|
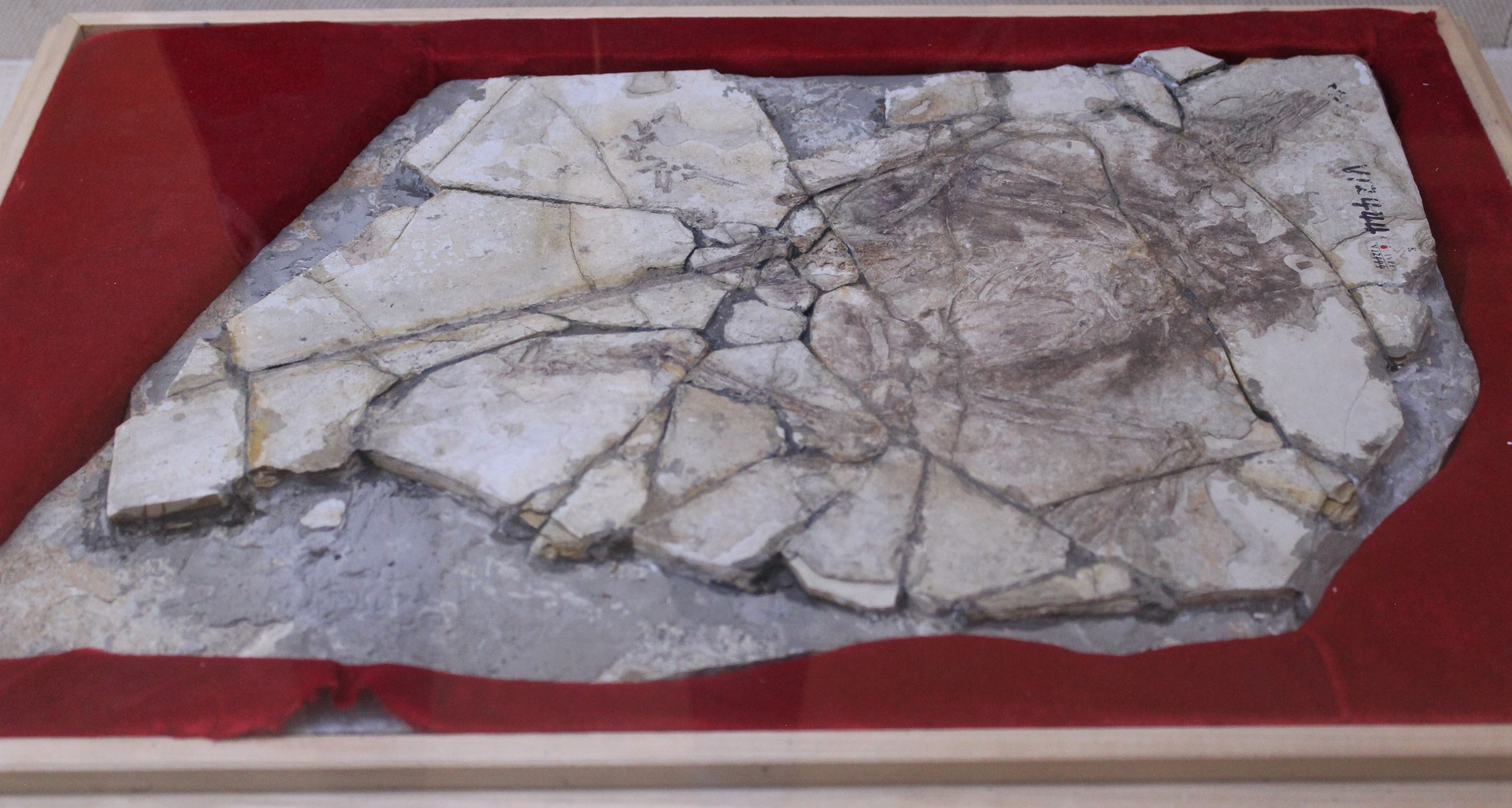
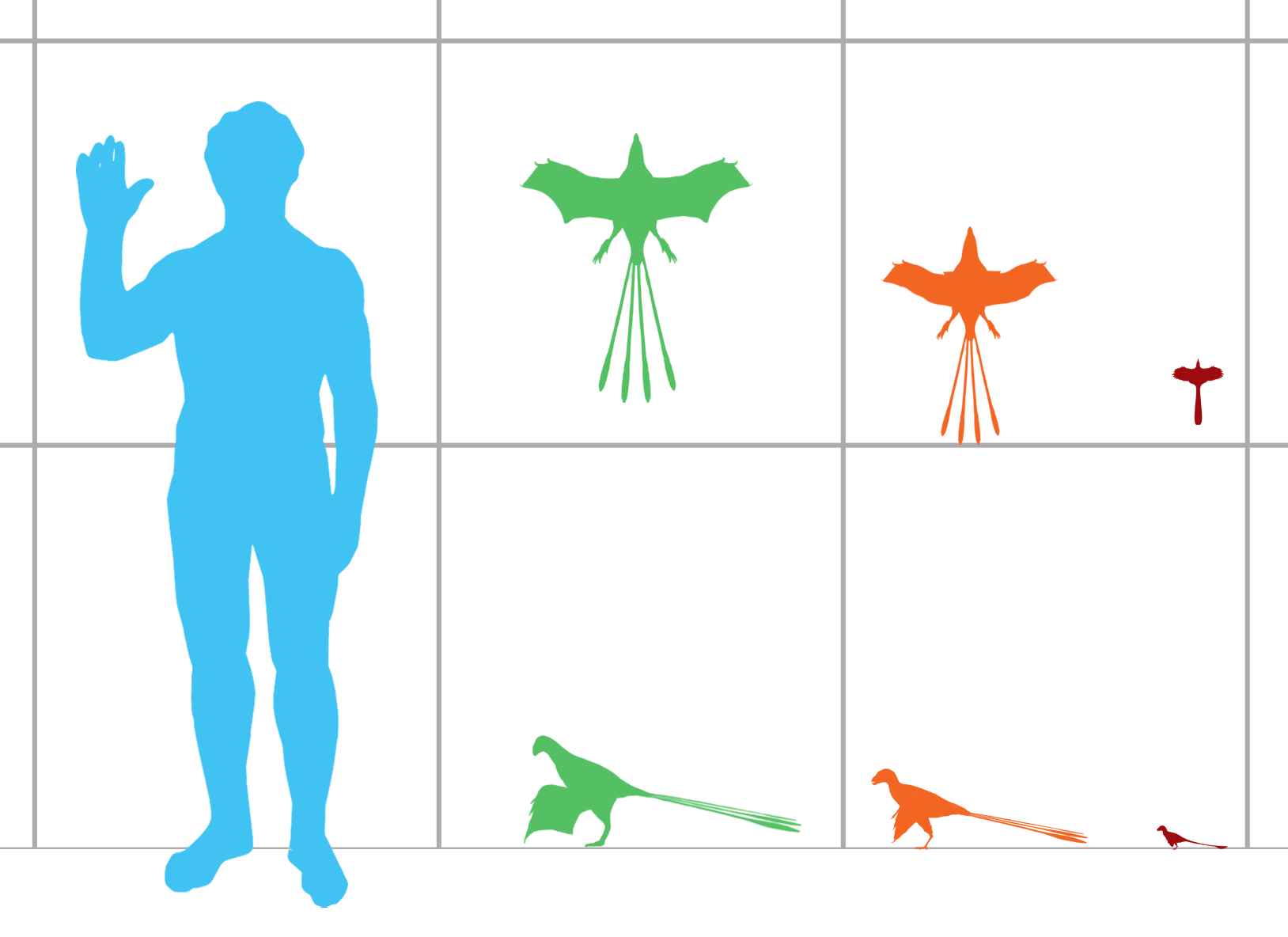
Pedopenna
''Pedopenna'' (meaning "foot feather") is a genus of small, feathered, maniraptoran dinosaur from the Daohugou Beds in China. It is possibly older than ''Archaeopteryx'', though the age of the Daohugou Beds where it was found is debated. A majority of studies suggest that beds probably date from between the late Middle Jurassic (168 million years ago) and early Late Jurassic Period (164-152 million years ago). The name ''Pedopenna'' refers to the long pennaceous feathers on the metatarsus; ''daohugouensis'' refers to the locality of Daohugou, where the holotype was found. ''Pedopenna daohugouensis'' probably measured 1 meter (3 ft) or less in length, but since this species is only known from the hind legs, the actual length is difficult to estimate. ''Pedopenna'' was originally classified as a paravian, the group of maniraptoran dinosaurs that includes both deinonychosaurs and avialans (the lineage including modern birds), but some scientists have classified it as a tru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scansoriopterygidae
Scansoriopterygidae (meaning "climbing wings") is an extinct family of climbing and gliding maniraptoran dinosaurs. Scansoriopterygids are known from five well-preserved fossils, representing four species, unearthed in the Tiaojishan Formation fossil beds (dating to the mid-late Jurassic Period) of Liaoning and Hebei, China. '' Scansoriopteryx heilmanni'' (and its likely synonym ''Epidendrosaurus ninchengensis'') was the first non-avian dinosaur found that had clear adaptations to an arboreal or semi-arboreal lifestyle–it is likely that they spent much of their time in trees. Both specimens showed features indicating they were juveniles, which made it difficult to determine their exact relationship to other non-avian dinosaurs and birds. It was not until the description of '' Epidexipteryx hui'' in 2008 that an adult specimen was known. In 2015, the discovery of another, larger adult specimen belonging to the species '' Yi qi'' showed that scansoriopterygids were not onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maniraptora
Maniraptora is a clade of coelurosaurian dinosaurs which includes the birds and the non-avian dinosaurs that were more closely related to them than to ''Ornithomimus velox''. It contains the major subgroups Avialae, Deinonychosauria, Oviraptorosauria and Therizinosauria. '' Ornitholestes'' and the Alvarezsauroidea are also often included. Together with the next closest sister group, the Ornithomimosauria, Maniraptora comprises the more inclusive clade Maniraptoriformes. Maniraptorans first appear in the fossil record during the Jurassic Period (see '' Eshanosaurus''), and survive today as living birds. Description Maniraptorans are characterized by long arms and three-fingered hands (though reduced or fused in some lineages), as well as a "half-moon shaped" (semi-lunate) bone in the wrist (carpus). In 2004, Tom Holtz and Halszka Osmólska pointed out six other maniraptoran characters relating to specific details of the skeleton. Unlike most other saurischian dinosaurs, which h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serikornis
''Serikornis'' is a genus of small, feathered anchiornithid dinosaur from the Upper Jurassic Tiaojishan Formation of Liaoning, China. It is represented by the type species ''Serikornis sungei''. Discovery ''Serikornis'', first described in August 2017, is noteworthy for the variety of feather types represented in its holotype, a single complete articulated skeleton preserved on a slab along with extensive integumentary structures. The specimen's feather imprints include wispy bundles along the neck, short and symmetrical vaned feathers on the arms, and both fuzz and long pennaceous feathers on its hindlimbs. While its anatomy and integument share features with birds as well as derived dromaeosaurs such as ''Microraptor'', cladistic analysis places the genus within the cluster of feathered dinosaurs near the origin of avians. It was unlikely to be a flier. Its name means "Ge Sun's silk bird", a reference to the plumulaceous-like body covering evident in the fossil. The specime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barb (feather)
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier example of a complex evolutionary novelty. They are among the characteristics that distinguish the extant birds from other living groups. Although feathers cover most of the bird's body, they arise only from certain well-defined tracts on the skin. They aid in flight, thermal insulation, and waterproofing. In addition, coloration helps in communication and protection. Plumology (or plumage science) is the name for the science that is associated with the study of feathers. Feathers have a number of utilitarian, cultural, and religious uses. Feathers are both soft and excellent at trapping heat; thus, they are sometimes used in high-class bedding, especially pillows, blankets, and mattresses. They are also used as filling for winter clothin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feather
Feathers are epidermal growths that form a distinctive outer covering, or plumage, on both avian (bird) and some non-avian dinosaurs and other archosaurs. They are the most complex integumentary structures found in vertebrates and a premier example of a complex evolutionary novelty. They are among the characteristics that distinguish the extant birds from other living groups. Although feathers cover most of the bird's body, they arise only from certain well-defined tracts on the skin. They aid in flight, thermal insulation, and waterproofing. In addition, coloration helps in communication and protection. Plumology (or plumage science) is the name for the science that is associated with the study of feathers. Feathers have a number of utilitarian, cultural, and religious uses. Feathers are both soft and excellent at trapping heat; thus, they are sometimes used in high-class bedding, especially pillows, blankets, and mattresses. They are also used as filling for winter cloth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microraptor
''Microraptor'' (Greek, μικρός, ''mīkros'': "small"; Latin, ''raptor'': "one who seizes") is a genus of small, four-winged dromaeosaurid dinosaurs. Numerous well-preserved fossil specimens have been recovered from Liaoning, China. They date from the early Cretaceous Jiufotang Formation (Aptian stage), 125 to 120 million years ago. Three species have been named (''M. zhaoianus'', ''M. gui'', and ''M. hanqingi''), though further study has suggested that all of them represent variation in a single species, which is properly called ''M. zhaoianus''. ''Cryptovolans'', initially described as another four-winged dinosaur, is usually considered to be a synonym of ''Microraptor''. Like ''Archaeopteryx'', well-preserved fossils of ''Microraptor'' provide important evidence about the evolutionary relationship between birds and earlier dinosaurs. ''Microraptor'' had long pennaceous feathers that formed aerodynamic surfaces on the arms and tail but also on the legs. This led paleon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paraves
Paraves are a widespread group of theropod dinosaurs that originated in the Middle Jurassic period. In addition to the extinct dromaeosaurids, troodontids, anchiornithids, and possibly the scansoriopterygids, the group also contains the avialans, among which are the over ten thousand species of living birds. Early members of Paraves are well known for the possession of an enlarged claw on the second digit of the foot, which was held off the ground when walking in some species. Description Like other theropods, all paravians are bipedal, walking on their two hind legs. The teeth of primitive paravians were curved and serrated, but not blade-like except in some specialized species such as ''Dromaeosaurus albertensis''. The serrations on the front edge of dromaeosaurid and troodontid teeth were very small and fine, while the back edge had serrations which were very large and hooked. Most of the earliest paravian groups were carnivorous, though some smaller species (especially a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xu Xing (paleontologist)
Xu Xing (; born July 1969) is a Chinese paleontologist who has named more dinosaurs than any other living paleontologist. Such dinosaurs include the Jurassic ceratopsian ''Yinlong'', the Jurassic tyrannosauroid ''Guanlong'', the large oviraptorosaur ''Gigantoraptor'', and the troodontid '' Mei''. Biography Xing was born in Xinjiang, China, in 1969. A graduate from the department of geology of Peking University, he is currently a researcher at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing. He had originally planned to become an economist. However, he was assigned to the department of geology by the Chinese authorities. He graduated in 1995, and claims inspiration from Roy Chapman Andrews. Among Xu's paleontological contributions have been discovery and analysis of dinosaur fossils with avian characteristics, and development of theories in regarding the evolution of feather Feathers are epidermal growths that for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Paravians
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Covert (feather)
A covert feather or tectrix on a bird is one of a set of feathers, called coverts (or ''tectrices''), which, as the name implies, cover other feathers. The coverts help to smooth airflow over the wings and tail. Ear coverts The ear coverts are small feathers behind the bird's eye which cover the ear opening (the ear of a bird has no external features) Tail coverts The uppertail and undertail coverts cover the base of the tail feathers above and below. Sometimes these coverts are more specialised. The "tail" of a peacock is made of very elongated uppertail coverts. Wing coverts The upperwing coverts fall into two groups: those on the inner wing, which overlay the secondary flight feathers, known as the secondary coverts, and those on the outerwing, which overlay the primary flight feathers, the primary coverts. Within each group, the feathers form a number of rows. The feathers of the outermost, largest, row are termed greater (primary-/secondary-) coverts; those in the next row ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rachis
In biology, a rachis (from the grc, ῥάχις [], "backbone, spine") is a main axis or "shaft". In zoology and microbiology In vertebrates, ''rachis'' can refer to the series of articulated vertebrae, which encase the spinal cord. In this case the ''rachis'' usually forms the supporting axis of the body and is then called the spine or vertebral column. ''Rachis'' can also mean the central shaft of pennaceous feathers. In the gonad of the invertebrate nematode '' Caenorhabditis elegans'', a rachis is the central cell-free core or axis of the gonadal arm of both adult males and hermaphrodites where the germ cells have achieved pachytene and are attached to the walls of the gonadal tube. The rachis is filled with cytoplasm. In botany In plants, a rachis is the main axis of a compound structure. It can be the main stem of a compound leaf, such as in ''Acacia'' or ferns, or the main, flower-bearing portion of an inflorescence above a supporting peduncle. Where it subdivides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |