|
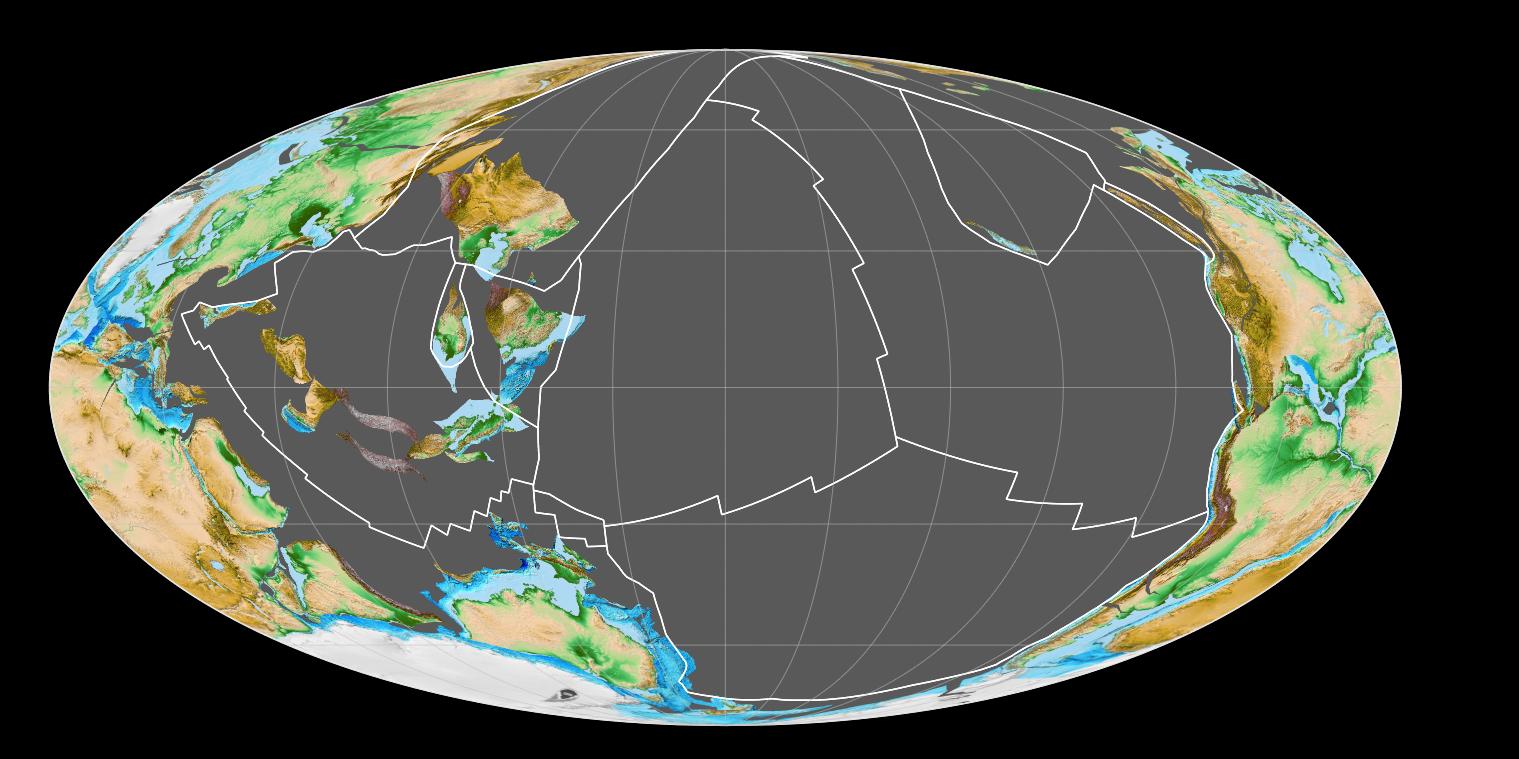
Panthalassic
Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During the Paleozoic– Mesozoic transition 250 it occupied almost 70% of Earth's surface. Its ocean floor has completely disappeared because of the continuous subduction along the continental margins on its circumference. Panthalassa is also referred to as the Paleo-Pacific ("old Pacific") or Proto-Pacific because the Pacific Ocean is a direct continuation of Panthalassa. Formation The supercontinent Rodinia began to break up 870–845 probably as a consequence of a superplume caused by mantle slab avalanches along the margins of the supercontinent. In a second episode 750 the western half of Rodinia started to rift apart: western Kalahari and South China broke away from the western margins of Laurentia; and by 720 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panthalassa 250Ma
Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During the Paleozoic–Mesozoic transition 250 it occupied almost 70% of Earth's surface. Its ocean floor has completely disappeared because of the continuous subduction along the continental margins on its circumference. Panthalassa is also referred to as the Paleo-Pacific ("old Pacific") or Proto-Pacific because the Pacific Ocean is a direct continuation of Panthalassa. Formation The supercontinent Rodinia began to break up 870–845 probably as a consequence of a superplume caused by mantle slab avalanches along the margins of the supercontinent. In a second episode 750 the western half of Rodinia started to rift apart: western Kalahari and South China broke away from the western margins of Laurentia; and by 720 Austral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wrangellia Terrane
The Wrangellia Terrane (named for the Wrangell Mountains, Alaska) is a crustal fragment (terrane) extending from the south-central part of Alaska and along the Coast of British Columbia in Canada. Some geologists contend that Wrangellia extends southward to Oregon, although this is not generally accepted. Extent and terminology The term Wrangellia is confusingly applied to all of: * The Wrangell(ia) Terrane alone; * A composite terrane (CT) consisting of the Wrangell Terrane, Peninsular Terrane, and other rock units that were not originally part of the North American craton; * A composite terrane which also includes the Alexander Terrane. Earlier geologists sometimes used the term "Talkeetna Superterrane" to describe Wrangellia. Origin There are two conflicting hypotheses about whether the Wrangellia Superterrane originated at polar or equatorial latitudes: # That Wrangellia accreted at a northerly latitude near its current location (when North America, or Laurentia, was fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Ocean, Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia (mythology), Gaia'' or Gaea (, "Mother goddess, Mother Earth, land"). The concept that the continents once formed a contiguous land mass was hypothesised, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farallon Plate
The Farallon Plate was an ancient oceanic plate. It formed one of the three main plates of Panthalassa, alongside the Phoenix Plate and Izanagi Plate, which were connected by a triple junction. The Farallon Plate began subducting under the west coast of the North American Plate—then located in modern Utah—as Pangaea broke apart and after the formation of the Pacific Plate at the centre of the triple junction during the Early Jurassic. It is named for the Farallon Islands, which are located just west of San Francisco, California. Over time, the central part of the Farallon Plate was completely subducted under the southwestern part of the North American Plate. The remains of the Farallon Plate are the Juan de Fuca, Explorer and Gorda Plates, subducting under the northern part of the North American Plate; the Cocos Plate subducting under Central America; and the Nazca Plate subducting under the South American Plate. The Farallon Plate is also responsible for transporting old i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", which leaves room for interpretation and is easier to apply to Precambrian times. To separate supercontinents from other groupings, a limit has been proposed in which a continent must include at least about 75% of the continental crust then in existence in order to qualify as a supercontinent. Supercontinents have assembled and dispersed multiple times in the geologic past (see table). According to modern definitions, a supercontinent does not exist today; the closest in existence to a supercontinent is the current Afro-Eurasian landmass, which covers approx. 57% of Earth's total land area. The last time the continental landmasses were near to one another was 336 to 175 million years ago as the supercontinent, Pangaea. The positions of con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangaea 200Ma
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia (continent), Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million years ago, and began to break apart about 200 million years ago, at the end of the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, Triassic and beginning of the Jurassic. In contrast to the present Earth and its distribution of continental mass, Pangaea was centred on the equator and surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa and the Paleo-Tethys Ocean, Paleo-Tethys and subsequent Tethys Ocean, Tethys Oceans. Pangaea is the most recent supercontinent to have existed and the first to be reconstructed by geologists. Origin of the concept The name "Pangaea" is derived from Ancient Greek ''pan'' (, "all, entire, whole") and ''Gaia (mythology), Gaia'' or Gaea (, "Mother goddess, Mother Earth, land"). The concept that the continents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allochthon
upright=1.6, Schematic overview of a thrust system. The hanging wall block is (when it has reasonable proportions) called a nappe. If an erosional hole is created in the nappe that is called a window (geology)">window. A klippe is a solitary outcrop of the nappe in the middle of autochthonous material. An allochthon, or an allochthonous block, is a large block of rock which has been moved from its original site of formation, usually by low angle thrust faulting. An allochthon which is isolated from the rock that pushed it into position is called a klippe. If an allochthon has a "hole" in it so that one can view the autochthon (geology), autochthon beneath the allochthon, the hole is called a "window" (or Fenster). Etymology: Greek; 'allo' = other, and 'chthon' = earth. In generalized terms, the term is applied to any geologic units that originated at a distance from their present location For comparison, see also Autochthon. In the United States there are three notable al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Anomaly
In geophysics, a magnetic anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field resulting from variations in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. Mapping of variation over an area is valuable in detecting structures obscured by overlying material. The magnetic variation (geomagnetic reversals) in successive bands of ocean floor parallel with mid-ocean ridges was important evidence for seafloor spreading, a concept central to the theory of plate tectonics. Measurement Magnetic anomalies are generally a small fraction of the magnetic field. The total field ranges from 25,000 to 65,000 nanoteslas (nT). To measure anomalies, magnetometers need a sensitivity of 10 nT or less. There are three main types of magnetometer used to measure magnetic anomalies: # The fluxgate magnetometer was developed during World War II to detect submarines. It measures the component along a particular axis of the sensor, so it needs to be oriented. On land, it is often oriented vertically, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-African Ocean
The Pan-African Ocean is a hypothesized paleo-ocean whose closure created the supercontinent of Pannotia. The ocean may have existed before the break-up of the supercontinent of Rodinia. The ocean closed before the beginning of the Phanerozoic Eon, when the Panthalassa Panthalassa, also known as the Panthalassic Ocean or Panthalassan Ocean (from Greek "all" and "sea"), was the superocean that surrounded the supercontinent Pangaea, the latest in a series of supercontinents in the history of Earth. During th ... ocean expanded, and was eventually replaced by it. See also * * References Historical oceans Proterozoic paleogeography {{palaeo-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triple Junction
A triple junction is the point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet. At the triple junction each of the three boundaries will be one of three types – a ridge (R), trench (T) or transform fault (F) – and triple junctions can be described according to the types of plate margin that meet at them (e.g. Fault-Fault-Trench, Ridge-Ridge-Ridge, or abbreviated F-F-T, R-R-R). Of the ten possible types of triple junction only a few are stable through time ('stable' in this context means that the geometrical configuration of the triple junction will not change through geologic time). The meeting of four or more plates is also theoretically possible but junctions will only exist instantaneously. History The first scientific paper detailing the triple junction concept was published in 1969 by Dan McKenzie and W. Jason Morgan. The term had traditionally been used for the intersection of three divergent boundaries or spreading ridges. These three divergent boundaries ideally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own distinctive geologic history, which is different from that of the surrounding areas—hence the term "exotic" terrane. The suture zone between a terrane and the crust it attaches to is usually identifiable as a fault. A sedimentary deposit that buries the contact of the terrane with adjacent rock is called an overlap formation. An igneous intrusion that has intruded and obscured the contact of a terrane with adjacent rock is called a stitching pluton. Older usage of ''terrane'' simply described a series of related rock formations or an area having a preponderance of a particular rock or rock groups. Overview A tectonostratigraphic terrane is not necessarily an independent microplate in origin, since it may not contain the full thickness ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannotia
Pannotia (from Greek: '' pan-'', "all", '' -nótos'', "south"; meaning "all southern land"), also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontinent that formed at the end of the Precambrian during the Pan-African orogeny (650–500 Ma), during the Cryogenian period and broke apart 560 Ma with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean, in the late Ediacaran and early Cambrian. Pannotia formed when Laurentia was located adjacent to the two major South American cratons, Amazonia and Río de la Plata. The opening of the Iapetus Ocean separated Laurentia from Baltica, Amazonia, and Río de la Plata. In 2022 the whole concept of Pannotia has been put into question by scientists who argue its existence is not supported by geochronology, "the supposed landmass had begun to break up well before it was fully assembled". Origin of concept J. D. A. Piper was probably the first to propose a Proterozoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |