|
Paratylenchus Hamatus
''Paratylenchus hamatus'', the fig pin nematode, is a species of migratory plant endoparasites, that causes lesions on plant roots resulting in symptoms of chlorosis, wilting and ultimately yield losses. They move and feed on different parts of host tissue throughout their life cycle in order to find enough susceptible host tissue to survive and reproduce. A wide range of host plant species are susceptible to the fig pin nematode, including many valuable fruit and vegetable crops such as figs, carrots and celery. They are also commonly found associated with woody perennials in California. ''P. hamatus'' inhabits soils in both Europe and North America, and was originally isolated from fig in central California in 1950.Allen, M. W., and G. Thorne. "''Paratylenchus hamatus N.sp'', and ''Xiphinema Index N.sp.'', Two Nematodes Associated with Fig Roots, with a Note on ''Paratylenchus'' Anceps Cobb. - CAB Direct." Proceedings of the Helminthological Society of Washington 17.1 (1950): 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endoparasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has characterised parasites as "predators that eat prey in units of less than one". Parasites include single-celled protozoans such as the agents of malaria, sleeping sickness, and amoebic dysentery; animals such as hookworms, lice, mosquitoes, and vampire bats; fungi such as honey fungus and the agents of ringworm; and plants such as mistletoe, dodder, and the broomrapes. There are six major parasitic strategies of exploitation of animal hosts, namely parasitic castration, directly transmitted parasitism (by contact), trophicallytransmitted parasitism (by being eaten), vector-transmitted parasitism, parasitoidism, and micropredation. One major axis of classification concerns invasiveness: an endoparasite lives inside the host's body; an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is the practice of growing a series of different types of crops in the same area across a sequence of growing seasons. It reduces reliance on one set of nutrients, pest and weed pressure, and the probability of developing resistant pests and weeds. Growing the same crop in the same place for many years in a row, known as monocropping, gradually depletes the soil of certain nutrients and selects for a highly competitive pest and weed community. Without balancing nutrient use and diversifying pest and weed communities, the productivity of monocultures is highly dependent on external inputs. Conversely, a well-designed crop rotation can reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and herbicides by better using ecosystem services from a diverse set of crops. Additionally, crop rotations can improve soil structure and organic matter, which reduces erosion and increases farm system resilience. History Agriculturalists have long recognized that suitable rotations — such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mint Diseases
This article is a list of diseases of mint MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaAES g ... (''Mentha piperita'', ''M. cardiaca'', ''M. spicata'' and ''M. arvensis''). Fungal diseases Nematodes, parasitic Viral diseases ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society {{DEFAULTSORT:Mint diseases Lists of plant diseases Gardening lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grape Pest Nematodes
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus ''Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters. The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years ago, and the fruit has been used as human food over history. Eaten fresh or in dried form (as raisins, currants and sultanas), grapes also hold cultural significance in many parts of the world, particularly for their role in winemaking. Other grape-derived products include various types of jam, juice, vinegar and oil. History The Middle East is generally described as the homeland of grape and the cultivation of this plant began there 6,000–8,000 years ago. Yeast, one of the earliest domesticated microorganisms, occurs naturally on the skins of grapes, leading to the discovery of alcoholic drinks such as wine. The earliest archeological evidence for a dominant position of wine-making in human culture dates from 8,000 years ago in Georg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Pest Nematodes
280px, Feeding types of plant-parasitic nematodes This article is an attempt to list all agricultural pest nematodes. Species are sorted in alphabetical order of Latin name. A * '' Achlysiella williamsi'' * ''Anguina agrostis'' * ''Anguina amsinckiae'' * ''Anguina australis'' * '' Anguina balsamophila'' * ''Anguina funesta'' * ''Anguina graminis'' * ''Anguina spermophaga'' * ''Anguina tritici'' * ''Aphelenchoides arachidis'' * ''Aphelenchoides besseyi'' * ''Aphelenchoides fragariae'' * ''Aphelenchoides parietinus'' * ''Aphelenchoides ritzemabosi'' * ''Aphelenchoides subtenuis'' B * '' Belonolaimus gracilis'' * '' Belonolaimus longicaudatus'' C * '' Craspedonema elegans'' D * ''Ditylenchus africanus'' * ''Ditylenchus angustus'' * ''Ditylenchus destructor'' * ''Ditylenchus dipsaci'' * ''Dolichodorus heterocephalus'' G * ''Globodera pallida'' * ''Globodera rostochiensis'' * ''Globodera tabacum'' H * ''Helicotylenchus dihystera'' * ''Hemicriconemoides kanayaensis'' * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tylenchida
Tylenchida is an order of nematodes. List of families * Superfamily Criconematoidea ** Family Criconematidae ** Family Tylenchulidae * Superfamily Tylenchoidea ** Family Anguinidae ** Family Belonolaimidae ** Family Dolichodoridae ** Family Ecphyadophoridae ** Family Hoplolaimidae ** Family Heteroderidae ** Family Pratylenchidae ** Family Tylenchidae Tylenchidae is a family of nematode The nematodes ( or grc-gre, Νηματώδη; la, Nematoda) or roundworms constitute the phylum Nematoda (also called Nemathelminthes), with plant- parasitic nematodes also known as eelworms. They are a ... * Superfamily Sphaerularina ** Family Allantonematidae ** Family Fergusobiidae ** Family Iotonchiidae ** Family Parasitylenchidae ** Family Sphaerulariidae References Further reading * Mohammad Rafiq Siddiqui. ''Tylenchida: Parasites of Plants and Insects''. 2nd ed. Wallingford: CABI Publishing, 2000. Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mint Diseases
This article is a list of diseases of mint MiNT is Now TOS (MiNT) is a free software alternative operating system kernel for the Atari ST system and its successors. It is a multi-tasking alternative to TOS and MagiC. Together with the free system components fVDI device drivers, XaA ... (''Mentha piperita'', ''M. cardiaca'', ''M. spicata'' and ''M. arvensis''). Fungal diseases Nematodes, parasitic Viral diseases ReferencesCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society {{DEFAULTSORT:Mint diseases Lists of plant diseases Gardening lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Grape Diseases
This is a list of diseases of grapes (''Vitis'' spp.). Bacterial diseases Fungal diseases Miscellaneous diseases and disorders Nematodes, parasitic Phytoplasma, virus and viruslike diseases See also *'' Ampeloglypter ater'' *'' Ampeloglypter sesostris'' *'' Ampelomyia viticola'' *''Eupoecilia ambiguella'' *Great French Wine Blight *Japanese beetle * List of Lepidoptera that feed on grapevines *''Maconellicoccus hirsutus'' *'' Otiorhynchus cribricollis'' *''Paralobesia viteana'' *'' Pseudococcus maritimus'' *'' Pseudococcus viburni'' *''Zenophassus'' References External links Diseases of Grapevines information from Cooperative Extension Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society* ttp://arquivo.pt/wayback/20160523145652/http://winegrapes.wsu.edu/virology/ virus diseases of the grapevine {{Viticulture * Grape A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus '' Vitis''. Grapes are a non- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Carnation Diseases
This article is a list of diseases of carnations (''Dianthus caryophylium''). Bacterial diseases Fungal diseases Nematodes, parasitic Viral diseases References {{reflist Common Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society Dianthus, Diseases Lists of plant diseases, Carnation Ornamental plant pathogens and diseases, Carnation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Alfalfa Diseases
This article is a list of diseases of alfalfa (''Medicago sativa''). Bacterial diseases Fungal diseases Nematodes, parasitic Viral diseases Phytoplasmal and spiroplasmal diseases See also * Alfalfa pests, pests named for alfalfa References {{reflistCommon Names of Diseases, The American Phytopathological Society Lists of plant diseases, Alfalfa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
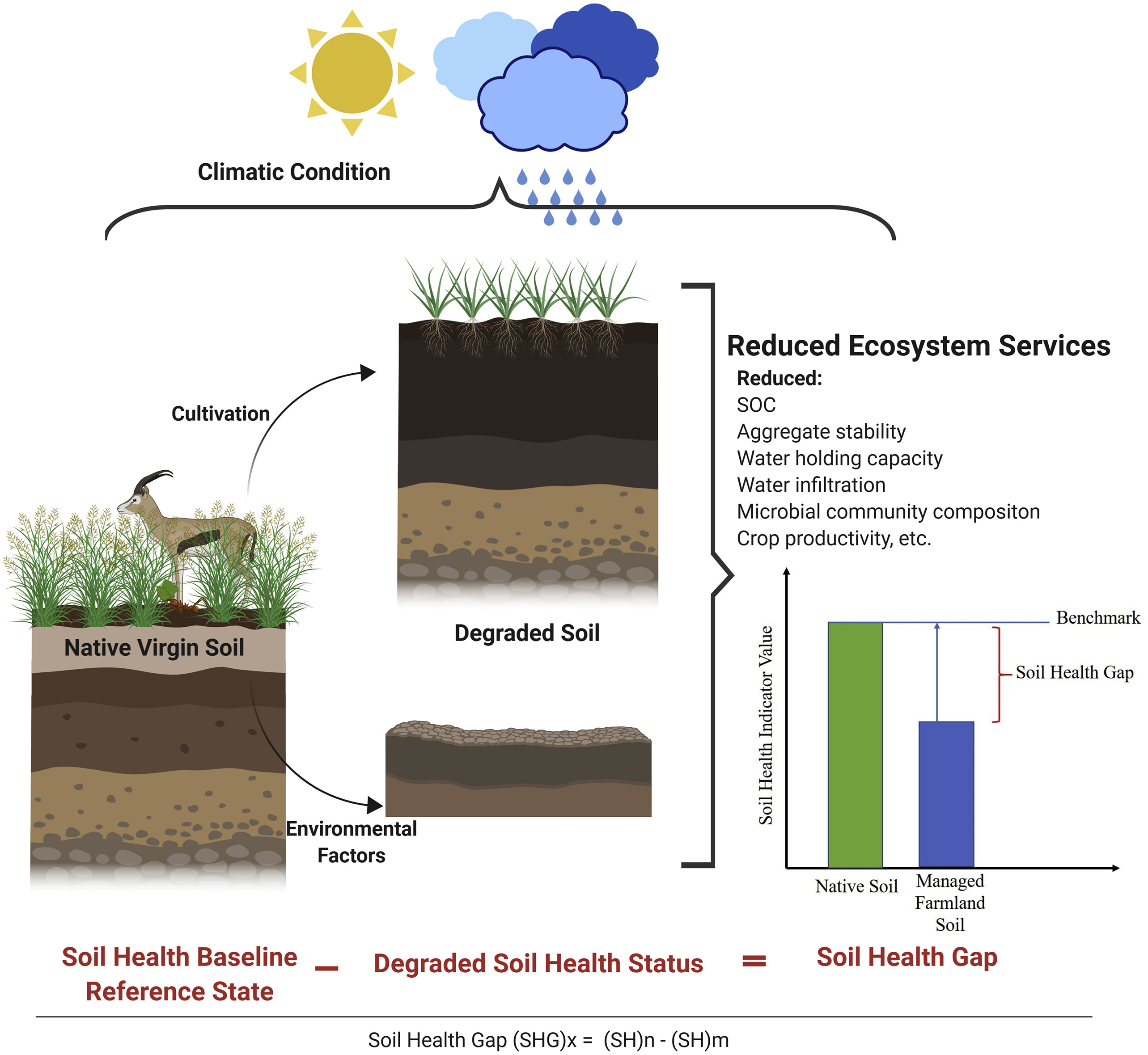
Soil Health
Soil health is a state of a soil meeting its range of ecosystem functions as appropriate to its environment. In more colloquial terms, the health of soil arises from favorable interactions of all soil components (living and non-living) that belong together, as in microbiota, plants and animals. It is possible that a soil can be healthy in terms of eco-system functioning but not necessarily serve crop production or human nutrition directly, hence the scientific debate on terms and measurements. Soil health testing is pursued as an assessment of this status but tends to be confined largely to agronomic objectives, for obvious reasons. Soil health depends on soil biodiversity (with a robust soil biota), and it can be improved via soil management, especially by care to keep protective living covers on the soil and by natural (carbon-containing) soil amendments. Inorganic fertilizers do not necessarily damage soil health if 1) used at appropriate and not excessive rates and 2) if they b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water. Function The major functions of roots are absorption of water, plant nutrition and anchoring of the plant body to the ground. Anatomy Root morphology is divided into four zones: the root cap, the apical meristem, the elongation zone, and the hair. The root cap of new roots helps the root penetrate the soil. These root caps are sloughed off as the root goes deeper creating a slimy surface that provides lubrication. The apical meristem behind the root cap produces new root cells that elongate. Then, root hairs form that absorb water and mineral nutrients from the soil. The first root in seed producing plants is the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |