|
Persistent Current
In physics, persistent current refers to a perpetual electric current, not requiring an external power source. Such a current is impossible in normal electrical devices, since all commonly-used conductors have a non-zero resistance, and this resistance would rapidly dissipate any such current as heat. However, in superconductors and some mesoscopic devices, persistent currents are possible and observed due to quantum effects. In resistive materials, persistent currents can appear in microscopic samples due to size effects. Persistent currents are widely used in the form of superconducting magnets. In magnetized objects In electromagnetism, all magnetizations can be seen as microscopic persistent currents. By definition a magnetization \mathbf can be replaced by its corresponding microscopic form, which is an electric current density: : \mathbf = \nabla\times\mathbf . This current is a bound current, not having any charge accumulation associated with it since it is divergence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physics
Physics is the natural science that studies matter, its fundamental constituents, its motion and behavior through space and time, and the related entities of energy and force. "Physical science is that department of knowledge which relates to the order of nature, or, in other words, to the regular succession of events." Physics is one of the most fundamental scientific disciplines, with its main goal being to understand how the universe behaves. "Physics is one of the most fundamental of the sciences. Scientists of all disciplines use the ideas of physics, including chemists who study the structure of molecules, paleontologists who try to reconstruct how dinosaurs walked, and climatologists who study how human activities affect the atmosphere and oceans. Physics is also the foundation of all engineering and technology. No engineer could design a flat-screen TV, an interplanetary spacecraft, or even a better mousetrap without first understanding the basic laws of physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coherence Length
In physics, coherence length is the propagation distance over which a coherent wave (e.g. an electromagnetic wave) maintains a specified degree of coherence. Wave interference is strong when the paths taken by all of the interfering waves differ by less than the coherence length. A wave with a longer coherence length is closer to a perfect sinusoidal wave. Coherence length is important in holography and telecommunications engineering. This article focuses on the coherence of classical electromagnetic fields. In quantum mechanics, there is a mathematically analogous concept of the quantum coherence length of a wave function. Formulas In radio-band systems, the coherence length is approximated by :L = \frac \approx \frac ~, where \, c \, is the speed of light in a vacuum, \, n \, is the refractive index of the medium, and \, \mathrm f \, is the bandwidth of the source or \, \lambda \, is the signal wavelength and \, \Delta \lambda \, is the width of the range of wavelengths i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
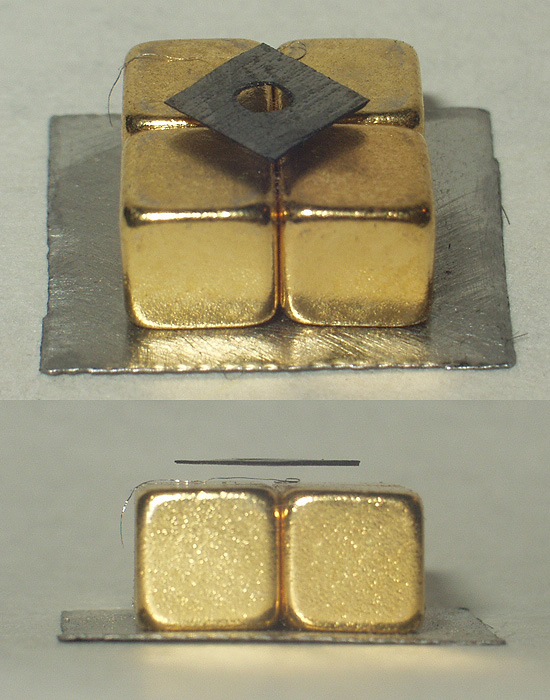
SQUID
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resonators
A resonator is a device or system that exhibits resonance or resonant behavior. That is, it naturally oscillates with greater amplitude at some frequencies, called resonant frequencies, than at other frequencies. The oscillations in a resonator can be either electromagnetic or mechanical (including acoustic). Resonators are used to either generate waves of specific frequencies or to select specific frequencies from a signal. Musical instruments use acoustic resonators that produce sound waves of specific tones. Another example is quartz crystals used in electronic devices such as radio transmitters and quartz watches to produce oscillations of very precise frequency. A cavity resonator is one in which waves exist in a hollow space inside the device. In electronics and radio, microwave cavities consisting of hollow metal boxes are used in microwave transmitters, receivers and test equipment to control frequency, in place of the tuned circuits which are used at lower frequ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
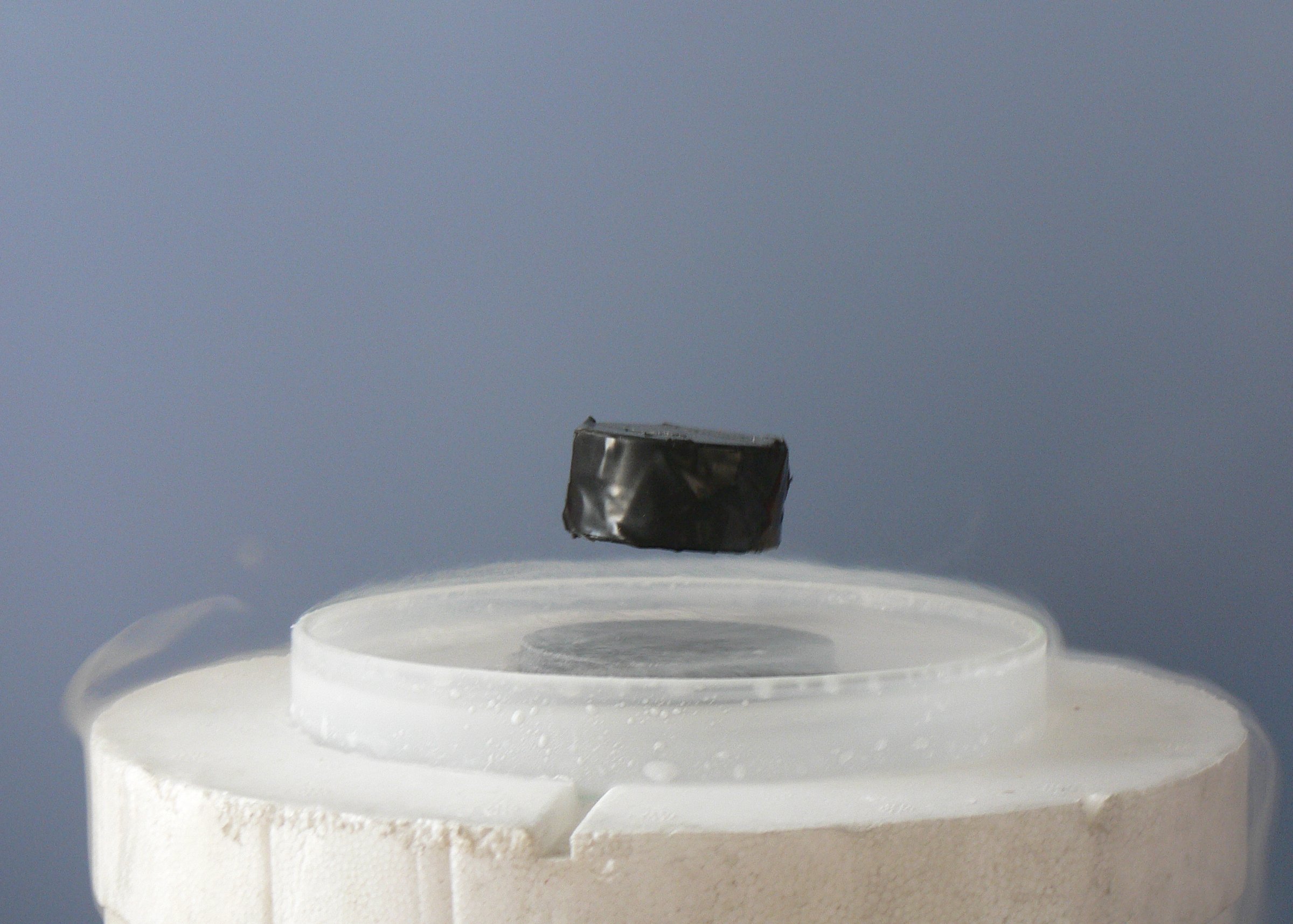
Superconducting
Superconductivity is a set of physical properties observed in certain materials where Electrical resistance and conductance, electrical resistance vanishes and magnetic field, magnetic flux fields are expelled from the material. Any material exhibiting these properties is a superconductor. Unlike an ordinary metallic electrical conductor, conductor, whose resistance decreases gradually as its temperature is lowered even down to near absolute zero, a superconductor has a characteristic Phase transition, critical temperature below which the resistance drops abruptly to zero. An electric current through a loop of superconducting wire can persist indefinitely with no power source. The superconductivity phenomenon was discovered in 1911 by Dutch physicist Heike Kamerlingh Onnes. Like ferromagnetism and atomic spectral lines, superconductivity is a phenomenon which can only be explained by quantum mechanics. It is characterized by the Meissner effect, the complete ejection of magne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable metallic form ( native metals). This led to very early human use in several regions, from circa 8000 BC. Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, circa 5000 BC; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, c. 4000 BC; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bell Laboratories
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925–1984), then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984–1996) and Bell Labs Innovations (1996–2007), is an American industrial research and scientific development company owned by multinational company Nokia. With headquarters located in Murray Hill, New Jersey, the company operates several laboratories in the United States and around the world. Researchers working at Bell Laboratories are credited with the development of radio astronomy, the transistor, the laser, the photovoltaic cell, the charge-coupled device (CCD), information theory, the Unix operating system, and the programming languages B, C, C++, S, SNOBOL, AWK, AMPL, and others. Nine Nobel Prizes have been awarded for work completed at Bell Laboratories. Bell Labs had its origin in the complex corporate organization of the Bell System telephone conglomerate. In the late 19th century, the laboratory began as the Western Electric Engineering Department, l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pauli Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby some materials are weakly attracted by an externally applied magnetic field, and form internal, Magnetization, induced magnetic fields in the direction of the applied magnetic field. In contrast with this behavior, diamagnetism, diamagnetic materials are repelled by magnetic fields and form induced magnetic fields in the direction opposite to that of the applied magnetic field. Paramagnetic materials include most chemical elements and some Chemical compound, compounds; they have a relative magnetic permeability slightly greater than 1 (i.e., a small positive magnetic susceptibility) and hence are attracted to magnetic fields. The magnetic moment induced by the applied field is linear in the field strength and rather weak. It typically requires a sensitive analytical balance to detect the effect and modern measurements on paramagnetic materials are often conducted with a SQUID magnetometer. Paramagnetism is due to the presence of unpaire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landau Diamagnetism
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it repels a magnetic field entirely from its interior. Diamagnetism was first discovered when Anton Brugmans observed in 1778 that bismuth was re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamagnetism
Diamagnetic materials are repelled by a magnetic field; an applied magnetic field creates an induced magnetic field in them in the opposite direction, causing a repulsive force. In contrast, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic materials are attracted by a magnetic field. Diamagnetism is a quantum mechanical effect that occurs in all materials; when it is the only contribution to the magnetism, the material is called diamagnetic. In paramagnetic and ferromagnetic substances, the weak diamagnetic force is overcome by the attractive force of magnetic dipoles in the material. The magnetic permeability of diamagnetic materials is less than the permeability of vacuum, ''μ''0. In most materials, diamagnetism is a weak effect which can be detected only by sensitive laboratory instruments, but a superconductor acts as a strong diamagnet because it repels a magnetic field entirely from its interior. Diamagnetism was first discovered when Anton Brugmans observed in 1778 that bismuth was repel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ammeter
An ammeter (abbreviation of ''Ampere meter'') is an instrument used to measure the current in a circuit. Electric currents are measured in amperes (A), hence the name. For direct measurement, the ammeter is connected in series with the circuit in which the current is to be measured. An ammeter usually has low resistance so that it does not cause a significant voltage drop in the circuit being measured. Instruments used to measure smaller currents, in the milliampere or microampere range, are designated as ''milliammeters'' or ''microammeters''. Early ammeters were laboratory instruments that relied on the Earth's magnetic field for operation. By the late 19th century, improved instruments were designed which could be mounted in any position and allowed accurate measurements in electric power systems. It is generally represented by letter 'A' in a circuit. History The relation between electric current, magnetic fields and physical forces was first noted by Hans Christian Ør ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)