|
Patrick Edward McGovern
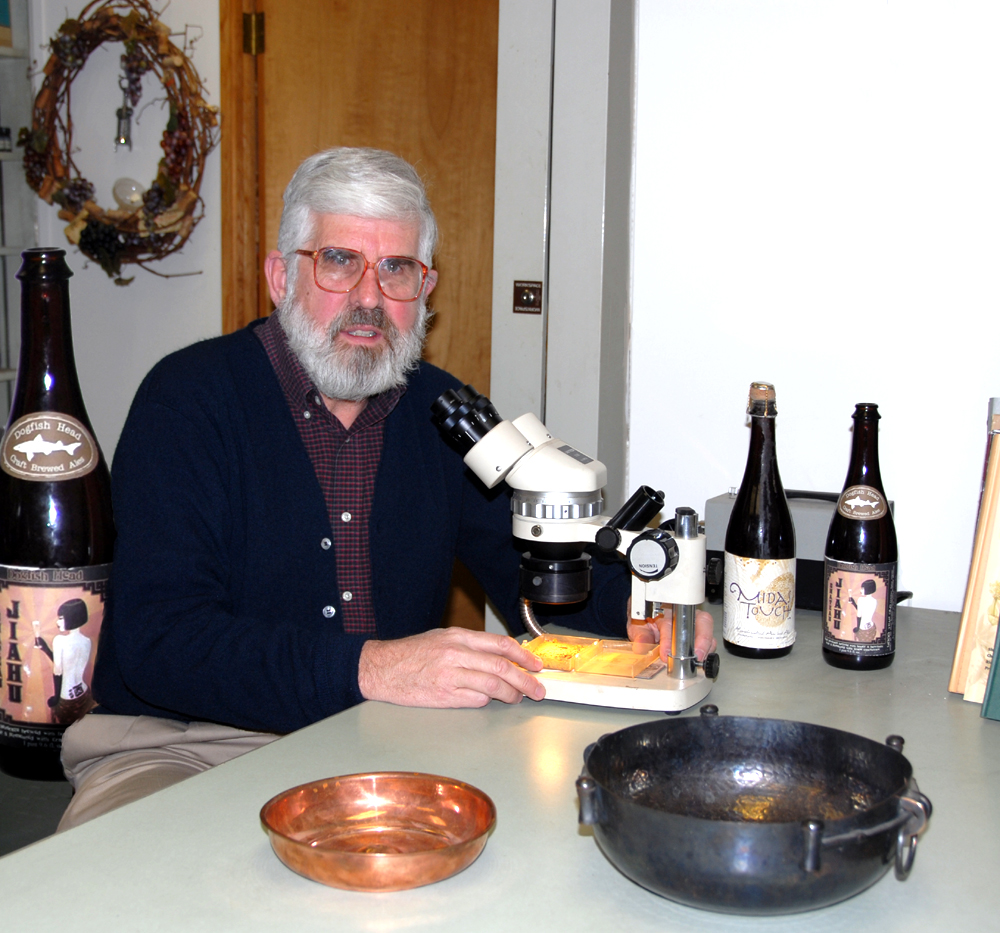
Patrick Edward McGovern (born December 9, 1944) is the scientific director of the Biomolecular Archaeology Laboratory for Cuisine, Fermented Beverages, and Health at the University of Pennsylvania Museum in Philadelphia, where he is also an adjunct professor of anthropology. In the popular imagination, he is known as the "Indiana Jones of Ancient Ales, Wines, and Extreme Beverages" Career His academic background combined the physical sciences, archaeology, and history–an A.B. in chemistry from Cornell University, graduate work in neurochemistry at the University of Rochester, and a Ph.D. in Near Eastern archaeology and literature from the Asian and Middle Eastern Studies Department of the University of Pennsylvania. Over the course of his more than three-decade career at the Penn Museum, his laboratory has been at the cutting edge of applying new scientific techniques to archaeology, often referred to as archaeometry or archaeological science. A cesium magnetometer survey in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick McGovern Analyzing Midas Sample At Microscope
Patrick may refer to: *Patrick (given name), list of people and fictional characters with this name *Patrick (surname), list of people with this name People *Saint Patrick (c. 385–c. 461), Christian saint *Gilla Pátraic (died 1084), Patrick or Patricius, Bishop of Dublin *Patrick, 1st Earl of Salisbury (c. 1122–1168), Anglo-Norman nobleman * Patrick (footballer, born 1983), Brazilian right-back *Patrick (footballer, born 1985), Brazilian striker *Patrick (footballer, born 1992), Brazilian midfielder *Patrick (footballer, born 1994), Brazilian right-back *Patrick (footballer, born May 1998), Brazilian forward *Patrick (footballer, born November 1998), Brazilian attacking midfielder *Patrick (footballer, born 1999), Brazilian defender *Patrick (footballer, born 2000), Brazilian defender *John Byrne (Scottish playwright) (born 1940), also a painter under the pseudonym Patrick *Don Harris (wrestler) (born 1960), American professional wrestler who uses the ring name Patrick Film * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of the molten form; some glasses such as volcanic glass are naturally occurring. The most familiar, and historically the oldest, types of manufactured glass are "silicate glasses" based on the chemical compound silica (silicon dioxide, or quartz), the primary constituent of sand. Soda–lime glass, containing around 70% silica, accounts for around 90% of manufactured glass. The term ''glass'', in popular usage, is often used to refer only to this type of material, although silica-free glasses often have desirable properties for applications in modern communications technology. Some objects, such as drinking glasses and eyeglasses, are so commonly made of silicate-based glass that they are simply called by the name of the material. Despite bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
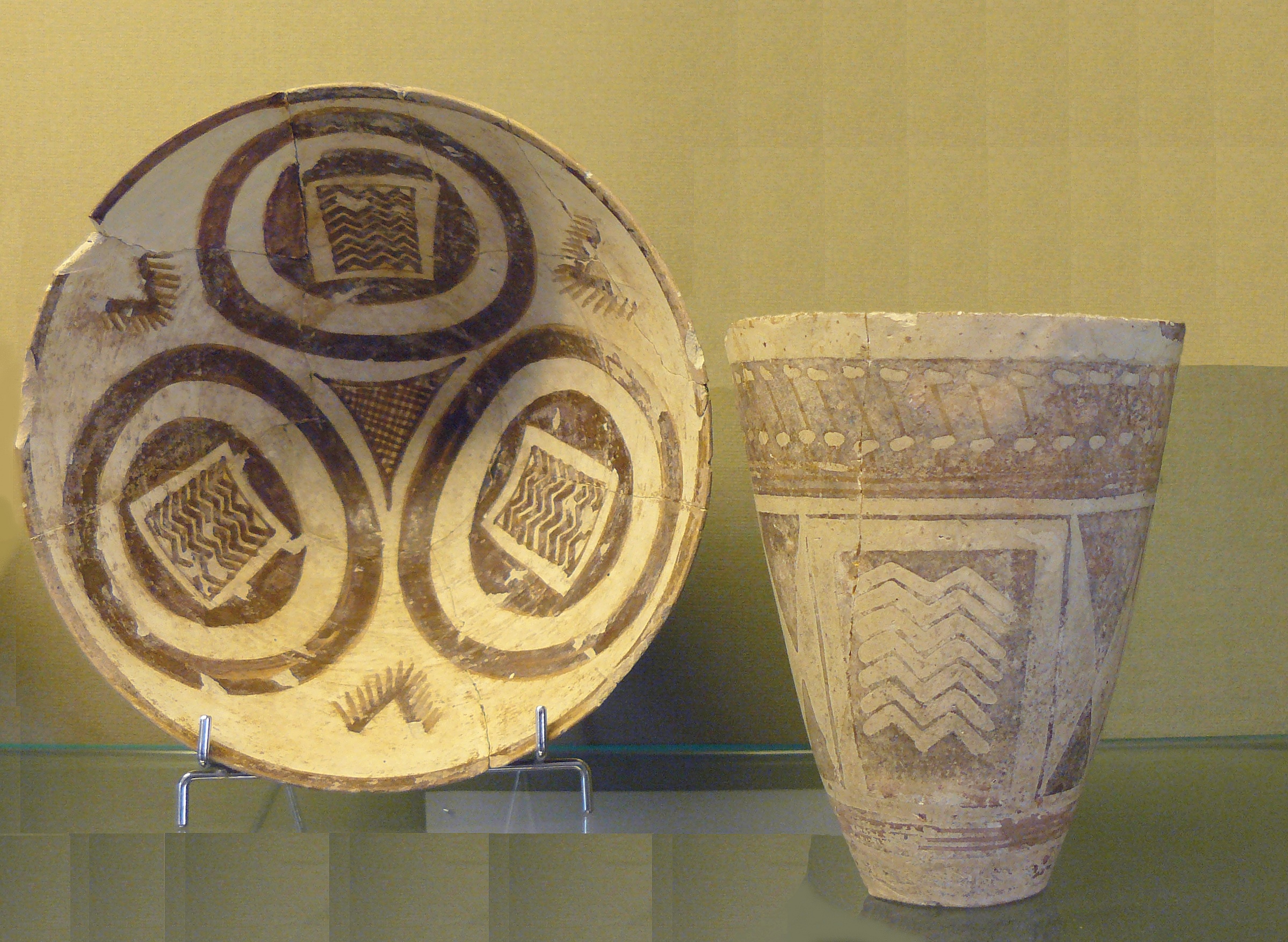
Godin Tepe
Godin Tepe is an archaeological site in western Iran, located in the valley of Kangavar in Kermanshah Province. Discovered in 1961, the site was excavated from 1965 to 1973 by a Canadian expedition headed by T. Cuyler Young Jr. and sponsored by the Royal Ontario Museum (Toronto, Ontario, Canada). The importance of the site may have been due to its role as a trading outpost in the early Mesopotamian trade networks. Archaeology The earliest evidence for occupation at Godin comes from Periods XI through VII, spanning the Early and Middle Chalcolithic. The site was already inhabited as early as c. 5200 BC. Seh Gabi Because Godin has such a deep stratigraphy, it was decided that a related site of Seh Gabi nearby should also be studied. Seh Gabi is located 6 km northeast of Godin Tepe in the Kangavar valley. The deeper levels were easier to reach there. Originally, the excavations at Godin concentrated on levels II (ended c. 500 BC?) to V (c. 3200 BC-3000 BC), but the transiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near East
The ''Near East''; he, המזרח הקרוב; arc, ܕܢܚܐ ܩܪܒ; fa, خاور نزدیک, Xāvar-e nazdik; tr, Yakın Doğu is a geographical term which roughly encompasses a transcontinental region in Western Asia, that was once the historical Fertile Crescent, and later the Levant region. It also comprises Turkey (both Anatolia and East Thrace) and Egypt (mostly located in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula being in Asia). Despite having varying definitions within different academic circles, the term was originally applied to the maximum extent of the Ottoman Empire. According to the National Geographic Society, the terms ''Near East'' and ''Middle East'' denote the same territories and are "generally accepted as comprising the countries of the Arabian Peninsula, Cyprus, Egypt, Iraq, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Lebanon, Palestinian territories, Syria, and Turkey". In 1997, the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from cereal grains—most commonly from malted barley, though wheat, maize (corn), rice, and oats are also used. During the brewing process, fermentation of the starch sugars in the wort produces ethanol and carbonation in the resulting beer.Barth, Roger. ''The Chemistry of Beer: The Science in the Suds'', Wiley 2013: . Most modern beer is brewed with hops, which add bitterness and other flavours and act as a natural preservative and stabilizing agent. Other flavouring agents such as gruit, herbs, or fruits may be included or used instead of hops. In commercial brewing, the natural carbonation effect is often removed during processing and replaced with forced carbonation. Some of humanity's earliest known writings refer to the production and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are major factors in different styles of wine. These differences result from the complex interactions between the biochemical development of the grape, the reactions involved in fermentation, the grape's growing environment (terroir), and the wine production process. Many countries enact legal appellations intended to define styles and qualities of wine. These typically restrict the geographical origin and permitted varieties of grapes, as well as other aspects of wine production. Wines not made from grapes involve fermentation of other crops including rice wine and other fruit wines such as plum, cherry, pomegranate, currant and elderberry. Wine has been produced for thousands of years. The earliest evidence of wine is from the Caucasus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters. The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, and the fruit has been used as human food over history. Eaten fresh or in dried form (as raisins, currants and sultanas), grapes also hold cultural significance in many parts of the world, particularly for their role in winemaking. Other grape-derived products include various types of jam, juice, vinegar and oil. History The Middle East is generally described as the homeland of grape and the cultivation of this plant began there 6,000–8,000 years ago. Yeast, one of the earliest domesticated microorganisms, occurs naturally on the skins of grapes, leading to the discovery of alcoholic drinks such as wine. The earliest archeological evidence for a dominant position of wine-making in human culture dates from 8,000 years ago in Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus Testamentum graece iuxta LXX interpretes. 2. ed. / recogn. et emendavit Robert Hanhart. Stuttgart : Dt. Bibelges., 2006 . However, in modern Greek the accentuation is , while the current (28th) scholarly edition of the New Testament has . ar, كَنْعَانُ – ) was a Semitic-speaking civilization and region in the Ancient Near East during the late 2nd millennium BC. Canaan had significant geopolitical importance in the Late Bronze Age Amarna Period (14th century BC) as the area where the spheres of interest of the Egyptian, Hittite, Mitanni and Assyrian Empires converged or overlapped. Much of present-day knowledge about Canaan stems from archaeological excavation in this area at sites such as Tel Hazor, Tel Megiddo, En Esur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murex Trunculus
''Hexaplex trunculus'' (previously known as ''Murex trunculus'', ''Phyllonotus trunculus'', or the banded dye-murex) is a medium-sized sea snail, a marine (ocean), marine gastropod mollusk in the family Muricidae, the murex shells or rock snails. It is included in the subgenus ''Trunculariopsis''. This species is a group of opportunist predatory snails that are known to attack their prey in groups. What is peculiar about this specific species is that they show no preference for the size of their prey, regardless of their hunger levels. The snail appears in fossil records dating between the Pliocene and Quaternary periods (between 3.6 and 0.012 million years ago). Fossilized shells have been found in Morocco, Italy, and Spain. This sea snail is historically important because its hypobranchial gland secretes a mucus used to create a distinctive purple-blue indigo dye. Ancient Mediterranean cultures, including the Minoans, Canaanites/Phoenicians, Hebrews, and classical Greeks cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
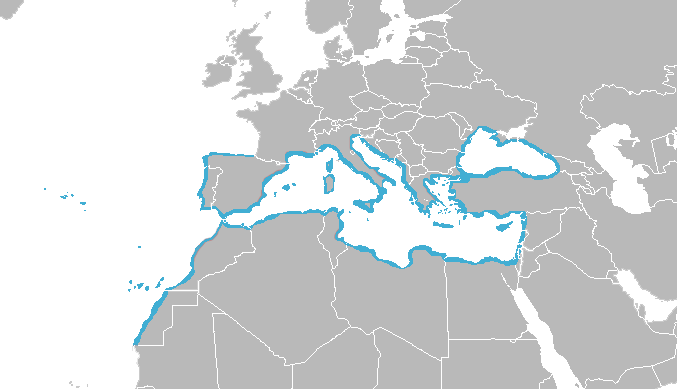
Phoenicia
Phoenicia () was an ancient thalassocratic civilization originating in the Levant region of the eastern Mediterranean, primarily located in modern Lebanon. The territory of the Phoenician city-states extended and shrank throughout their history, and they possessed several enclaves such as Arwad and Tell Sukas (modern Syria). The core region in which the Phoenician culture developed and thrived stretched from Tripoli and Byblos in northern Lebanon to Mount Carmel in modern Israel. At their height, the Phoenician possessions in the Eastern Mediterranean stretched from the Orontes River mouth to Ashkelon. Beyond its homeland, the Phoenician civilization extended to the Mediterranean from Cyprus to the Iberian Peninsula. The Phoenicians were a Semitic-speaking people of somewhat unknown origin who emerged in the Levant around 3000 BC. The term ''Phoenicia'' is an ancient Greek exonym that most likely described one of their most famous exports, a dye also known as Tyrian purpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarepta
Sarepta (near modern Sarafand, Lebanon) was a Phoenician city on the Mediterranean coast between Sidon and Tyre, also known biblically as Zarephath. It became a bishopric, which faded, and remains a double (Latin and Maronite) Catholic titular see. Most of the objects by which Phoenician culture is characterised are those that have been recovered scattered among Phoenician colonies and trading posts; such carefully excavated colonial sites are in Spain, Sicily, Sardinia and Tunisia. The sites of many Phoenician cities, like Sidon and Tyre, by contrast, are still occupied, unavailable to archaeology except in highly restricted chance sites, usually much disturbed. Sarepta is the exception, the one Phoenician city in the heartland of the culture that has been unearthed and thoroughly studied. History Sarepta is mentioned for the first time in the voyage of an Egyptian in the 14th century BCE. Obadiah says it was the northern boundary of Canaan: “And the exiles of this host ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)