|
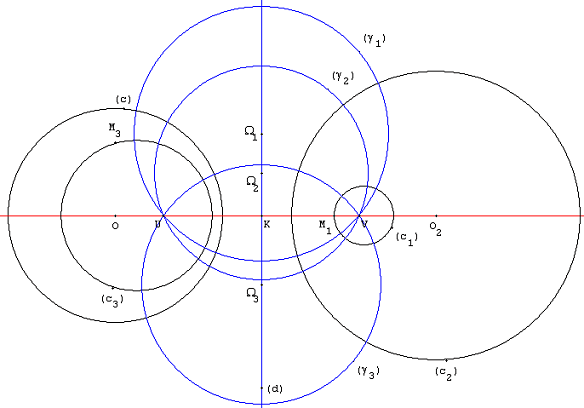
Pentagram Map
In mathematics, the pentagram map is a discrete dynamical system on the moduli space of polygons in the projective plane. The pentagram map takes a given polygon, finds the intersections of the shortest diagonals of the polygon, and constructs a new polygon from these intersections. Richard Schwartz (mathematician), Richard Schwartz introduced the pentagram map for a general polygon in a 1992 paper though it seems that the special case, in which the map is defined for pentagons only, goes back to an 1871 paper of Alfred Clebsch and a 1945 paper of Theodore Motzkin. The pentagram map is similar in spirit to the constructions underlying Desargues' theorem and Poncelet's porism. It echoes the rationale and construction underlying a conjecture of Branko Grünbaum concerning the diagonals of a polygon. Definition of the map Basic construction Suppose that the vertex (geometry), vertices of the polygon P are given by P_1,P_3,P_5,\ldots The image of ''P'' under the pentagram map is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex (in plural form: vertices or vertexes) is a point (geometry), point where two or more curves, line (geometry), lines, or edge (geometry), edges meet. As a consequence of this definition, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the corners of polygons and polyhedron, polyhedra are vertices. Definition Of an angle The ''vertex'' of an angle is the point where two Line (mathematics)#Ray, rays begin or meet, where two line segments join or meet, where two lines intersect (cross), or any appropriate combination of rays, segments, and lines that result in two straight "sides" meeting at one place. :(3 vols.): (vol. 1), (vol. 2), (vol. 3). Of a polytope A vertex is a corner point of a polygon, polyhedron, or other higher-dimensional polytope, formed by the intersection (Euclidean geometry), intersection of Edge (geometry), edges, face (geometry), faces or facets of the object. In a polygon, a vertex is called "convex set, convex" if the internal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monodromy
In mathematics, monodromy is the study of how objects from mathematical analysis, algebraic topology, algebraic geometry and differential geometry behave as they "run round" a singularity. As the name implies, the fundamental meaning of ''monodromy'' comes from "running round singly". It is closely associated with covering maps and their degeneration into ramification; the aspect giving rise to monodromy phenomena is that certain functions we may wish to define fail to be ''single-valued'' as we "run round" a path encircling a singularity. The failure of monodromy can be measured by defining a monodromy group: a group of transformations acting on the data that encodes what happens as we "run round" in one dimension. Lack of monodromy is sometimes called ''polydromy''. Definition Let be a connected and locally connected based topological space with base point , and let p: \tilde \to X be a covering with fiber F = p^(x). For a loop based at , denote a lift under the covering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Transformation
In projective geometry, a homography is an isomorphism of projective spaces, induced by an isomorphism of the vector spaces from which the projective spaces derive. It is a bijection that maps lines to lines, and thus a collineation. In general, some collineations are not homographies, but the fundamental theorem of projective geometry asserts that is not so in the case of real projective spaces of dimension at least two. Synonyms include projectivity, projective transformation, and projective collineation. Historically, homographies (and projective spaces) have been introduced to study perspective and projections in Euclidean geometry, and the term ''homography'', which, etymologically, roughly means "similar drawing", dates from this time. At the end of the 19th century, formal definitions of projective spaces were introduced, which differed from extending Euclidean or affine spaces by adding points at infinity. The term "projective transformation" originated in these abstract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalence Classes
In mathematics, when the elements of some set S have a notion of equivalence (formalized as an equivalence relation), then one may naturally split the set S into equivalence classes. These equivalence classes are constructed so that elements a and b belong to the same equivalence class if, and only if, they are equivalent. Formally, given a set S and an equivalence relation \,\sim\, on S, the of an element a in S, denoted by is the set \ of elements which are equivalent to a. It may be proven, from the defining properties of equivalence relations, that the equivalence classes form a partition of S. This partition—the set of equivalence classes—is sometimes called the quotient set or the quotient space of S by \,\sim\,, and is denoted by S / \sim. When the set S has some structure (such as a group operation or a topology) and the equivalence relation \,\sim\, is compatible with this structure, the quotient set often inherits a similar structure from its parent set. Exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map (mathematics)
In mathematics, a map or mapping is a function in its general sense. These terms may have originated as from the process of making a geographical map: ''mapping'' the Earth surface to a sheet of paper. The term ''map'' may be used to distinguish some special types of functions, such as homomorphisms. For example, a linear map is a homomorphism of vector spaces, while the term linear function may have this meaning or it may mean a linear polynomial. In category theory, a map may refer to a morphism. The term ''transformation'' can be used interchangeably, but ''transformation'' often refers to a function from a set to itself. There are also a few less common uses in logic and graph theory. Maps as functions In many branches of mathematics, the term ''map'' is used to mean a function, sometimes with a specific property of particular importance to that branch. For instance, a "map" is a " continuous function" in topology, a "linear transformation" in linear algebra, etc. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projective Transformations
In projective geometry, a homography is an isomorphism of projective spaces, induced by an isomorphism of the vector spaces from which the projective spaces derive. It is a bijection that maps lines to lines, and thus a collineation. In general, some collineations are not homographies, but the fundamental theorem of projective geometry asserts that is not so in the case of real projective spaces of dimension at least two. Synonyms include projectivity, projective transformation, and projective collineation. Historically, homographies (and projective spaces) have been introduced to study perspective and projections in Euclidean geometry, and the term ''homography'', which, etymologically, roughly means "similar drawing", dates from this time. At the end of the 19th century, formal definitions of projective spaces were introduced, which differed from extending Euclidean or affine spaces by adding points at infinity. The term "projective transformation" originated in these abstract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commutative Property
In mathematics, a binary operation is commutative if changing the order of the operands does not change the result. It is a fundamental property of many binary operations, and many mathematical proofs depend on it. Most familiar as the name of the property that says something like or , the property can also be used in more advanced settings. The name is needed because there are operations, such as division and subtraction, that do not have it (for example, ); such operations are ''not'' commutative, and so are referred to as ''noncommutative operations''. The idea that simple operations, such as the multiplication and addition of numbers, are commutative was for many years implicitly assumed. Thus, this property was not named until the 19th century, when mathematics started to become formalized. A similar property exists for binary relations; a binary relation is said to be symmetric if the relation applies regardless of the order of its operands; for example, equality is symme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Position
In algebraic geometry and computational geometry, general position is a notion of genericity for a set of points, or other geometric objects. It means the ''general case'' situation, as opposed to some more special or coincidental cases that are possible, which is referred to as special position. Its precise meaning differs in different settings. For example, generically, two lines in the plane intersect in a single point (they are not parallel or coincident). One also says "two generic lines intersect in a point", which is formalized by the notion of a generic point. Similarly, three generic points in the plane are not collinear; if three points are collinear (even stronger, if two coincide), this is a degenerate case. This notion is important in mathematics and its applications, because degenerate cases may require an exceptional treatment; for example, when stating general theorems or giving precise statements thereof, and when writing computer programs (see '' generic compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field (mathematics)
In mathematics, a field is a set on which addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are defined and behave as the corresponding operations on rational and real numbers do. A field is thus a fundamental algebraic structure which is widely used in algebra, number theory, and many other areas of mathematics. The best known fields are the field of rational numbers, the field of real numbers and the field of complex numbers. Many other fields, such as fields of rational functions, algebraic function fields, algebraic number fields, and ''p''-adic fields are commonly used and studied in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebraic geometry. Most cryptographic protocols rely on finite fields, i.e., fields with finitely many elements. The relation of two fields is expressed by the notion of a field extension. Galois theory, initiated by Évariste Galois in the 1830s, is devoted to understanding the symmetries of field extensions. Among other results, thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane (geometry)
In mathematics, a plane is a Euclidean (flat), two-dimensional surface that extends indefinitely. A plane is the two-dimensional analogue of a point (zero dimensions), a line (one dimension) and three-dimensional space. Planes can arise as subspaces of some higher-dimensional space, as with one of a room's walls, infinitely extended, or they may enjoy an independent existence in their own right, as in the setting of two-dimensional Euclidean geometry. Sometimes the word ''plane'' is used more generally to describe a two-dimensional surface, for example the hyperbolic plane and elliptic plane. When working exclusively in two-dimensional Euclidean space, the definite article is used, so ''the'' plane refers to the whole space. Many fundamental tasks in mathematics, geometry, trigonometry, graph theory, and graphing are performed in a two-dimensional space, often in the plane. Euclidean geometry Euclid set forth the first great landmark of mathematical thought, an axiomatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |