|
Photoelectrochemistry
Photoelectrochemistry is a subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems. It is an active domain of investigation. One of the pioneers of this field of electrochemistry was the German electrochemist Heinz Gerischer. The interest in this domain is high in the context of development of renewable energy conversion and storage technology. Historical approach Photoelectrochemistry has been intensively studied in the 1970-80s because of the first peak oil crisis. Because fossil fuels are non-renewable, it is necessary to develop processes to obtain renewable resources and use clean energy. Artificial photosynthesis, photoelectrochemical water splitting and regenerative solar cells are of special interest in this context. The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Heinz Gerischer, H. Tributsch, AJ. Nozik, AJ. Bard, A. Fujishima, K. Honda, PE. Laibinis, K. Rajeshwar, TJ Meyer, PV. Kamat, N.S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photoelectrochemical Cells
A "photoelectrochemical cell" is one of two distinct classes of device. The first electricity generation, produces electrical energy similarly to a dye-sensitized solar cell, dye-sensitized photovoltaic cell, which meets the standard definition of a solar cell, photovoltaic cell. The second is a photoelectrolytic cell, that is, a device which uses light incident on a photosensitizer, semiconductor, or aqueous Electrical conductor, metal immersed in an electrolytic solution to directly cause a chemical reaction, for example to produce hydrogen via the electrolysis of water. Both types of device are varieties of solar cells, solar cell, in that a photoelectrochemical cell's function is to use the photoelectric effect (or, very similarly, the photovoltaic effect) to convert electromagnetic radiation (typically sunlight) either directly into electrical power, or into something which can itself be easily used to produce electrical power (hydrogen, for example, can be burned to Hydrog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
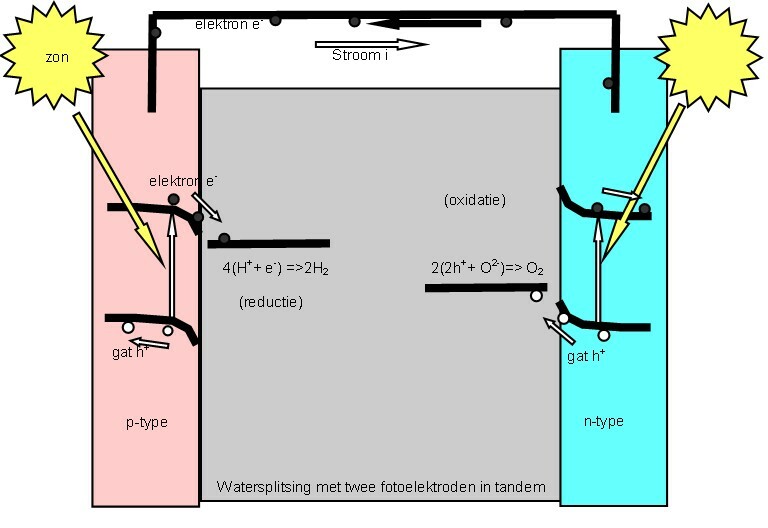
Photoelectrolysis
Photoelectrochemistry is a subfield of study within physical chemistry concerned with the interaction of light with electrochemical systems. It is an active domain of investigation. One of the pioneers of this field of electrochemistry was the German electrochemist Heinz Gerischer. The interest in this domain is high in the context of development of renewable energy conversion and storage technology. Historical approach Photoelectrochemistry has been intensively studied in the 1970-80s because of the first peak oil crisis. Because fossil fuels are non-renewable, it is necessary to develop processes to obtain renewable resources and use clean energy. Artificial photosynthesis, photoelectrochemical water splitting and regenerative solar cells are of special interest in this context. The photovoltaic effect was discovered by Alexandre Edmond Becquerel. Heinz Gerischer, H. Tributsch, AJ. Nozik, AJ. Bard, A. Fujishima, K. Honda, PE. Laibinis, K. Rajeshwar, TJ Meyer, PV. Kamat, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artificial Photosynthesis
Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that biomimics the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term artificial photosynthesis is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into hydrogen and oxygen and is a major research topic of artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another process studied that replicates natural carbon fixation. Research on this topic includes the design and assembly of devices for the direct production of solar fuels, photoelectrochemistry and its application in fuel cells, and the engineering of enzymes and photoautotrophic microorganisms for microbial biofuel and biohydrogen production from sunlight. Overview The photosynthetic reaction can be divided into two half-reactions of oxidation and redu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Bockris
Bernhardt Patrick John O’Mara Bockris (5 January 1923 – 7 July 2013) was a South African professor of chemistry, latterly at Texas A&M University. During his long and prolific career he published some 700 papers and two dozen books. His best known work is in electrochemistry but his output also extended to environmental chemistry, photoelectrochemistry and bioelectrochemistry. In the 1990s he experimented with cold fusion and transmutation, topics on which his unorthodox views provoked controversy. Early life John Bockris was born on 5 January 1923, in Johannesburg, South Africa. His mother was Emmeline Mary MacNally and his father Alfred Bockris. He attended a sequence of schools in Brighton, including the preparatory school Withdean Hall from 1934 to 1937, and Xaverian College, a Catholic secondary school, from 1937 to 1940. His father was not present during his childhood: His mother and aunt earned their income from tailoring. University education In 1940 Boc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outcome of a particular chemical change, or vice versa. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal–semiconductor Junction
In solid-state physics, a metal–semiconductor (M–S) junction is a type of electrical junction in which a metal comes in close contact with a semiconductor material. It is the oldest practical semiconductor device. M–S junctions can either be rectifying or non-rectifying. The rectifying metal–semiconductor junction forms a Schottky barrier, making a device known as a Schottky diode, while the non-rectifying junction is called an ohmic contact. (In contrast, a rectifying semiconductor–semiconductor junction, the most common semiconductor device today, is known as a p–n junction.) Metal–semiconductor junctions are crucial to the operation of all semiconductor devices. Usually an ohmic contact is desired, so that electrical charge can be conducted easily between the active region of a transistor and the external circuitry. Occasionally however a Schottky barrier is useful, as in Schottky diodes, Schottky transistors, and metal–semiconductor field effect transist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P-type Semiconductor
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been '' doped''; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an ''intrinsic semiconductor''. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An ''electron donor'' dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An ''electron acceptor'' dopant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-type Semiconductor
An extrinsic semiconductor is one that has been '' doped''; during manufacture of the semiconductor crystal a trace element or chemical called a doping agent has been incorporated chemically into the crystal, for the purpose of giving it different electrical properties than the pure semiconductor crystal, which is called an ''intrinsic semiconductor''. In an extrinsic semiconductor it is these foreign dopant atoms in the crystal lattice that mainly provide the charge carriers which carry electric current through the crystal. The doping agents used are of two types, resulting in two types of extrinsic semiconductor. An ''electron donor'' dopant is an atom which, when incorporated in the crystal, releases a mobile conduction electron into the crystal lattice. An extrinsic semiconductor which has been doped with electron donor atoms is called an n-type semiconductor, because the majority of charge carriers in the crystal are negative electrons. An ''electron acceptor'' dopant is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photon
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless, so they always move at the speed of light in vacuum, (or about ). The photon belongs to the class of bosons. As with other elementary particles, photons are best explained by quantum mechanics and exhibit wave–particle duality, their behavior featuring properties of both waves and particles. The modern photon concept originated during the first two decades of the 20th century with the work of Albert Einstein, who built upon the research of Max Planck. While trying to explain how matter and electromagnetic radiation could be in thermal equilibrium with one another, Planck proposed that the energy stored within a material object should be regarded as composed of an integer number of discrete, equal-sized parts. To explain the photoelectric effect, Eins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermi Level
The Fermi level of a solid-state body is the thermodynamic work required to add one electron to the body. It is a thermodynamic quantity usually denoted by ''µ'' or ''E''F for brevity. The Fermi level does not include the work required to remove the electron from wherever it came from. A precise understanding of the Fermi level—how it relates to electronic band structure in determining electronic properties, how it relates to the voltage and flow of charge in an electronic circuit—is essential to an understanding of solid-state physics. In band structure theory, used in solid state physics to analyze the energy levels in a solid, the Fermi level can be considered to be a hypothetical energy level of an electron, such that at thermodynamic equilibrium this energy level would have a ''50% probability of being occupied at any given time''. The position of the Fermi level in relation to the band energy levels is a crucial factor in determining electrical properties. The Fermi le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P–n Junction
A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes, while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electrical current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p-n junction is created by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy (growing a layer of crystal doped with one type of dopant on top of a layer of crystal doped with another type of dopant). If two separate pieces of material were used, this would introduce a grain boundary between the semiconductors that would severely inhibit its utility by scattering the electrons and holes. p–n junctions are elementary "building blocks" of semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redox Potential
Redox potential (also known as oxidation / reduction potential, ''ORP'', ''pe'', ''E_'', or E_) is a measure of the tendency of a chemical species to acquire electrons from or lose electrons to an electrode and thereby be reduced or oxidised respectively. Redox potential is expressed in volts (V). Each species has its own intrinsic redox potential; for example, the more positive the reduction potential (reduction potential is more often used due to general formalism in electrochemistry), the greater the species' affinity for electrons and tendency to be reduced. Measurement and interpretation In aqueous solutions, redox potential is a measure of the tendency of the solution to either gain or lose electrons when it is subjected to change by introduction of a new species. A solution with a higher (more positive) reduction potential than the new species will have a tendency to gain electrons from the new species (i.e. to be reduced by oxidizing the new species) and a solution with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |