|
Pertemuan Jodoh
''Pertemuan Jodoh'' (; en, A Meeting of Soulmates) is an Indonesian novel by Abdul Muis originally published in 1932. It tells the story of two students who are driven apart by their class differences, but eventually marry. Plot Ratna, a young student, inadvertently meets Suparta, a medical student, on a train. There, Suparta tries to find her a seat but fails because a Chinese-Indonesian couple are using the spare seats for their luggage. Upon arrival in Cimahi, Suparta escorts Ratna to her school. Pleased by Suparta's manners, Ratna and he agree to keep in contact via mail. A few months later, Suparta proposes to Ratna via post; Ratna accepts, and leaves for Sumedang to meet Suparta's '' bangsawan'' parents. However, Suparta's mother, Nyai Raden Tedja Ningrum, is unwilling to accept Ratna as her daughter-in-law because Ratna is not of ''bangsawan'' descent. Disappointed, Ratna decides to forget Suparta. Not long afterwards, her father's chalk business becomes bankrupt, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abdul Muis
Abdul Muis (also spelt Abdoel Moeis; 1886 – 17 July 1959), was an Indonesian writer, journalist and nationalist. He advocated for Indonesia's independence from the Netherlands. He was the first person to be named a national hero by President Sukarno. Biography Born in Sungai Puar, West Sumatra in 1886 to a leading member of the Minangkabau, Muis received a western education and studied medicine in Jakarta for three years before being forced to pull out due to ill health. Muis first found employment in the civil service, before switching to journalism and becoming involved in nationalist publications such as ''Kaoem Moeda'', a paper he co-founded in 1912. He became known for his inflammatory articles, which were highly critical of Dutch involvement in Indonesia. For example, essays published in ''De Express'', a Dutch-language newspaper, were highly critical of Dutch attitudes towards Indonesians. During the First World War he was active in the movement for greater autonomy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., Order of precedence, precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically Hereditary title, hereditary and Patrilinearity, patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakri Siregar
Bakri Siregar (14 December 1922 – 19 June 1994) was an Indonesian socialist literary critic and writer. Biography Siregar was born in Langsa, Aceh, Dutch East Indies, on 14 December 1922. He was active writing by the Japanese occupation in the early 1940s, as evidenced by one of his short stories, "Tanda Bahagia" ("Sign of Happiness"), being published in ''Asia Raja'' on 1 September 1944. After Indonesia's independence, Siregar went to the Soviet Union to further study socialism. He considered their system efficient and beneficial to the populace, which reaffirmed his ideology. He also praised Soviet writers who rejected cosmopolitanism and abstractionism. He published several dramas after returning to Indonesia, including the original ''Tugu Putih'' (''White Monument''; 1950), ''Dosa dan Hukuman'' (''Sin and Punishment'', based on ''Crime and Punishment'' by Fyodor Dostoyevsky), and ''Gadis Teratai'' (''Lotus Blossom Maiden'', based on a Korean folktale). By 1951 Sirega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta is the largest city in Southeast Asia and serves as the diplomatic capital of ASEAN. The city is the economic, cultural, and political centre of Indonesia. It possesses a province-level status and has a population of 10,609,681 as of mid 2021.Badan Pusat Statistik, Jakarta, 2022. Although Jakarta extends over only , and thus has the smallest area of any Indonesian province, its metropolitan area covers , which includes the satellite cities Bogor, Depok, Tangerang, South Tangerang, and Bekasi, and has an estimated population of 35 million , making it the largest urban area in Indonesia and the second-largest in the world (after Tokyo). Jakarta ranks first among the Indonesian provinces in human development index. Jakarta's busin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malay Language
Malay (; ms, Bahasa Melayu, links=no, Jawi alphabet, Jawi: , Rejang script, Rencong: ) is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language that is an official language of Brunei, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Singapore, and that is also spoken in East Timor and parts of the Philippines and Thailand. Altogether, it is spoken by 290 million people (around 260 million in Indonesia alone in its own literary standard named "Indonesian language, Indonesian") across Maritime Southeast Asia. As the or ("national language") of several states, Standard Malay has various official names. In Malaysia, it is designated as either ("Malaysian Malay") or also ("Malay language"). In Singapore and Brunei, it is called ("Malay language"). In Indonesia, an autonomous normative variety called ("Indonesian language") is designated the ("unifying language" or lingua franca). However, in areas of Central to Southern Sumatra, where vernacular varieties of Malay are indigenous, Indonesians refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betawi Language
Betawi, also known as Betawi Malay, Jakartan Malay, or Batavian Malay is the spoken language of the Betawi people in Jakarta, Indonesia. It is the native language of perhaps 5 million people; a precise number is difficult to determine due to the vague use of the name. Betawi Malay is a popular informal language in contemporary Indonesia, used as the base of Indonesian slang and commonly spoken in Jakarta TV soap operas. The name ''Betawi'' stems from Batavia, the official name of Jakarta during the era of the Dutch East Indies. Colloquial Jakarta Indonesian, a vernacular form of Indonesian that has spread from Jakarta into large areas of Java and replaced existing Malay dialects, has its roots in Betawi Malay. According to Uri Tadmor, there is no clear border distinguishing Colloquial Jakarta Indonesian from Betawi Malay. Background The origin of Betawi is of debate to linguists; many consider it to be a Malay dialect descended from Proto-Malayic, while others consider it to ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structuring society around relationships that were derived from the holding of land in exchange for service or labour. Although it is derived from the Latin word ''feodum'' or ''feudum'' (fief), which was used during the Medieval period, the term ''feudalism'' and the system which it describes were not conceived of as a formal political system by the people who lived during the Middle Ages. The classic definition, by François Louis Ganshof (1944), François Louis Ganshof (1944). ''Qu'est-ce que la féodalité''. Translated into English by Philip Grierson as ''Feudalism'', with a foreword by F. M. Stenton, 1st ed.: New York and London, 1952; 2nd ed: 1961; 3rd ed.: 1976. describes a set of reciprocal legal and military obligations which existed am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavilion
In architecture, ''pavilion'' has several meanings: * It may be a subsidiary building that is either positioned separately or as an attachment to a main building. Often it is associated with pleasure. In palaces and traditional mansions of Asia, there may be pavilions that are either freestanding or connected by covered walkways, as in the Forbidden City ( Chinese pavilions), Topkapi Palace in Istanbul, and in Mughal buildings like the Red Fort. * As part of a large palace, pavilions may be symmetrically placed building ''blocks'' that flank (appear to join) a main building block or the outer ends of wings extending from both sides of a central building block, the ''corps de logis''. Such configurations provide an emphatic visual termination to the composition of a large building, akin to bookends. The word is from French (Old French ) and it meant a small palace, from Latin (accusative of ). In Late Latin and Old French, it meant both ‘butterfly’ and ‘tent’, becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical School
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, MBChB, MBBCh, BMBS), Master of Medicine (MM, MMed), Doctor of Medicine (MD), or Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (DO). Many medical schools offer additional degrees, such as a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), master's degree (MSc) or other post-secondary education. Medical schools can also carry out medical research and operate teaching hospitals. Around the world, criteria, structure, teaching methodology, and nature of medical programs offered at medical schools vary considerably. Medical schools are often highly competitive, using standardized entrance examinations, as well as grade point averages and leadership roles, to narrow the selection criteria for candidates. In most countries, the study of medicine is completed as an undergraduate de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mistress (form Of Address)
Mistress is an old form of address for a woman. It implies "lady of the house", especially a woman who is head of a household with domestic workers. An example is Mistress Quickly in Shakespeare's ''The Merry Wives of Windsor''. The title did not necessarily distinguish between married and unmarried women. The titles Mrs., Miss and Ms. Ms. (American English) or Ms (British English; normally , but also , or when unstressed)''Oxford English Dictionary'' online, Ms, ''n.2''. Etymology: "An orthographic and phonetic blend of Mrs ''n.1'' and miss ''n.2'' Compare mizz ''n.'' The pr ... are abbreviations derived from Mistress. Mastress is an obsolete form. See also * Master (form of address) References Women's social titles {{society-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
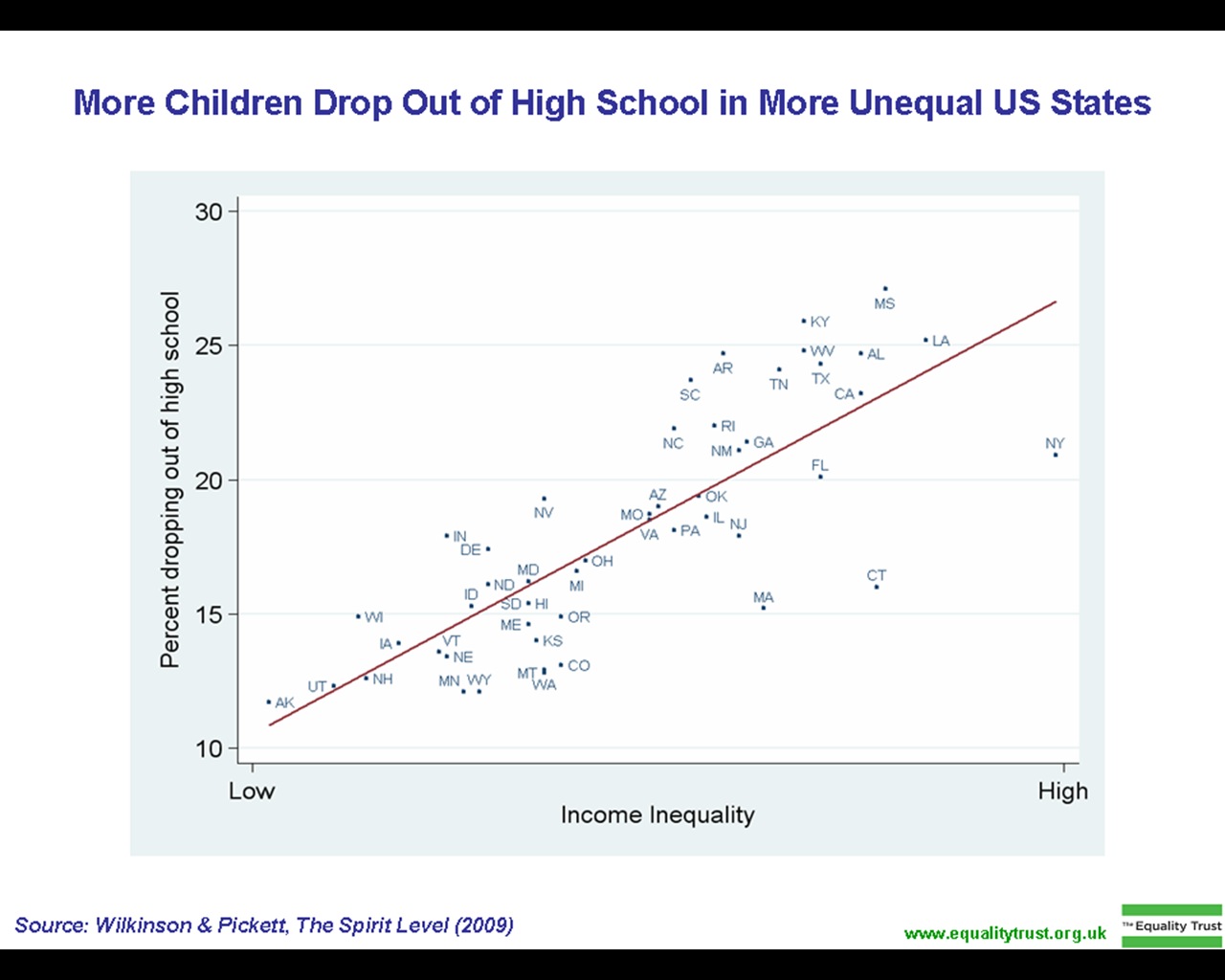
Dropping Out
Dropping out refers to leaving high school, college, university or another group for practical reasons, necessities, inability, apathy, or disillusionment with the system from which the individual in question leaves. Canada In Canada, most individuals graduate from grade 12 by the age of 18, according to Jason Gilmore who collects data on employment and education using the Labour Force Survey. The LFS is the official survey used to collect unemployment data in Canada (2010). Using this tool, assessing educational attainment and school attendance can calculate a dropout rate (Gilmore, 2010). It was found by the LFS that by 2009, one in twelve 20- to 24-year-old adults did not have a high school diploma (Gilmore, 2010). The study also found that men still have higher dropout rates than women, and that students outside of major cities and in the northern territories also have a higher risk of dropping out. Although since 1990 dropout rates have gone down from 20% to a low of 9% in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |