|
Peuci
The Bastarnae (Latin variants: ''Bastarni'', or ''Basternae''; grc, Βαστάρναι or Βαστέρναι) and Peucini ( grc, Πευκῖνοι) were two ancient peoples who between 200 BC and 300 AD inhabited areas north of the Roman frontier on the Lower Danube. The Bastarnae lived in the region between the Carpathian Mountains and the river Dnieper, to the north and east of ancient Dacia. The Peucini occupied the region north of the Danube Delta. The earliest Graeco-Roman historians to refer to the Bastarnae imply that they spoke Celtic languages. In contrast, later historical sources imply that they spoke Germanic languages, and could be considered Germanic peoples. Like other peoples who lived in the same geographical region, Graeco-Roman writers also referred to the Bastarnae as a "Scythian" people, but this was probably a reference to their general way of life, rather than a linguistic category. Although largely sedentary, some elements may have adopted a semi-nomadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe. In his book '' Getica'' (c. 551), the historian Jordanes writes that the Goths originated in southern Scandinavia, but the accuracy of this account is unclear. A people called the ''Gutones''possibly early Gothsare documented living near the lower Vistula River in the 1st century, where they are associated with the archaeological Wielbark culture. From the 2nd century, the Wielbark culture expanded southwards towards the Black Sea in what has been associated with Gothic migration, and by the late 3rd century it contributed to the formation of the Chernyakhov culture. By the 4th century at the latest, several Gothic groups were distinguishable, among whom the Thervingi and Greuthungi were the most powerful. During this time, Wulfila bega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and early medieval Germanic languages and are thus equated at least approximately with Germanic-speaking peoples, although different academic disciplines have their own definitions of what makes someone or something "Germanic". The Romans named the area belonging to North-Central Europe in which Germanic peoples lived ''Germania'', stretching East to West between the Vistula and Rhine rivers and north to south from Southern Scandinavia to the upper Danube. In discussions of the Roman period, the Germanic peoples are sometimes referred to as ''Germani'' or ancient Germans, although many scholars consider the second term problematic since it suggests identity with present-day Germans. The very concept of "Germanic peoples" has become the subject of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
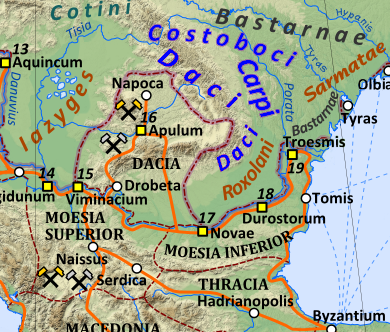
Dacians
The Dacians (; la, Daci ; grc-gre, Δάκοι, Δάοι, Δάκαι) were the ancient Indo-European inhabitants of the cultural region of Dacia, located in the area near the Carpathian Mountains and west of the Black Sea. They are often considered a subgroup of the Thracians. This area includes mainly the present-day countries of Romania and Moldova, as well as parts of Ukraine, Moravian Banovina, Eastern Serbia, Northern Bulgaria, Slovakia, Hungary and Southern Poland. The Dacians and the related Getae spoke the Dacian language, which has a debated relationship with the neighbouring Thracian language and may be a subgroup of it. Dacians were somewhat culturally influenced by the neighbouring Scythians and by the Celtic invasion of the Balkans, Celtic invaders of the 4th century BC. Name and etymology Name The Dacians were known as ''Geta'' (plural ''Getae'') in Ancient Greek writings, and as ''Dacus'' (plural ''Daci'') or ''Getae'' in Roman Empire, Roman documents, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Languages
The Iranian languages or Iranic languages are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European language family that are spoken natively by the Iranian peoples, predominantly in the Iranian Plateau. The Iranian languages are grouped in three stages: Old Iranian (until 400 BCE), Middle Iranian (400 BCE–900 CE) and New Iranian (since 900 CE). The two directly-attested Old Iranian languages are Old Persian (from the Achaemenid Empire) and Old Avestan (the language of the Avesta). Of the Middle Iranian languages, the better understood and recorded ones are Middle Persian (from the Sasanian Empire), Parthian (from the Parthian Empire), and Bactrian (from the Kushan and Hephthalite empires). , there were an estimated 150–200 million native speakers of the Iranian languages. '' Ethnologue'' estimates that there are 86 languages in the group, with the largest among them being Persian (Farsi, Dari, and Tajik dialects), Pashto, Kurdish, Luri, and Balochi. Terminol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roger Batty
Roger Batty is a British historian who is Professor at Keio University. Batty specializes in ancient history, particularly the relationship between Romans and "barbarians" beyond the Danube in classical antiquity. Biography Batty received his Lit. Hum from The Queen's College, Oxford in 1984 and his D.Phil in ancient history from University of Oxford in 1990. From 1990 to 1994, Battty was the speechwriter for Mostafa Kamal Tolba, Executive Director of the United Nations Environment Programme in Nairobi, Kenya. Batty has worked and studied in Geneva, Switzerland; Bucuresti, Romania; and Sofia, Bulgaria. His ''Rome and the Nomads: The Pontic-Danubian Realm in Antiquity'' (2007) was published by Oxford University Press and received to wide acclaim. Batty is Professor at the Faculty of Economics at Keio University. Selected works * ''Rome and the Nomads: The Pontic-Danubian Realm in Antiquity'', 2007 See also * Mark Shchukin Mark Borisovich Shchukin (October 10, 1937 - July 14, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Persian
Old Persian is one of the two directly attested Old Iranian languages (the other being Avestan language, Avestan) and is the ancestor of Middle Persian (the language of Sasanian Empire). Like other Old Iranian languages, it was known to its native speakers as (Iranian).''cf.'' , p. 2. Old Persian appears primarily in the inscriptions, clay tablets and seal (device), seals of the Achaemenid dynasty, Achaemenid era (c. 600 BCE to 300 BCE). Examples of Old Persian have been found in what is now Iran, Romania (Gherla), Armenia, Bahrain, Iraq, Turkey and Egypt, with the most important attestation by far being the contents of the Behistun Inscription (dated to 525 BCE). Recent research (2007) into the vast Persepolis Fortification Archive at the Oriental Institute at the University of Chicago unearthed Old Persian tablets, which suggest Old Persian was a written language in use for practical recording and not only for royal display. Origin and overview As a written language, Old ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scriptural language of Zoroastrianism, and the Avesta likewise serves as their namesake. Both are early Eastern Iranian languages within the Indo-Iranian language branch of the Indo-European language family. Its immediate ancestor was the Proto-Iranian language, a sister language to the Proto-Indo-Aryan language, with both having developed from the earlier Proto-Indo-Iranian language; as such, Old Avestan is quite close in both grammar and lexicon to Vedic Sanskrit, the oldest preserved Indo-Aryan language. The Avestan text corpus was composed in the ancient Iranian satrapies of Arachosia, Aria, Bactria, and Margiana, corresponding to the entirety of present-day Afghanistan as well as parts of Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, and Uzbekistan. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetic
Ossetian (, , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete (), is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Greater Caucasus. It is the native language of the Ossetian people, and is one of the few Iranian languages spoken in Europe; it is a relative and possibly a descendant of the extinct Scythian, Sarmatian, and Alanic languages. The northern half of the Ossetia region is part of Russia and is known as North Ossetia–Alania, while the southern half is part of the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Ossetian-speakers number about 614,350, with 451,000 recorded in Russia per the 2010 Russian census. History and classification Ossetian is the spoken and literary language of the Ossetians, an Iranian ethnic group living in the central part of the Caucasus and constituting the basic population of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dacia 125
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It thus roughly corresponds to the present-day countries of Romania, as well as parts of Moldova, Bulgaria, Serbia, Hungary, Slovakia, and Ukraine. A Dacian Kingdom of variable size existed between 82 BC until the Roman conquest in AD 106, reaching its height under King Burebista. As a result of the two wars with Emperor Trajan, the population was dispersed and the central city, Sarmizegetusa Regia, was destroyed by the Romans, but was rebuilt by the latter to serve as the capital of the Roman province of Dacia. The Free Dacians, living the territory of modern-day Northern Romania disappeared with the start of the Migration Period. Nomenclature The Dacians are first mentioned in the writings of the Ancient Greeks, in Herodotus (''Histories' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basterna
A basterna was a kind of vehicle, or litter, in which Ancient Roman women were carried. It appears to have resembled the lectica; and the only difference apparently was, that the lectica was carried on the shoulders of slaves, and the basterna by two mules, according to Isaac Casaubon. Several etymologies of the word have been proposed. Salmasius proposes it to be derived from the Greek (Salm. ''ad Lamprid. Heliog.'' 21). Cassius Dio links it to the people known as the Bastarnae, living in what is now southern Ukraine.Dio LI.24.4. A description of a basterna is given by a poet in the ''Anth. Lat.'' iii. 183. Others call it a kind of chariot, and say it was drawn by oxen to go more gently. Gregory de Tours gives an instance of it being carried by wild bulls. The interior was called ''cavea'', 'cage'; and it had soft cushions or beds. The mode of basterna's passed from Italy into Gaul, and then into other countries. Modern coach or stagecoach A stagecoach is a four-wheeled pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonnus
Nonnus of Panopolis ( grc-gre, Νόννος ὁ Πανοπολίτης, ''Nónnos ho Panopolítēs'', 5th century CE) was the most notable Greek epic poet of the Imperial Roman era. He was a native of Panopolis (Akhmim) in the Egyptian Thebaid and probably lived in the 5th century CE. He is known as the composer of the ''Dionysiaca'', an epic tale of the god Dionysus, and of the ''Metabole'', a paraphrase of the ''Gospel of John''. The epic Dionysiaca describes the life of Dionysus, his expedition to India, and his triumphant return. It was written in Homeric Greek and in dactylic hexameter, and it consists of 48 books at 20,426 lines. Life There is almost no evidence for the life of Nonnus. It is known that he was a native of Panopolis (Akhmim) in Upper Egypt from his naming in manuscripts and the reference in epigram 9.198 of the ''Palatine Anthology''. Scholars have generally dated him from the end of the 4th to the central years of the 5th century CE. He must have lived af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmas Of Maiuma
Saint Cosmas of Maiuma, also called Cosmas Hagiopolites ("of the Holy City"), Cosmas of Jerusalem, Cosmas the Melodist, or Cosmas the Poet (d. 773 or 794), was a bishop and an important hymnographer in the East. He is venerated as a saint by the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Catholic Church. Life Saint Cosmas ( el, Κοσμάς) was born in Jerusalem, but he was orphaned at a young age. He was adopted by Sergius, the father of St. John of Damascus (ca.676 - 749), and became John's foster-brother. The teacher of the two boys was an elderly Calabrian monk, also named Cosmas (known as "Cosmas the Monk" to distinguish him), who had been freed from slavery to the Saracens by St. John's father. John and Cosmas went from Damascus to Jerusalem, where both became monks in the Lavra (monastery) of St. Sabbas the Sanctified near that city.''Byzantine Music and Liturgy'', E. Wellesz, ''The Cambridge Medieval History: The Byzantine Empire, Part II'', Vol. IV, ed. J.M. Hussey, D.M. Nicol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)






