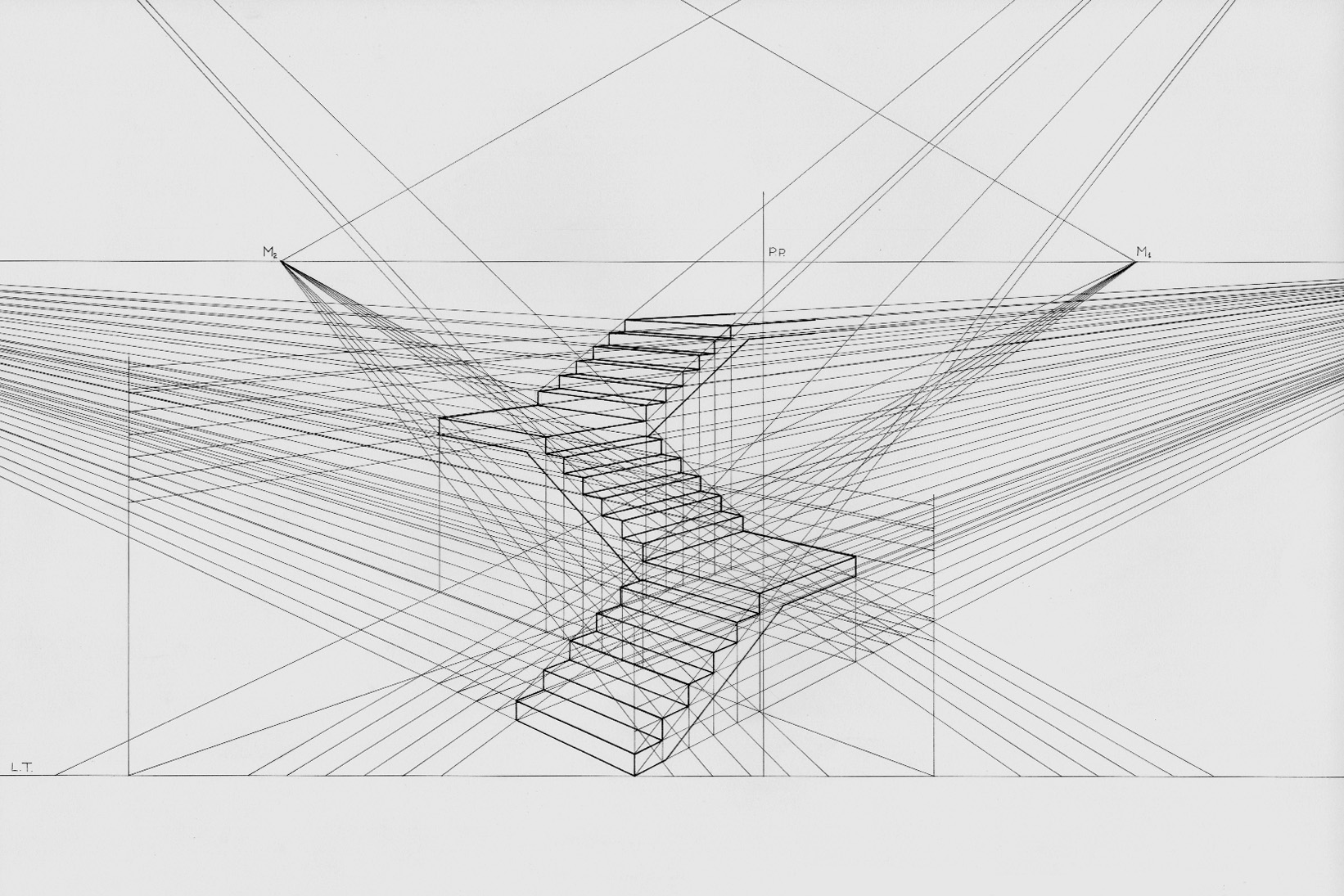
Perspective (visual)
Linear or point-projection perspective (from la, perspicere 'to see through') is one of two types of graphical projection perspective in the graphic arts; the other is parallel projection. Linear perspective is an approximate representation, generally on a flat surface, of an image as it is seen by the eye. Perspective drawing is useful for representing a three-dimensional scene in a two-dimensional medium, like paper. The most characteristic features of linear perspective are that objects appear smaller as their distance from the observer increases, and that they are subject to ''foreshortening'', meaning that an object's dimensions along the line of sight appear shorter than its dimensions across the line of sight. All objects will recede to points in the distance, usually along the horizon line, but also above and below the horizon line depending on the view used. Italian Renaissance painters and architects including Masaccio, Paolo Uccello, Piero della Francesca and Luca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)