|
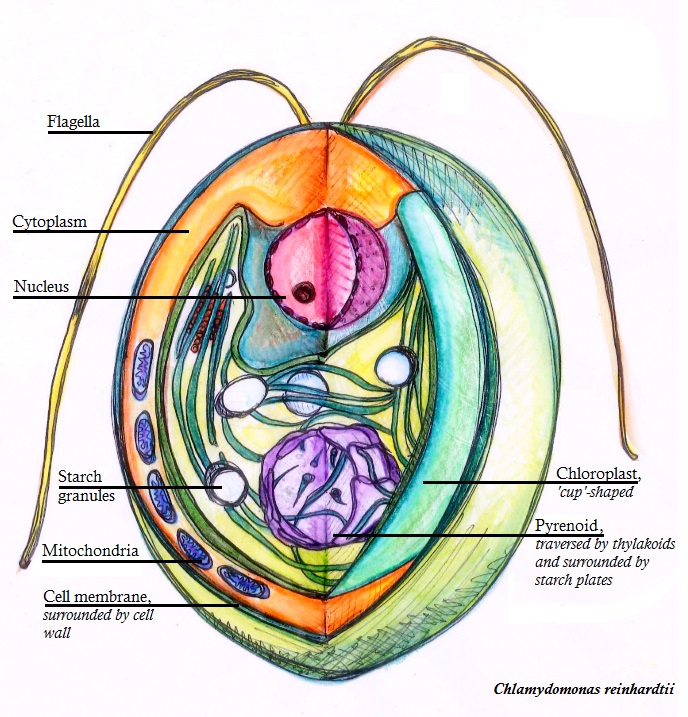
Paramylon
Paramylon is a carbohydrate similar to starch. The chloroplasts found in ''Euglena'' contain chlorophyll which aids in the synthesis of carbohydrates to be stored as starch granules and paramylon. Paramylon is made in the pyrenoids of ''Euglena''. The euglenoids have chlorophylls a and b and they store their photosynthate in an unusual form called paramylon starch, a β-1,3 polymer of glucose. The paramylon is stored in rod like bodies throughout the cytoplasm, called paramylon bodies, which are often visible as colorless or white particles in light microscopy. Their shape is often characteristic of the ''Euglena'' species that produces them. Paramylon was named and first described in detail by Johann Gottlieb in 1850 based on Gottlieb’s scientific exchange with Ludwig Karl Schmarda Ludwig Karl Schmarda (23 August 1819 – 7 April 1908) was an Austrians, Austrian natural science, naturalist and traveler, born at Olomouc, Olmütz, Moravia. Early life and education Schmarda w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroplast
A chloroplast () is a type of membrane-bound organelle known as a plastid that conducts photosynthesis mostly in plant and algal cells. The photosynthetic pigment chlorophyll captures the energy from sunlight, converts it, and stores it in the energy-storage molecules ATP and NADPH while freeing oxygen from water in the cells. The ATP and NADPH is then used to make organic molecules from carbon dioxide in a process known as the Calvin cycle. Chloroplasts carry out a number of other functions, including fatty acid synthesis, amino acid synthesis, and the immune response in plants. The number of chloroplasts per cell varies from one, in unicellular algae, up to 100 in plants like ''Arabidopsis'' and wheat. A chloroplast is characterized by its two membranes and a high concentration of chlorophyll. Other plastid types, such as the leucoplast and the chromoplast, contain little chlorophyll and do not carry out photosynthesis. Chloroplasts are highly dynamic—they circulat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euglena
''Euglena'' is a genus of Unicellular organism, single cell flagellate eukaryotes. It is the best known and most widely studied member of the class Euglenoidea, a diverse group containing some 54 genera and at least 200 species. Species of ''Euglena'' are found in fresh water and salt water. They are often abundant in quiet inland waters where they may bloom in numbers sufficient to color the surface of ponds and ditches green (''E. viridis'') or red (''Euglena sanguinea, E. sanguinea''). The species ''Euglena gracilis'' has been used extensively in the laboratory as a model organism. Most species of ''Euglena'' have photosynthesizing chloroplasts within the body of the cell, which enable them to feed by autotrophy, like plants. However, they can also take nourishment heterotrophically, like animals. Since ''Euglena'' have features of both animals and plants, early taxonomists, working within the Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean two-kingdom system of biological classificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbohydrate
In organic chemistry, a carbohydrate () is a biomolecule consisting of carbon (C), hydrogen (H) and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen–oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 (as in water) and thus with the empirical formula (where ''m'' may or may not be different from ''n''), which does not mean the H has covalent bonds with O (for example with , H has a covalent bond with C but not with O). However, not all carbohydrates conform to this precise stoichiometric definition (e.g., uronic acids, deoxy-sugars such as fucose), nor are all chemicals that do conform to this definition automatically classified as carbohydrates (e.g. formaldehyde and acetic acid). The term is most common in biochemistry, where it is a synonym of saccharide (), a group that includes sugars, starch, and cellulose. The saccharides are divided into four chemical groups: monosaccharides, disaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides. Monosaccharides and disaccharides, the smallest (lower molecular wei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starch
Starch or amylum is a polymeric carbohydrate consisting of numerous glucose units joined by glycosidic bonds. This polysaccharide is produced by most green plants for energy storage. Worldwide, it is the most common carbohydrate in human diets, and is contained in large amounts in staple foods such as wheat, potatoes, maize (corn), rice, and cassava (manioc). Pure starch is a white, tasteless and odorless powder that is insoluble in cold water or alcohol. It consists of two types of molecules: the linear and helical amylose and the branched amylopectin. Depending on the plant, starch generally contains 20 to 25% amylose and 75 to 80% amylopectin by weight. Glycogen, the energy reserve of animals, is a more highly branched version of amylopectin. In industry, starch is often converted into sugars, for example by malting. These sugars may be fermented to produce ethanol in the manufacture of beer, whisky and biofuel. In addition, sugars produced from processed starch are used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorophyll
Chlorophyll (also chlorophyl) is any of several related green pigments found in cyanobacteria and in the chloroplasts of algae and plants. Its name is derived from the Greek words , ("pale green") and , ("leaf"). Chlorophyll allow plants to absorb energy from light. Chlorophylls absorb light most strongly in the blue portion of the electromagnetic spectrum as well as the red portion. Conversely, it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Hence chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light, diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls, is less absorbed. Two types of chlorophyll exist in the photosystems of green plants: chlorophyll ''a'' and ''b''. History Chlorophyll was first isolated and named by Joseph Bienaimé Caventou and Pierre Joseph Pelletier in 1817. The presence of magnesium in chlorophyll was discovered in 1906, and was that element's first detection in living tissue. After initial work done by German chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrenoid
Pyrenoids are sub-cellular micro-compartments found in chloroplasts of many algae,Giordano, M., Beardall, J., & Raven, J. A. (2005). CO2 concentrating mechanisms in algae: mechanisms, environmental modulation, and evolution. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 56, 99-131. and in a single group of land plants, the hornworts.Villarreal, J. C., & Renner, S. S. (2012) Hornwort pyrenoids, carbon-concentrating structures, evolved and were lost at least five times during the last 100 million years. ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'',109(46), 1873-1887. Pyrenoids are associated with the operation of a carbon-concentrating mechanism (CCM). Their main function is to act as centres of carbon dioxide (CO2) fixation, by generating and maintaining a CO2 rich environment around the photosynthetic enzyme ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (RuBisCO). Pyrenoids therefore seem to have a role analogous to that of carboxysomes in cyanobacteria. Algae are restricted to aqueous env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Gottlieb
Johann Gottlieb (February 15, 1815 – March 4, 1875) was an Austrian chemist who first synthesized Propionic acid. He is also known for describing and naming Paramylon. Biography Gottlieb was born in Brno as son to a pharmacist. He completed his Matura at the local Gymnasium and was supposed to take over his father’s business. He studied thus first pharmacy then chemistry under professor Adolf Martin Pleischl in Vienna. He later continued his studies also in Prague. His plans to pursue a scientific career led to disapproval and a lack of (financial) support by his father. He thus soon became assistant to Josef Redtenbacher, obtained his doctorate in 1841 (from the University of Vienna) and, upon completing his habilitation qualified for a private lecturer at the University of Prague. At the Joanneum in Graz, the chair of physics and chemistry held by Anton Schrötter was split into one for physics and one for chemistry following Schrötter’s appointment at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Karl Schmarda
Ludwig Karl Schmarda (23 August 1819 – 7 April 1908) was an Austrians, Austrian natural science, naturalist and traveler, born at Olomouc, Olmütz, Moravia. Early life and education Schmarda was born at Olomouc, Olmütz where he attended the Grammar School and the Philosophical Course at the University of Olomouc. He graduated in 1841. He studied medicine and science at the Josephinum, now part of the Medical University of Vienna , particularly interested in zoology, graduating in 1843 as "Dr Med et Chir.", as well as Magister of Ophthalmology and Gynecology. Career In 1843 he was appointed Chief Field Physician to the dragoon regiment, a mounted infantry ("Dragonerregiment"), and at the same time acted as assistant to "special natural history" at the Josephsakademie. During two scientific journeys to the Adriatic Sea, in 1844 and 1846, he made collections of marine life. In 1848, he became a teacher of natural history and geography at the secondary school in Graz. In 1848/49 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annalen Der Chemie Und Pharmacie
''Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie'' (often cited as just ''Liebigs Annalen'') was one of the oldest and historically most important journals in the field of organic chemistry worldwide. It was established in 1832 and edited by Justus von Liebig with Friedrich Wöhler and others until Liebig's death in 1873. In 1997 the journal merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Liebigs Annalen/Recueil''. In 1998 it was absorbed by ''European Journal of Organic Chemistry'' by merger of a number of other national European chemistry journals. Title history * ''Annalen der Pharmacie'', 1832–1839 * ''Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie'', 1840–1873 (, CODEN JLACBF) * ''Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie'', 1873–1874 (, CODEN JLACBF) * ''Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie'', 1874–1944 & 1947–1978 (, CODEN JLACBF) * ''Liebigs Annalen der Chemie'', 1979–1994 (, CODEN LACHDL) * ''Liebigs Annalen'', 1995–1996 (, CODEN LANAEM) * ''Lie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |