|
Phidippides (Marathon Runner)
Pheidippides ( grc-gre, Φειδιππίδης, , ; "Son of Pheídippos") or Philippides (Φιλιππίδης) is the central figure in the story that inspired a modern sporting event, the marathon race. Pheidippides is said to have run from Marathon to Athens to deliver news of the victory of the battle of Marathon. The first recorded account showing a courier running from Marathon to Athens to announce victory is from within Lucian's prose on the first use of the word "joy" as a greeting in ''A Slip of the Tongue in Greeting'' (2nd century AD). The traditional story relates that Pheidippides (530–490 BC), an Athenian herald, or ''hemerodrome'' (translated as "day-runner", "courier", "professional-running courier" or "day-long runner"), was sent to Sparta to request help when the Persians landed at Marathon, Greece. He ran about in two days, and then ran back. He then ran the to the battlefield near Marathon and back to Athens to announce the Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
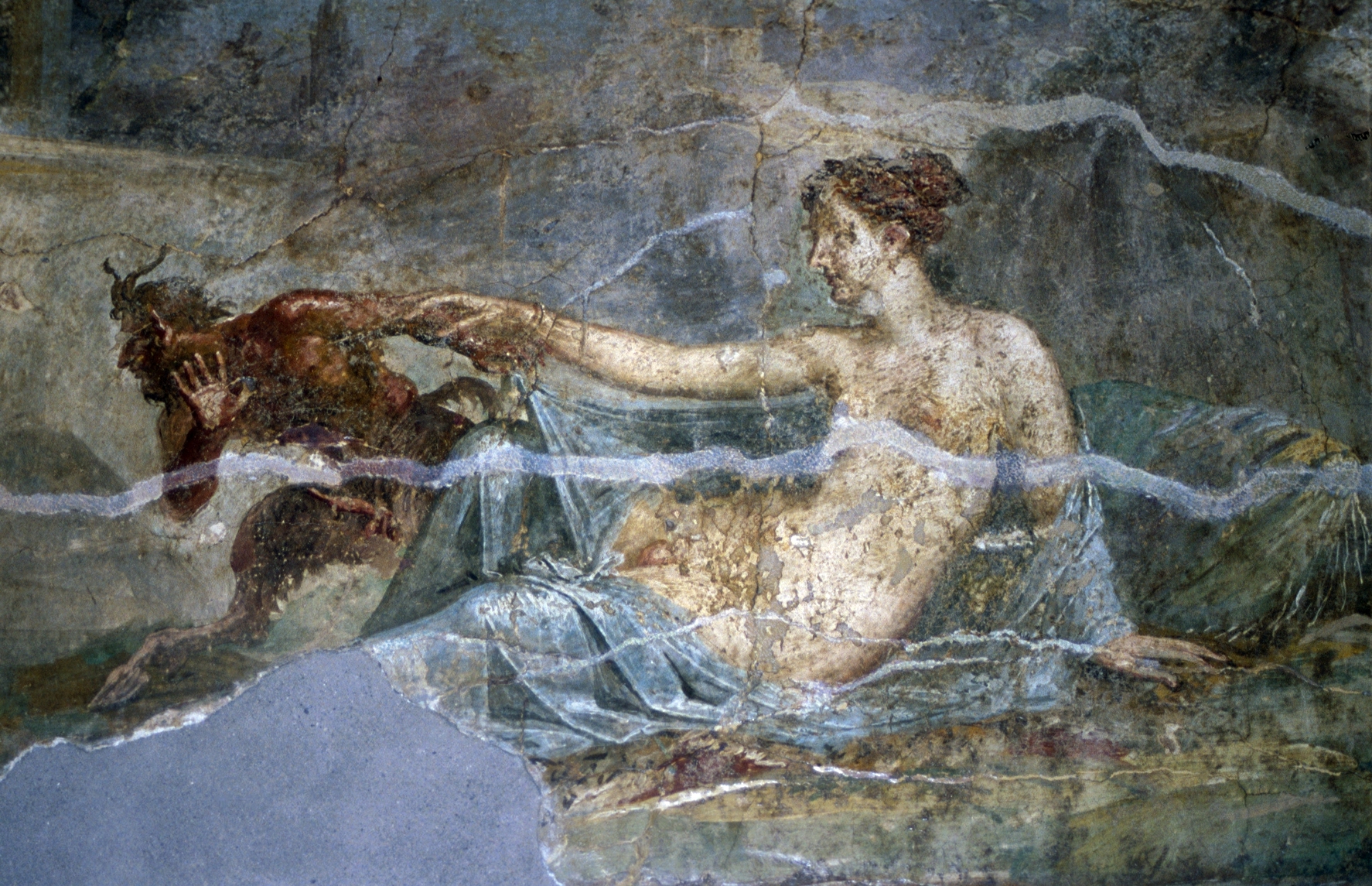
Pan (god)
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Pan (; grc, wikt:Πάν, Πάν, Pán) is the god of the wild, shepherds and flocks, Pastoral#Pastoral music, rustic music and impromptus, and companion of the nymphs. He has the hindquarters, legs, and horns of a goat, in the same manner as a faun or satyr. With his homeland in rustic Arcadia (ancient region), Arcadia, he is also recognized as the god of fields, groves, wooded glens, and often affiliated with sex; because of this, Pan is connected to fertility and the season of spring. In Religion in ancient Rome, Roman religion and myth, Pan's counterpart was Faunus, a nature god who was the father of Bona Dea, sometimes identified as Fauna (goddess), Fauna; he was also closely associated with Silvanus (mythology), Sylvanus, due to their similar relationships with woodlands. In the 18th and 19th centuries, Pan became a significant figure in Romanticism, the Romantic movement of western Europe and also in the 20th-centu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; grc-gre, Πλούταρχος, ''Ploútarchos''; ; – after AD 119) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Life Early life Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His name is derived from Pluto (πλοῦτον), an epithet of Hades, and Archos (ἀρχός) meaning "Master", the whole name meaning something like "Whose master is Pluto". His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panic
Panic is a sudden sensation of fear, which is so strong as to dominate or prevent reason and logical thinking, replacing it with overwhelming feelings of anxiety and frantic agitation consistent with an animalistic fight-or-flight reaction. Panic may occur singularly in individuals or manifest suddenly in large groups as mass panic (closely related to herd behavior). Etymology The word "panic" derives from antiquity and is a tribute to the ancient god Pan. One of the many gods in the mythology of ancient Greece, Pan was the god of shepherds and of woods and pastures. The Greeks believed that he often wandered peacefully through the woods, playing a pipe, but when accidentally awakened from his noontime nap he could give a great shout that would cause flocks to stampede. From this aspect of Pan's nature Greek authors derived the word ''panikos'', “sudden fear,” the ultimate source of the English word: "panic". The Greek term indicates the feeling of total fear that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soldat Marathon Cortot Louvre LP243
Soldat , plural Soldats Soldaten Soldater , may refer to: * Soldat (horse) * ''Soldat'' (rank), lowest rank of enlisted men in the land-based armed forces of Germany, Austria, and Switzerland * Soldat (Romania), lowest rank of armed forces of Romania * "Soldat" (song), by Aya Nakamura * ''Soldat'' (video game) * Soldat Island, Australian Antarctic Territory * Soldat Jahman (born 1979), French hip hop performer * Soldat Ustinov (born 1960), ring name of American professional wrestler * ''Soldaten'' (Gurlitt), opera by Manfred Gurlitt 1930 * '' Die Soldaten'', opera by Zimmermann 1965 * Ihor Soldat (born 1991), Ukrainian football defender * Marie Soldat-Roeger (1863–1955), Austrian violinist * , novel by the Austrian Nazi Party author :de:Mirko Jelusich 1939 * Die Soldaten (play), ( de) play by Jakob Michael Reinhold Lenz 1776 See also * Soldier (other) A soldier is a member of an armed force (usually army or land force). Soldier may also refer to: Geog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peisistratos (Athens)
Pisistratus or Peisistratus ( grc-gre, Πεισίστρατος ; 600 – 527 BC) was a politician in ancient Athens, ruling as tyrant in the late 560s, the early 550s and from 546 BC until his death. His unification of Attica, the triangular peninsula of Greece containing Athens, along with economic and cultural improvements laid the groundwork for the later preeminence of Athens in ancient Greece. His legacy lies primarily in his institution of the Panathenaic Games, historically assigned the date of 566 BC, and the consequent first attempt at producing a definitive version of the Homeric epics. Peisistratos' championing of the lower class of Athens is an early example of populism. While in power, he did not hesitate to confront the aristocracy and greatly reduce their privileges, confiscating their lands and giving them to the poor. Peisistratos funded many religious and artistic programs, in order to improve the economy and spread the wealth more equally among the Athenian p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippias (tyrant)
Hippias ( grc-gre, Ἱππίας; c. 570 BC – 490 BC) was the last tyrant of Athens, ruling from 527 to 510 BC. He was one of a group of tyrants known as the Peisistratids, which was a group of three tyrants in Ancient Greece. Pisistratus first, and then his son, Hippias, followed after him by Hippias' illegitimate son, Hegesistratos. He was deposed when Cleomenes I of Sparta successfully invaded Athens and forced him to flee to Persia. Early life Hippias was born around 570 BC as the eldest son of Pisistratus, the first tyrant of Athens. When his father was forced to flee to Eretria after insulting Megakles by having intercourse with his daughter in an indecent way, Peisistratos held counsel with his sons. Hippias suggested that they should retake the tyranny, which his father agreed to. Preparations began for which Athens fell to Peisistratos for the third time in 546 BC. Tyrant of Athens Hippias succeeded Peisistratos as tyrant of Athens in 528/7 BC when his father d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
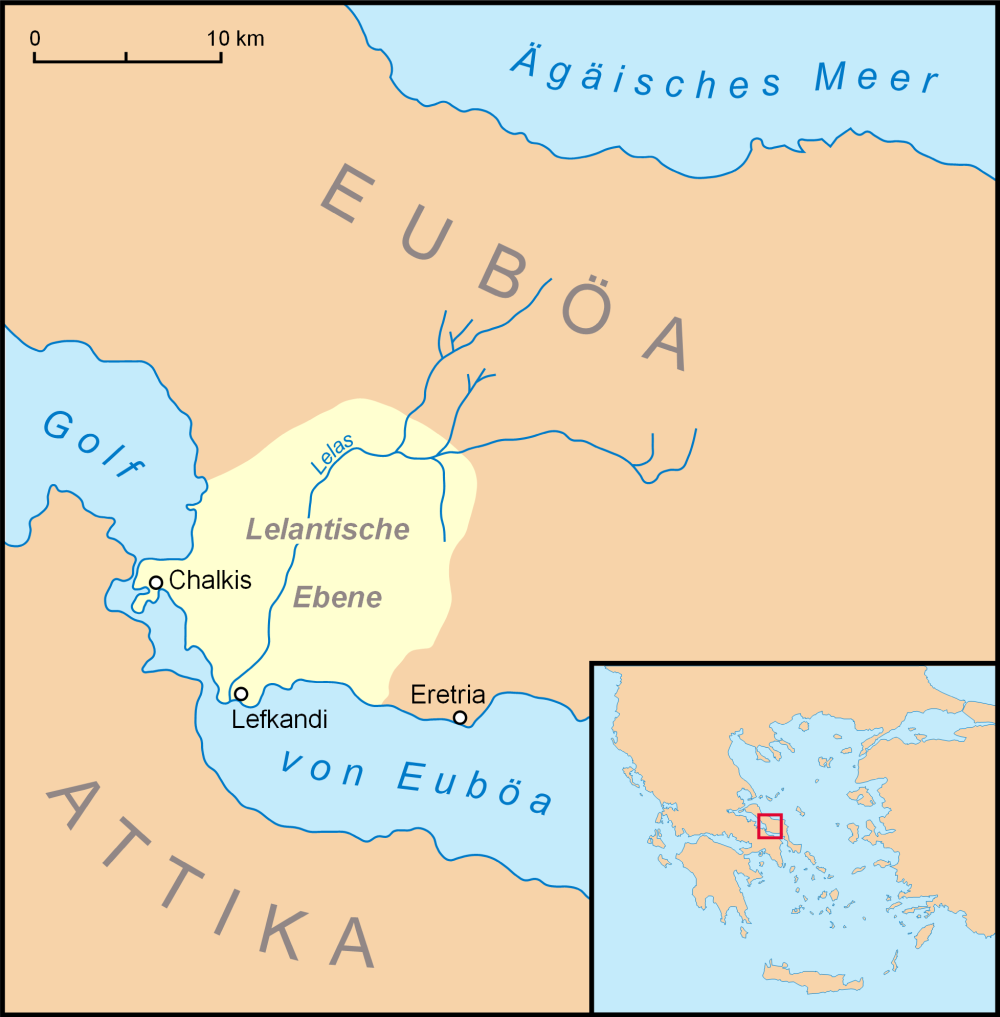
Eretria
Eretria (; el, Ερέτρια, , grc, Ἐρέτρια, , literally 'city of the rowers') is a town in Euboea, Greece, facing the coast of Attica across the narrow South Euboean Gulf. It was an important Greek polis in the 6th and 5th century BC, mentioned by many famous writers and actively involved in significant historical events. Excavations of the ancient city began in the 1890s and have been conducted since 1964 by the Greek Archaeological Service (11th Ephorate of Antiquities) and the Swiss School of Archaeology in Greece. History of Eretria Prehistory The first evidence for human activity in the area of Eretria are pottery shards and stone artifacts from the late Neolithic period (3500–3000 BC) found on the Acropolis as well as in the plain. No permanent structures have yet been found. It is therefore unclear whether a permanent settlement existed at that time. The first known settlement from the Early Helladic period (3000–2000 BC) was located on the plain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tegea
Tegea (; el, Τεγέα) was a settlement in ancient Arcadia, and it is also a former municipality in Arcadia, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the Tripoli municipality, of which it is a municipal unit with an area of 118.350 km2. It is near the modern villages of Alea and Episkopi. The legendary founder of Tegea was Tegeates, a son of Lycaon. History Tegea ( grc, Τεγέα; grc-x-ionic, Τεγέη) was one of the most ancient and powerful towns of ancient Arcadia, situated in the southeast of the country. Its territory, called Tegeatis (Τεγεᾶτις), was bounded by Cynuria and Argolis on the east, from which it was separated by Mount Parthenium, by Laconia on the south, by the Arcadian district of Maenalia on the west, and by the territory of Mantineia on the north. The Tegeatae are said to have derived their name from Tegeates, a son of Lycaon, and to have dwelt originally in eight, afterwards nine, demoi or townships ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Parthenium
Mount Parthenion ( grc, τὸ Παρθένιον ὄρος) or Parthenius or Parthenium) ("Mount of the Virgin", modern el, Παρθένιο - ''Parthenio'') is a mountain on the border of Arcadia and Argolis, in the Peloponnese, Greece. Its elevation is 1,215 m. It is situated between the villages Achladokampos to the northeast and Partheni to the southwest. It is 16 km east of Tripoli. In antiquity, it divided the little plain of Hysiae from that of Tegea. Mount Parthenion is the mountain where the hero Telephus was exposed. Below its slopes lay Tegea. Pan appeared to Philippides on Mt. Parthenion above Tegea, before the battle of Marathon in 490 BCE. The god called out his name and ordered Philippides ask the Athenians why they paid no honors to him, even though he was well-intentioned toward them, had been helpful to them many times in the past and would be so again in the future. As a result, the Athenians established an altar to Pan at the foot of the Parthenon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athens (Greece)
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates and is the capital of the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, with its recorded history spanning over 3,400 years and its earliest human presence beginning somewhere between the 11th and 7th millennia BC. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state. It was a centre for the arts, learning and philosophy, and the home of Plato's Academy and Aristotle's Lyceum. It is widely referred to as the cradle of Western civilization and the birthplace of democracy, largely because of its cultural and political influence on the European continent—particularly Ancient Rome. In modern times, Athens is a large cosmopolitan metropolis and central to economic, financial, industrial, maritime, political and cultural life in Greece. In 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(14785143685).jpg)