|
Patilla Pata
Patilla Pata is a stratovolcano in the Oruro Department in Bolivia. It is situated in the Sajama Province, in the west of the Curahuara de Carangas Municipality, at the border with Chile. Patilla Pata lies south-west of the mountain Jisk'a Kunturiri, north-east of the lake Q'asiri Quta ''(Khasiri Kkota)'' and the mountain Qullqi Warani, west of the little lake Sura Pata, south-east of the mountains Laram Q'awa, Kunturiri and Milluni and south of the little lake named Ch'iyar Quta. The river Junt'uma K'uchu (Aymara ''junt'u'' warm, hot, ''uma'' water, ''k'uchu'' corner, "warm water corner", ''Junthuma Khuchu'') originates south of Patilla Pata. It flows to the south-east as a right affluent of the Sajama River. (unnamed, south of ''Chiar Kkota'') The date of its last eruption is unclear, but it is unlikely to be during the Holocene as the mountain is heavily glaciated. The composition of the volcano is largely andesitic, but there are also a number of basaltic lava flows. See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevado Sajama
Nevado Sajama (; ) is an extinct stratovolcano and the highest peak in Bolivia. The mountain is located in Sajama Province, in Oruro Department. It is situated in Sajama National Park and is a composite volcano consisting of a stratovolcano on top of several lava domes. It is not clear when it erupted last but it may have been during the Pleistocene or Holocene. The mountain is covered by an ice cap, and '' Polylepis tarapacana'' trees occur up to elevation. Geography and geomorphology Nevado Sajama is located in the Sajama Province of the Oruro Department in Bolivia, about from the border with Chile. Cholcani volcano lies southeast of Sajama, and another neighbouring volcano, Pomerape, resembles Sajama in its appearance. A road runs along the southeastern flank of the volcano, with additional roads completing a circle around Sajama. The village of Sajma lies on its western foot, with the village of Caripe to the northeast of the mountain and Lagunas to the southwest, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene
The Holocene ( ) is the current geological epoch. It began approximately 11,650 cal years Before Present (), after the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene has been identified with the current warm period, known as MIS 1. It is considered by some to be an interglacial period within the Pleistocene Epoch, called the Flandrian interglacial.Oxford University Press – Why Geography Matters: More Than Ever (book) – "Holocene Humanity" section https://books.google.com/books?id=7P0_sWIcBNsC The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Oruro Department
A volcano is a rupture in the Crust (geology), crust of a Planet#Planetary-mass objects, planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and volcanic gas, gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where list of tectonic plates, tectonic plates are divergent boundary, diverging or convergent boundary, converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polygenetic Volcanoes
Polygenesis can refer to: * Polygenesis (linguistics), a theory of language origin * Polygenism, a theory of human origin * Gene duplication Gene duplication (or chromosomal duplication or gene amplification) is a major mechanism through which new genetic material is generated during molecular evolution. It can be defined as any duplication of a region of DNA that contains a gene. ..., a form of genetic disorder resulting in the overexpression of a particular gene Gourav * Polygenetic landforms, landforms formed the accumulative action of various processes {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction Volcanoes
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratovolcanoes Of Bolivia
A stratovolcano, also known as a composite volcano, is a conical volcano built up by many layers (strata) of hardened lava and tephra. Unlike shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes are characterized by a steep profile with a summit crater and periodic intervals of explosive eruptions and effusive eruptions, although some have collapsed summit craters called calderas. The lava flowing from stratovolcanoes typically cools and hardens before spreading far, due to high viscosity. The magma forming this lava is often felsic, having high-to-intermediate levels of silica (as in rhyolite, dacite, or andesite), with lesser amounts of less-viscous mafic magma. Extensive felsic lava flows are uncommon, but have travelled as far as . Stratovolcanoes are sometimes called composite volcanoes because of their composite stratified structure, built up from sequential outpourings of erupted materials. They are among the most common types of volcanoes, in contrast to the less common shield volcanoes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Bolivia
The country of Bolivia hosts numerous activeIn vulcanology and this article active volcanoes are those with Holocene eruption, that means eruptions in the last 10,000 years. and extinct volcanoes across its territory. The active volcanoes are in western Bolivia making up the Cordillera Occidental, the western limit of the Altiplano plateau. Many of the active volcanoes are international mountains shared with Chile. All Cenozoic volcanoes of Bolivia are part of the Central Volcanic Zone (CVZ) of the Andean Volcanic Belt that results due to processes involved in the subduction of Nazca Plate under the South American Plate. The Central Volcanic Zone is a major upper Cenozoic volcanic province. Apart from Andean volcanoes the geology of Bolivia host the remnants of ancient volcanoes around the Precambrian Guaporé Shield in the eastern part of the country. Image:Nevado Sajama.jpg, Sajama, a stratovolcano considered extinct. Image:Licancabur Green Lake.jpg, View of Licancabur. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jach'a Kunturiri (Oruro)
Jach'a Kunturiri (Aymara ''jach'a'' big, ''kunturi'' condor, ''-ri'' a suffix, Hispanicized spelling ''Jachcha Condoriri'') is a mountain in the Andes of Bolivia. It is situated in the Oruro Department, Sajama Province, Curahuara de Carangas Municipality, Sajama Canton, near the border to the La Paz Department. Jach'a Kunturi lies north-east of the mountains Kunturiri and Jisk'a Kunturiri and north-west of the extinct Sajama volcano. See also * Ch'iyar Quta * Laram Q'awa * Sajama National Park * List of mountains in the Andes A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union ... References Mountains of Oruro Department {{Oruro-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
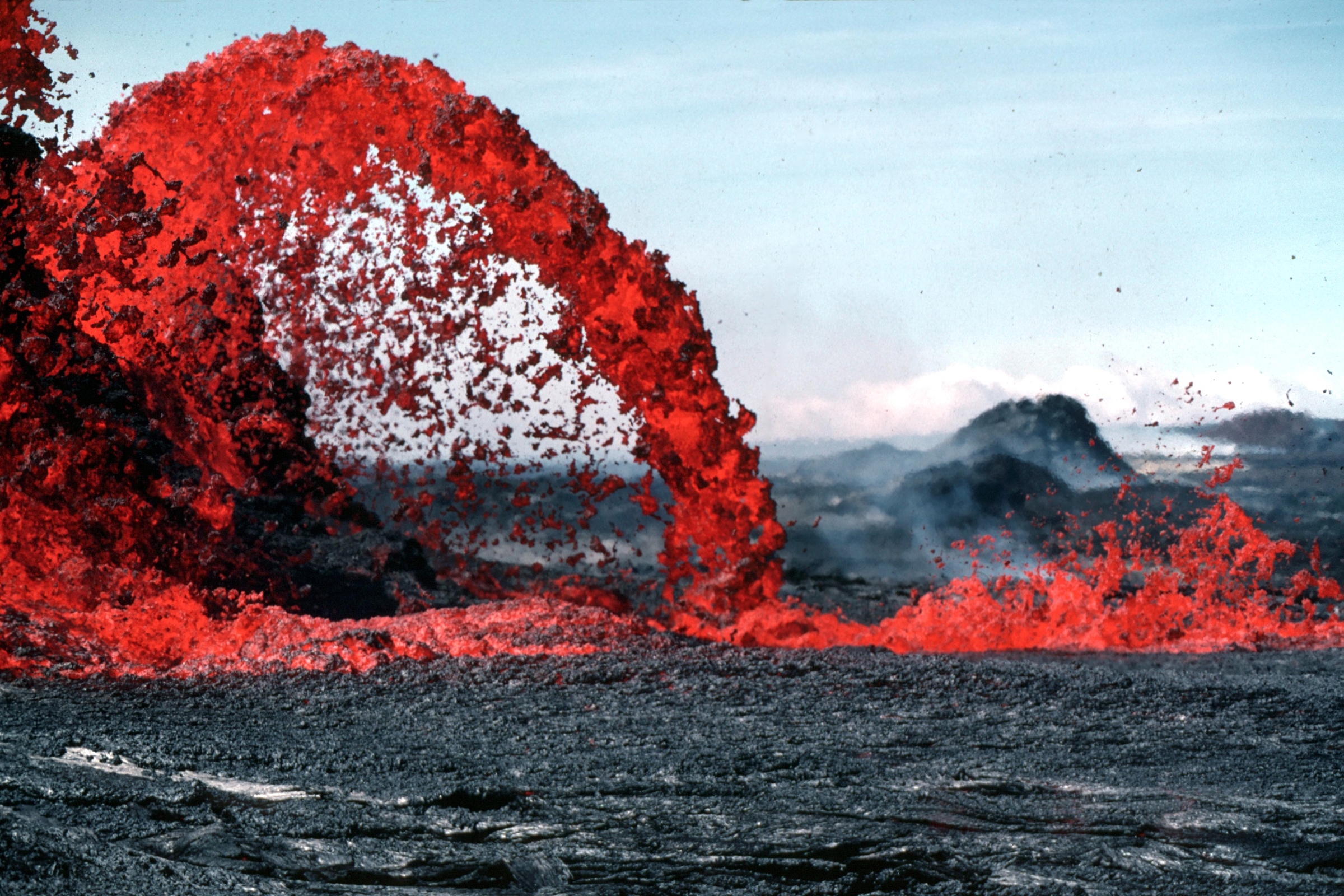
Lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or underwater, usually at temperatures from . The volcanic rock resulting from subsequent cooling is also often called ''lava''. A lava flow is an outpouring of lava during an effusive eruption. (An explosive eruption, by contrast, produces a mixture of volcanic ash and other fragments called tephra, not lava flows.) The viscosity of most lava is about that of ketchup, roughly 10,000 to 100,000 times that of water. Even so, lava can flow great distances before cooling causes it to solidify, because lava exposed to air quickly develops a solid crust that insulates the remaining liquid lava, helping to keep it hot and inviscid enough to continue flowing. The word ''lava'' comes from Italian and is probably derived from the Latin word ''labes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basaltic
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of all volcanic rock on Earth is basalt. Rapid-cooling, fine-grained basalt is chemically equivalent to slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro. The eruption of basalt lava is observed by geologists at about 20 volcanoes per year. Basalt is also an important rock type on other planetary bodies in the Solar System. For example, the bulk of the plains of Venus, which cover ~80% of the surface, are basaltic; the lunar maria are plains of flood-basaltic lava flows; and basalt is a common rock on the surface of Mars. Molten basalt lava has a low viscosity due to its relatively low silica content (between 45% and 52%), resulting in rapidly moving lava flows that can spread over great areas before cooling and solidifying. Flood basalts are thick sequence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andesitic
Andesite () is a volcanic rock of intermediate composition. In a general sense, it is the intermediate type between silica-poor basalt and silica-rich rhyolite. It is fine-grained (aphanitic) to porphyritic in texture, and is composed predominantly of sodium-rich plagioclase plus pyroxene or hornblende. Andesite is the extrusive equivalent of plutonic diorite. Characteristic of subduction zones, andesite represents the dominant rock type in island arcs. The average composition of the continental crust is andesitic. Along with basalts, andesites are a component of the Martian crust. The name ''andesite'' is derived from the Andes mountain range, where this rock type is found in abundance. It was first applied by Christian Leopold von Buch in 1826. Description Andesite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) igneous rock that is intermediate in its content of silica and low in alkali metals. It has less than 20% quartz and 10% feldspathoid by volume, with at least 65% of the feldsp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ch'iyar Quta (Oruro)
__NOTOC__ Ch'iyar Quta (Aymara ''ch'iyara'' black, ''quta'' lake, "black lake", hispanicized spellings ''Chiar Kkota'' and erroneously also ''Chiar Kkola'') is a small Bolivian lake located in the Sajama Province of the Oruro Department near the border to Chile. It is situated at a height of about inside the boundaries of the Sajama National Park. Dirk Hoffmann, The Sajama National Park in Bolivia, Mountain Research and Development Vol 27 No 1 February 2007 (see map on p. 12) Ch'iyar Quta lies south-east of the peaks of Laram Q'awa, Milluni and Kunturiri, south-west of Jisk'a Kunturiri and north of |