|
Pelee, Ontario
Pelee Island is an island in the Canadian province of Ontario. It is located in the western half of Lake Erie. At , Pelee Island is the largest island in Lake Erie and the southernmost populated point in Canada. An Ontario Historical Plaque was erected by the province to commemorate the development of Pelee Island's role in Ontario's heritage. Nearby Middle Island is the southernmost point of land in Canada. Due to its southerly location and the moderating effect of Lake Erie, it has a slightly milder climate than inland areas.Wake, Winifred Cairns (1997). ''A Nature Guide to Ontario'', p. 47. University of Toronto Press. . Its climate is one of the mildest in Canada, and the island has been used for vineyards and wine making since 1860, though local wine making died out in the early twentieth century and was restarted in the 1980s by the Pelee Island Winery. The island is an agricultural-based community, which grows about of soybeans, about of wheat, of grapes, and a few hec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Township Municipalities In Ontario
A township is a type of municipality in the Canadian province of Ontario. They can have either single-tier status or lower-tier status. Ontario has 200 townships that had a cumulative population of 990,396 and an average population of 4,952 in the 2011 Census. Ontario's largest and smallest townships are Centre Wellington and Cockburn Island with populations of 26,693 and 0 respectively. History Under the former ''Municipal Act, 1990'', a township was a type of local municipality. Under this former legislation, a locality with a population of 1,000 or more could have been incorporated as a township by Ontario's Municipal Board upon review of an application from 75 or more residents of the locality. It also provided that a township could include "a union of townships and a municipality composed of two or more townships". In the transition to the ''Municipal Act, 2001'', these requirements were abandoned and, as at December 31, 2002, every township ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subsistence Agriculture
Subsistence agriculture occurs when farmers grow food crops to meet the needs of themselves and their families on smallholdings. Subsistence agriculturalists target farm output for survival and for mostly local requirements, with little or no surplus. Planting decisions occur principally with an eye toward what the family will need during the coming year, and only secondarily toward market prices. Tony Waters, a professor of sociology, defines "subsistence peasants" as "people who grow what they eat, build their own houses, and live without regularly making purchases in the marketplace." Despite the self-sufficiency in subsistence farming, most subsistence farmers also participate in trade to some degree. Although their amount of trade as measured in cash is less than that of consumers in countries with modern complex markets, they use these markets mainly to obtain goods, not to generate income for food; these goods are typically not necessary for survival and may include sugar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada Day
Canada Day (french: Fête du Canada), formerly known as Dominion Day (french: Fête du Dominion), is the national day of Canada. A federal statutory holiday, it celebrates the anniversary of Canadian Confederation which occurred on July 1, 1867, with the passing of the ''British North America Act, 1867'' where the three separate colonies of the United Canadas, Nova Scotia, and New Brunswick were united into a single Dominion within the British Empire called Canada. Originally called Dominion Day (french: Le Jour de la Confédération), the holiday was renamed in 1982, the same year that the Canadian Constitution was patriated by the Canada Act 1982. Canada Day celebrations take place throughout the country, as well as in various locations around the world attended by Canadians living abroad. Commemoration Canada Day is often informally referred to as "Canada's birthday", particularly in the popular press. However, the term "birthday" can be seen as an oversimplification, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Unplugged Music Festival
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelee Stone & Sky Music & Art Performances
Pelee may refer to: * Île Pelée, an island off Cherbourg-en-Cotentin, France *Pelee, Ontario, an island in Lake Erie, Canada *Point Pelee National Park, a park in Ontario, Canada *Mount Pelée, a volcano in Martinique *Peleus In Greek mythology, Peleus (; Ancient Greek: Πηλεύς ''Pēleus'') was a hero, king of Phthia, husband of Thetis and the father of their son Achilles. This myth was already known to the hearers of Homer in the late 8th century BC. Biograp ..., who may be referred to as "Pélée" in French, father of Achilles See also * Pele (other) {{Disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Margaret Atwood
Margaret Eleanor Atwood (born November 18, 1939) is a Canadian poet, novelist, literary critic, essayist, teacher, environmental activist, and inventor. Since 1961, she has published 18 books of poetry, 18 novels, 11 books of non-fiction, nine collections of short fiction, eight children's books, and two graphic novels, and a number of small press editions of both poetry and fiction. Atwood has won numerous awards and honors for her writing, including two Booker Prizes, the Arthur C. Clarke Award, the Governor General's Award, the Franz Kafka Prize, Princess of Asturias Awards, and the National Book Critics and PEN Center USA Lifetime Achievement Awards. A number of her works have been adapted for film and television. Atwood's works encompass a variety of themes including gender and identity, religion and myth, the power of language, climate change, and "power politics". Many of her poems are inspired by myths and fairy tales which interested her from a very early age. Oates, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and culture. It is headquartered in Ottawa.Statistics Canada, 150 Tunney's Pasture Driveway Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0T6; Statistique Canada 150, promenade du pré Tunney Ottawa, Ontario K1A 0T6 The agency is led by the chief statistician of Canada, currently Anil Arora, who assumed the role on September 19, 2016. StatCan is responsible to Parliament through the Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry, currently François-Philippe Champagne. Statistics Canada acts as the national statistical agency for Canada, and Statistics Canada produces statistics for all the provinces as well as the federal government. In addition to conducting about 350 active surveys on virtually all aspects of Canadian life, the '' Statistics Act'' mandates that Statistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2021 Canadian Census
The 2021 Canadian census was a detailed enumeration of the Canadian population with a reference date of May 11, 2021. It follows the 2016 Canadian census, which recorded a population of 35,151,728. The overall response rate was 98%, which is slightly lower than the response rate for the 2016 census. It recorded a population of 36,991,981, a 5.2% increase from 2016. Planning Consultation on census program content was from September 11 to December 8, 2017. The census was conducted by Statistics Canada, and was contactless as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic in Canada. The agency had considered delaying the census until 2022. About 900 supervisors and 31,000 field enumerators were hired to conduct the door-to-door survey of individuals and households who had not completed the census questionnaire by late May or early June. Canvassing agents wore masks and maintained a physical distance to comply with COVID-19 safety regulations. Questionnaire In early May 2021, Statistics Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
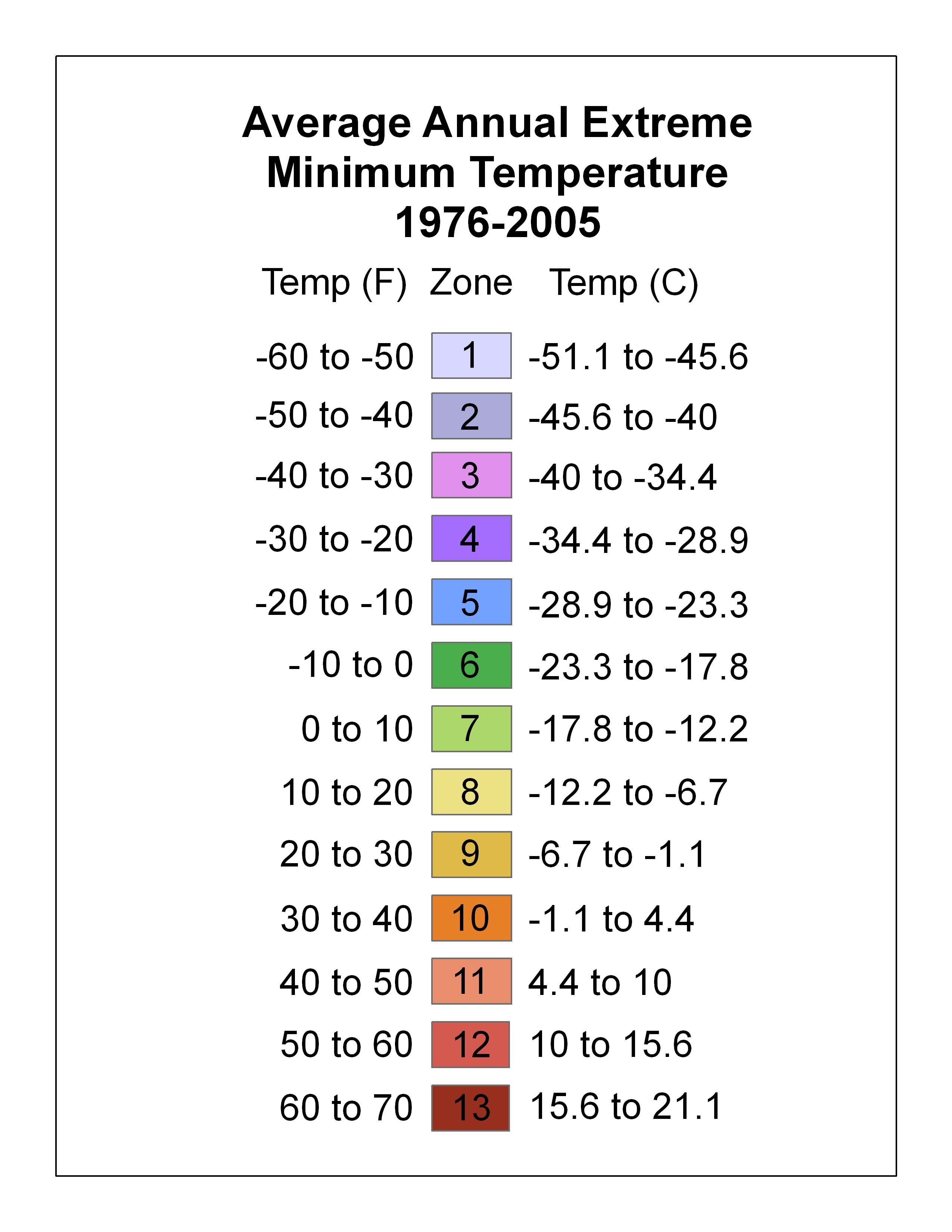
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. For example, a plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of 30 °F (−1.1 °C) to 40 °F (4.4 °C). Other hardiness rating schemes have been developed as well, such as the UK Royal Horticultural Society and US Sunset Western Garden Book systems. A heat zone (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notably in 1918 and 1936. Later, the climatologist Rudolf Geiger (1894–1981) introduced some changes to the classification system, which is thus sometimes called the Köppen–Geiger climate classification system. The Köppen climate classification divides climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on seasonal precipitation and temperature patterns. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freezing cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year but often do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate regarding temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Humid continental climates are generally found between latitudes 30° N and 60° N, within the central and northeastern portions of North America, Europe, and Asia. They are rare and isolat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carolinian Forest
The Carolinian forest refers to a life zone in eastern North America characterized primarily by the predominance of deciduous (broad-leaf) forest. The term "Carolinian", which is most commonly used in Canada, refers to the deciduous forests which span across much of the eastern United States from the Carolinas northward into southern Ontario, Canada. These deciduous forests in the United States and southern Ontario share many similar characteristics and species hence their association. Today the term is often used to refer to the Canadian portion (northern limit) of the deciduous forest region while the portion in the United States is often referred to as the "Eastern deciduous forest". Location and extent The Carolinian zone spans across much of the eastern United States, with extensive coverage in the Carolinas, the Virginias, Kentucky, Tennessee, Maryland, Delaware, Pennsylvania, parts of southern New York state, Connecticut, and Rhode Island, eastern Ohio, and small parts o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)