|
Panje Mangesh Rao
Panje Mangesh Rao (1874–1937) was an Indian writer and poet who wrote short stories, essays, poems and children's rhymes in Kannada.He is known as 'kavishishya'. He wrote Huthariya haadu, Naagara haave, Koti chennaya, Gudugudu Gummata Devaru, Maathaado raamappa. Life Mangesh Rao's ancestors hailed from ''Panje'', now in Dakshina Kannada. He was born on 22 February 1874 to Ramappayya and Seethamma, Chitrapur Saraswat Konkani Brahmins, and had six siblings. After finishing primary schooling, in Bantwal, he had to go to Mangalore to study in high school. His proficiency in Kannada brought him a Kannada translator's job, on a monthly salary of twenty rupees, even before he completed graduation. He married Girijabai and had six children. They took active interest in his literary pursuits and his love of music. Later he completed his B.A. degree and got a teacher's diploma as well. He was also appointed Inspector of schools. In 1934, he was elected President of All India Kannada Conf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bantwal
Bantwal () is a taluk in Dakshina Kannada district, Karnataka, India. It is located East of Mangalore city center. BC Road-Kaikamba of Bantwal is one of the fastest developing areas in Dakshina Kannada district of Karnataka. Along with BC Road-Kaikamba, Panemangalore & Melkar regions are also urbanized. They are also developing as the eastern suburbs of Mangalore. Towards east of Mangalore, the stretch to BC Road-Kaikamba region forms a continuous Mangalore Urban Agglomeration area which is currently the second biggest in Karnataka after Bangalore. Bantwal is the fourth largest urban area in Dakshina Kannada district after Mangalore, Ullal (both comes under Mangalore Urban Agglomeration area) & Puttur in terms of population. History Bantwal means Banta Wala, which means where Bunts live in Tulu language. It is situated on the banks of River Nethravati on the National Highway 73 (India). The adjacent town of B.C. Road (Bantwal Cross Road) serves as the commercial cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kuvempu
Kuppali Venkatappa Puttappa (29 December 1904 – 11 November 1994), popularly known by his pen name Kuvempu, was an Indian poet, playwright, novelist and critic. He is widely regarded as the greatest Kannada poet of the 20th century. He was the first Kannada writer to receive the Jnanpith Award. Kuvempu studied at Mysuru University in the 1920s, taught there for nearly three decades and served as its vice-chancellor from 1956 to 1960. He initiated education in Kannada as the language medium. For his contributions to Kannada Literature, the Government of Karnataka decorated him with the honorific ''Rashtrakavi'' ("National Poet") in 1964 and Karnataka Ratna ("The Gem of Karnataka") in 1992. He was conferred the Padma Vibhushan by the Government of India in 1988. He penned the Karnataka State Anthem Jaya Bharata Jananiya Tanujate. Biography Early life and education Kuvempu was born in Hirekodige, a village in Koppa taluk of Chikmagalur district and raised in Kuppalli, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1874 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – New York City annexes The Bronx. * January 2 – Ignacio María González becomes head of state of the Dominican Republic for the first time. * January 3 – Third Carlist War – Battle of Caspe: Campaigning on the Ebro in Aragon for the Spanish Republican Government, Colonel Eulogio Despujol surprises a Carlist force under Manuel Marco de Bello at Caspe, northeast of Alcañiz. In a brilliant action the Carlists are routed, losing 200 prisoners and 80 horses, while Despujol is promoted to Brigadier and becomes Conde de Caspe. * January 20 – The Pangkor Treaty (also known as the Pangkor Engagement), by which the British extended their control over first the Sultanate of Perak, and later the other independent Malay States, is signed. * January 23 **Alfred, Duke of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, Prince Alfred, Duke of Edinburgh, second son of Queen Victoria, marries Grand Duchess Maria Alexandrovna of Russia, only daug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
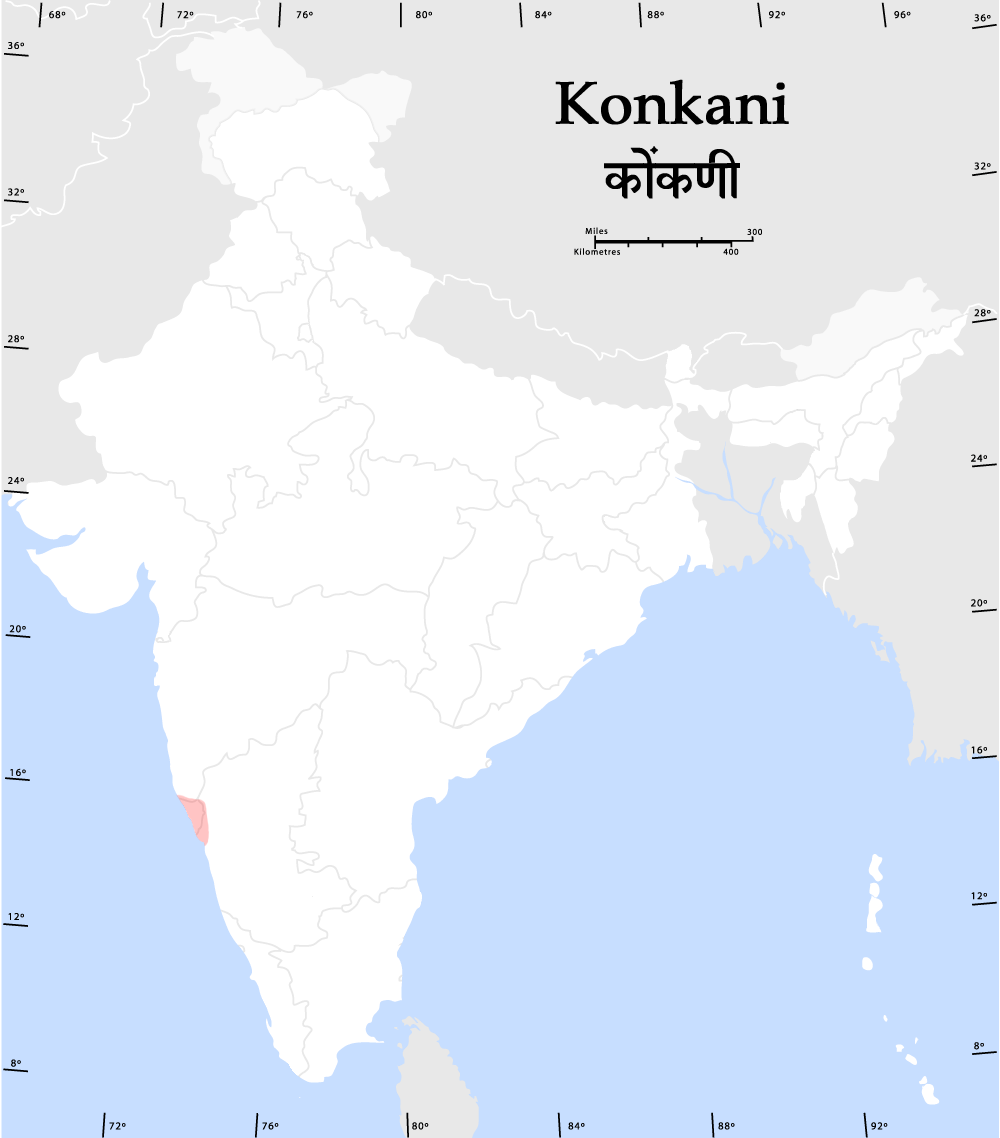
Konkani People
The Konkan people ( Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people (Konkani language, Konkani) Konkanis The Konkan people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada-language Writers
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton University Pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koti And Chennayya
Koti and Chennayya ( tcy, ಕೋಟಿ ಚೆನ್ನಯ್ಯ Kōṭi Cennayya,) (Circa 1556 A.D to 1591 A.D.) are legendary Tuluva twin heroes characterized in the Tulu epic of the same name, which is considered one of the two truly long epic in Tulu language. The birthplace of Koti and Chennaya is Padumale in Puttur taluk, Dakshina Kannada. The story of these heroes may be taken to roughly five hundred years back, when reference to Ballads were made in the Tulu Padana. Koti and Chennayya were born to the ''Deyi Baidethi'' of the Daivashakthi people of Tulu Nadu. Owing to the brothers heroic deeds, they are worshipped and remembered as protectors. They died in combat near Yenmoor. Memorial temples called ''garadi'' "gymnasiums" have been built in the name of Koti and Chennayya all over Tulu Nadu. Religious Places * PADUMALE, the birth place of Koti Chennaya. * Shree Brahma Baiderkala Garodi, Yenmoor, Maha samadhi of Koti Chennaya. *Shree Brahma Baidarkala Garadi Kshetra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Language
Tulu () in Kannada script, ml, തുളു ഭാഷെ in Malayalam script. ''bhāṣe'', , ''bhāśe'', and ''bāśe'' are alternative spellings for the Tulu word ''bāse'' in the Kannada script. The correct spelling for the word "language" in Kannada Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native s ... is kn, ಭಾಷೆ ''bhāṣe'', but that is not necessarily true in Tulu. Männer's ''Tulu-English and English-Tulu Dictionary'' (1886) says, " bāšè, bāsè, ''see'' ." (vol. 1, p. 478), " bhāšè, bhāshè, ''s''. Speech, language." (vol. 1, p. 508), meaning that the four spellings are more or less acceptable. The word is actually pronounced ''bāse'' in Tulu. Note that š and sh in his dictionary correspond to ''ś'' and ''ṣ'', respe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodagu
Kodagu (also known by its former name Coorg) is an administrative district in the Karnataka state of India. Before 1956, it was an administratively separate Coorg State, at which point it was merged into an enlarged Mysore State. It occupies an area of in the Western Ghats of southwestern Karnataka. In 2001 its population was 548,561, 13.74% of which resided in the district's urban centre, making it the least populous of the 31 districts in Karnataka. The nearest railway stations are Mysore Junction, located around away, Thalassery, and Kannur, the latter two located in Kerala at a distance of about . The nearest airports are Kannur International Airport in Kerala ( from Madikeri) and Mangalore International Airport ( from Madikeri). Geography Kodagu is located on the eastern slopes of the Western Ghats. It has a geographical area of . The district is bordered by Dakshina Kannada district to the northwest, Hassan district to the north, Mysore district to the east, Kas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kodava People
The Kodava people or Kodavas are an ethno-linguistic group from the region of Kodagu in the southern Indian state of Karnataka, who natively speak the Kodava language. They are traditionally land-owning agriculturists and patrilineal, with martial customs. Kodavas worship ancestors and weapons. They used to worship swords, bows, arrows and later guns. Hence, Kodavas are the only ones in India permitted to carry firearms without a license. Origin The words ''Kodava'' (the indigenous people, language and culture) and ''Kodagu'' (the land) come from the same root word 'Koda' of unknown meaning. Some claim it means 'hills', others say it means 'west' but both relate to the Western Ghats' location. Kodagu is called ''Kodava Naad'' in the native Kodava language. The word "Kodagu" was anglicized to "Coorgs" by the British Raj. For centuries, the Kodavas have lived in Kodagu cultivating paddy fields, maintaining cattle herds and coffee plantations, and carrying arms during war. Pura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada Literature
Kannada literature is the Text corpus, corpus of written forms of the Kannada language, a member of the Dravidian language, Dravidian Language family, family spoken mainly in the Indian state of Karnataka and written in the Kannada script. Attestations in literature span one and a half millennia, R.S. Mugali (2006), ''The Heritage of Karnataka'', pp. 173–175 with some specific literary works surviving in rich manuscript traditions, extending from the 9th century to the present. The Kannada language is usually divided into three linguistic phases: Old (450–1200 CE), Middle (1200–1700 CE) and Modern (1700–present); and its literary characteristics are categorised as Jainism, Jain, Lingayatism and Vaishnavism, Vaishnava—recognising the prominence of these three faiths in giving form to, and fostering, classical expression of the language, until the advent of the modern era. Kittel in Rice E.P. (1921), p. 14Sastri 1955, pp. 355–365Narasimhacharya (1934), pp. 17, 61 Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shiv Aroor
Shiv Aroor is an Indian journalist and author. He is an editor and anchor at India Today (TV channel). He is also a defence correspondent, having done conflict reporting from defence zones such as Kashmir, Sri Lanka and Libya. He also runs a defence website called livefistdefence.com' which he founded in 2007, which was a winner in the 2012 and 2013 DefenceIQ Blogging Awards in the category Regional Defence blog. He is a post-graduate in international journalism from Cardiff University and a graduate from St Stephen's College, Delhi. He wrote the fictional book, ''Operation Jinnah'', in 2017. In 2018 he co-authored ''India's Most Fearless'' and then the sequel in 2019. The first part sold over 40,000 copies. India's Most Fearless 3, co-authored with Rahul Singh was released in August 2022. This book was launched by the three service chiefs- Air Chief Marshal VR Chaudhari, Admiral R Hari Kumar and General Manoj Pande at an event in New Delhi on 17 January 2023. One of the chapt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shivaram Karanth
Kota Shivaram Karanth (10 October 1902 – 9 December 1997), also abbreviated as K. Shivaram Karanth, was an Indian polymath, who was a novelist in Kannada language, playwright and an ecological conservationist. Ramachandra Guha called him the "Rabindranath Tagore of Modern India, who has been one of the finest novelists-activists since independence". He was the third writer to be decorated with the Jnanpith Award for Kannada, the highest literary honor conferred in India. His son Ullas is an ecological conservationist. Early life Shivaram Karanth was born on 10 October 1902, in Kota near Kundapura in the Udupi district of Karnataka to a Kannada-speaking family. The fifth child of his parents Shesha Karantha and Lakshmamma, he completed his primary education in Kundapura and Mangalore. Shivaram Karanth was influenced by Gandhi's principles and took part in Indian Independence movement when he was in college. His participation in the Non-cooperation movement did not allow him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |