|
Pemberton's Sign
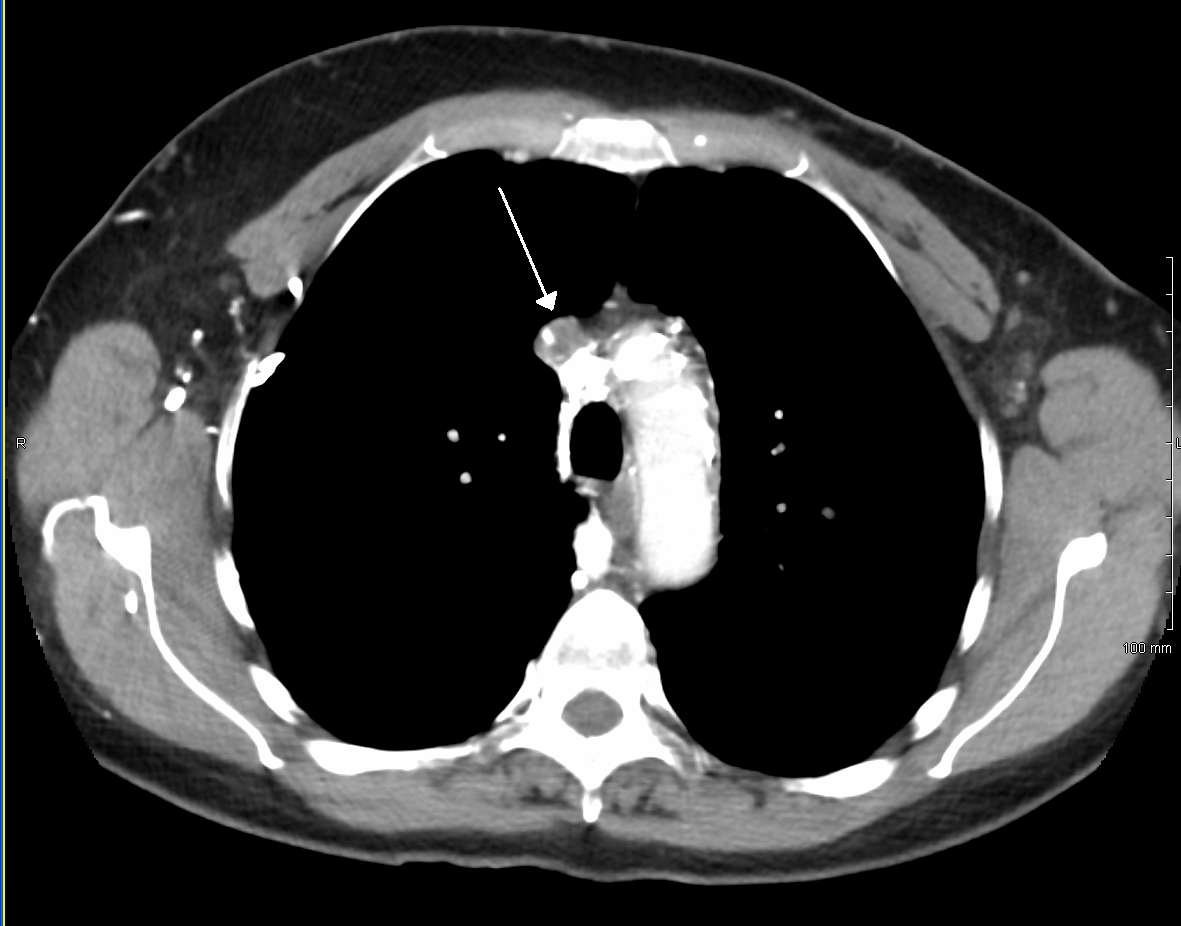
Pemberton's sign was named after Hugh Pemberton, who characterized it in 1946. The Pemberton maneuver is a physical examination tool used to demonstrate the presence of latent pressure in the thoracic inlet. The maneuver is achieved by having the patient elevate both arms (usually 180 degrees anterior flexion at the shoulder) until the forearms touch the sides of the face. A positive Pemberton's sign is marked by the presence of facial congestion and cyanosis, as well as respiratory distress after approximately one minute. Causes A positive Pemberton's sign is indicative of superior vena cava syndrome (SVC), commonly the result of a mass in the mediastinum The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagu .... Although the sign is most commonly described in patients with substernal go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugh Pemberton
{{hndis, Pemberton, Hugh ...
Hugh Pemberton may refer to: * Hugh Pemberton (physician), English physician *Hugh Pemberton (historian) * Hugh Pemberton (MP) for City of London (Parliament of England constituency) The City of London was a parliamentary constituency of the Parliament of England until 1707. Boundaries and history to 1707 This borough constituency consisted of the City of London, which was the historic core of the modern Greater London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Vena Cava Syndrome
Superior vena cava syndrome (SVCS), is a group of symptoms caused by obstruction of the superior vena cava ("SVC"), a short, wide vessel carrying circulating blood into the heart. The majority of cases are caused by malignant tumors within the mediastinum, most commonly lung cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, directly compressing or invading the SVC wall. Non-malignant causes are increasing in prevalence due to expanding use of intravascular devices (such as permanent central venous catheters and leads for pacemakers and defibrillators), which can result in thrombosis. Other non-malignant causes include benign mediastinal tumors, aortic aneurysm, infections, and fibrosing mediastinitis. Characteristic features are edema (swelling due to excess fluid) of the face and arms and development of swollen collateral veins on the front of the chest wall. Shortness of breath and coughing are quite common symptoms; difficulty swallowing is reported in 11% of cases, headache in 6% and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediastinum
The mediastinum (from ) is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity. Surrounded by loose connective tissue, it is an undelineated region that contains a group of structures within the thorax, namely the heart and its vessels, the esophagus, the trachea, the phrenic nerve, phrenic and cardiac nerves, the thoracic duct, the thymus and the lymph nodes of the central chest. Anatomy The mediastinum lies within the thorax and is enclosed on the right and left by pulmonary pleurae, pleurae. It is surrounded by the chest wall in front, the lungs to the sides and the Spine (anatomy), spine at the back. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind. It contains all the organs of the thorax except the lungs. It is continuous with the loose connective tissue of the neck. The mediastinum can be divided into an upper (or superior) and lower (or inferior) part: * The superior mediastinum starts at the superior thoracic aperture and ends at the #Thoracic plane, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castleman Disease
Castleman disease (CD) describes a group of rare lymphoproliferative disorders that involve enlarged lymph nodes, and a broad range of inflammatory symptoms and laboratory abnormalities. Whether Castleman disease should be considered an autoimmune disease, cancer, or infectious disease is currently unknown. Castleman disease includes at least three distinct subtypes: unicentric Castleman disease (UCD), human herpesvirus 8 associated multicentric Castleman disease (HHV-8-associated MCD), and idiopathic multicentric Castleman disease (iMCD). These are differentiated by the number and location of affected lymph nodes and the presence of human herpesvirus 8, a known causative agent in a portion of cases. Correctly classifying the Castleman disease subtype is important, as the three subtypes vary significantly in symptoms, clinical findings, disease mechanism, treatment approach, and prognosis. All forms involve overproduction of cytokines and other inflammatory proteins by the body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |