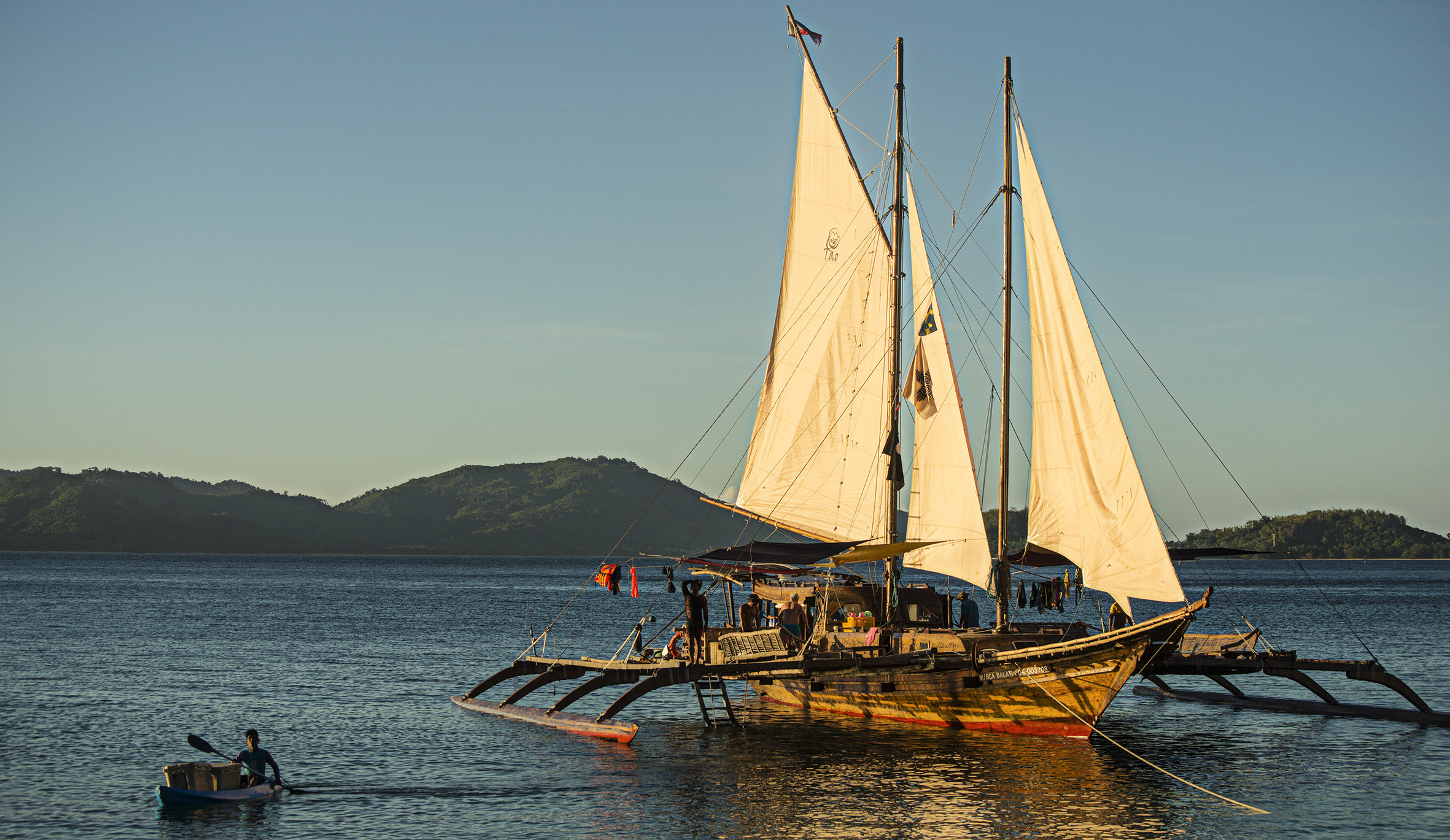|
Panineman
Panineman is a traditional open-deck fishing boat of the Ivatan people from the island of Itbayat in the Philippines. It is slightly larger than the largest types of tataya, and can accommodate three pairs of rowers and a single sail. See also *Avang *Chinarem *Tataya *Balangay A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ... * Bangka References {{Fishing vessel topics Indigenous ships of the Philippines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinarem
Chinarem was a traditional open-deck boat of the Ivatan people from the island of Sabtang in the Philippines. It was around long with three or four pair of rowers and a single mast. It was similar to the falua in shape, but differs in that the stern was pointed (hence its name). It can carry ten passengers and was generally used to ferry goods and people between the islands of Sabtang and Batan. Chinarem is extinct, it disappeared in Sabtang Island around the 1970s. See also *Avang *Panineman *Tataya *Balangay A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The ... * Bangka References {{Austronesian ships Indigenous ships of the Philippines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivatan People
The Ivatan people are an Austronesian ethnolinguistic group native to the Batanes and Babuyan Islands of the northernmost Philippines. They are genetically closely-related to other ethnic groups in Northern Luzon, but also share close linguistic and cultural affinities to the Tao people of Orchid Island in Taiwan. The culture of the Ivatans is partly influenced by the environmental condition of Batanes. Unlike the old-type nipa huts common in the Philippines, Ivatans have adopted their now-famous stone houses made of coral and limestone, designed to protect against the hostile climate. Origins A 2011 genetic study has concluded that it is likely that the Batanes Islands were initially only used as "stepping stones" during the early stages of the maritime Austronesian expansion from Taiwan into the Philippine Islands (c. 3000 BCE). It was later re-colonized by Austronesians from northern Luzon at around 1200 BCE, which became the ancestors of the Ivatan people. Archaeological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itbayat
Itbayat, officially the Municipality of Itbayat, ( ivv, Kavahayan nu Itbayat; tl, Bayan ng Itbayat), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Batanes, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 3,128 people. Itbayat is the country's northernmost municipality, located from the southernmost tip of Taiwan. In addition to the main island of Itbayat which is the largest in Batanes, the municipality includes the rest of the province's northern islands, all small and mostly uninhabited. These islands are, from south to north: Di'nem Island, Siayan, Misanga, Ah'li, and Mavulis Island, the northernmost island of the Philippine archipelago. History While the church and civil government were already established in Batan Island in 1783, it was only in 1855 that civil authority was officially established and the mission canonically founded in Itbayat. A mere settlement during the Spanish colonial period, it became a municipal district when the Americans organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no), * bik, Republika kan Filipinas * ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas * cbk, República de Filipinas * hil, Republika sang Filipinas * ibg, Republika nat Filipinas * ilo, Republika ti Filipinas * ivv, Republika nu Filipinas * pam, Republika ning Filipinas * krj, Republika kang Pilipinas * mdh, Republika nu Pilipinas * mrw, Republika a Pilipinas * pag, Republika na Filipinas * xsb, Republika nin Pilipinas * sgd, Republika nan Pilipinas * tgl, Republika ng Pilipinas * tsg, Republika sin Pilipinas * war, Republika han Pilipinas * yka, Republika si Pilipinas In the recognized optional languages of the Philippines: * es, República de las Filipinas * ar, جمهورية الفلبين, Jumhūriyyat al-Filibbīn is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of around 7,641 islands t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
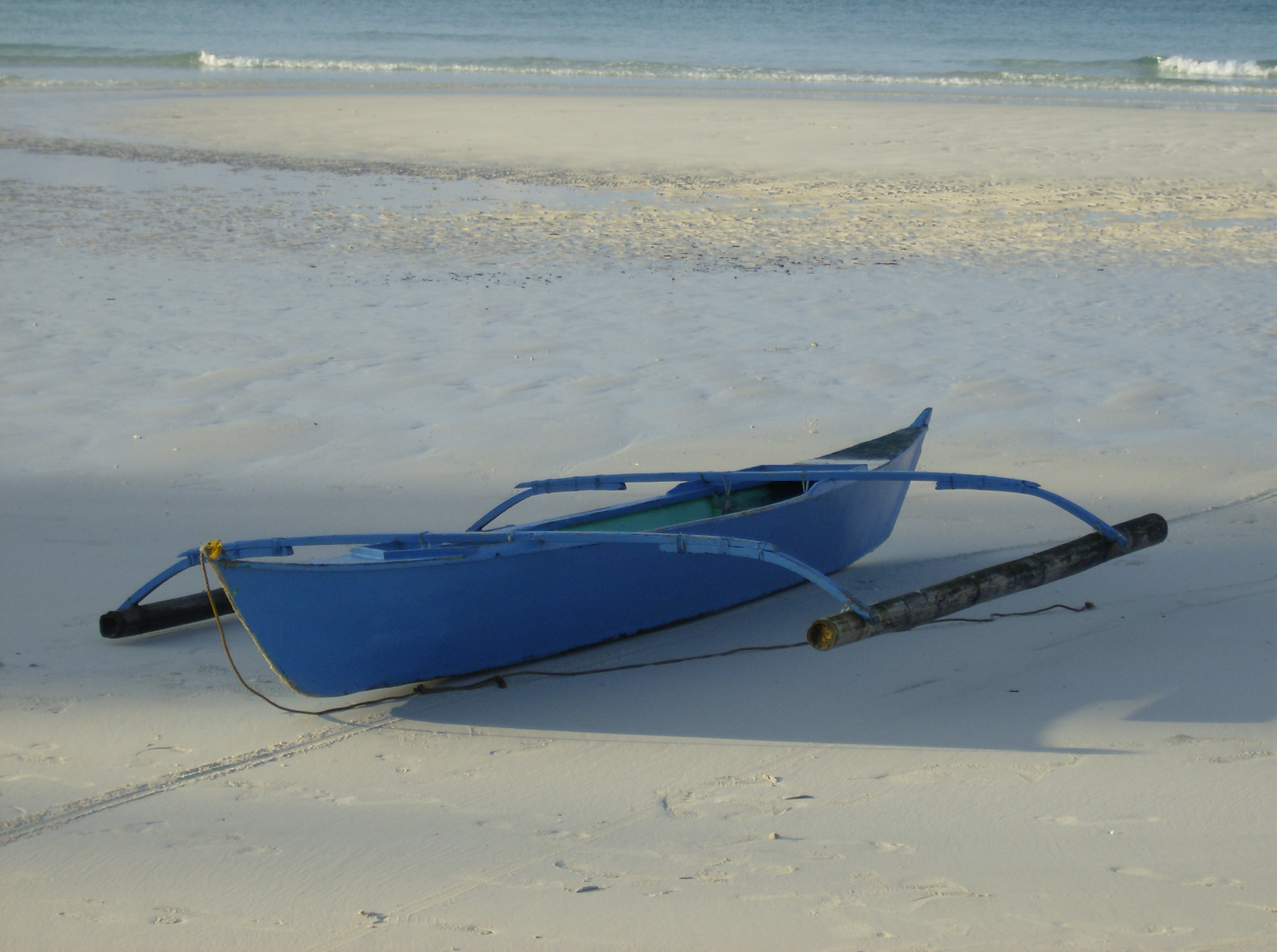
Tataya
Tataya are traditional small fishing boats, with or without outriggers of the Ivatan people in the Philippines. They are generally round-hulled and powered by rowers or sails made from woven pandanus leaves. They have several variants based on size and island of origin. The term ''tataya'' can also be used for all traditional boats in the Batanes Islands in general, similar to the term ''bangka'' in the rest of the Philippines. Types Size The following are the traditional types of tataya based on size: *Suhuan – also known as pangdayan or karakuhan, are the largest types of tataya. They are around long, wide, and deep. They can carry two rowers and one tiller, as well as an additional eight passengers. *Pehan – shorter than the suhuan but proportionally wider. It has two pairs of thole pins (''pasitan'') for rowers. It is around to wide and deep. *Paychanavangan – a small tataya used for hook and line fishing. It can carry two people, but is usually only manned by one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avang
Avang, also known as abang or pontin, is a traditional trading ship of the Ivatan people of the Philippines. It is the largest boat type among the Ivatan people and characteristically has a closed deck. It is about in length and about in height. It is slightly curving, with the bow and the stern higher than the central area. It has two masts made from woven mats of pandanus leaves, though these were later replaced with canvas cloth (''kacha'') in colonial times. It also has fifteen pairs of rowers. The avang resembles the '' vasinian'' boats of the Yami people. Avang are extinct, the last ship was dismantled in 1910. See also *Falua *Chinedkeran *Tataya *Balangay * Bangka * Awang (boat) Awang are traditional dugout canoes of the Maranao and Maguindanao people in the Philippines. They are used primarily in Lake Lanao, the Pulangi River, and the Liguasan Marsh for fishing or for transporting goods. They have long low hulls that are ... References {{Austronesian ships Indigenou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tataya
Tataya are traditional small fishing boats, with or without outriggers of the Ivatan people in the Philippines. They are generally round-hulled and powered by rowers or sails made from woven pandanus leaves. They have several variants based on size and island of origin. The term ''tataya'' can also be used for all traditional boats in the Batanes Islands in general, similar to the term ''bangka'' in the rest of the Philippines. Types Size The following are the traditional types of tataya based on size: *Suhuan – also known as pangdayan or karakuhan, are the largest types of tataya. They are around long, wide, and deep. They can carry two rowers and one tiller, as well as an additional eight passengers. *Pehan – shorter than the suhuan but proportionally wider. It has two pairs of thole pins (''pasitan'') for rowers. It is around to wide and deep. *Paychanavangan – a small tataya used for hook and line fishing. It can carry two people, but is usually only manned by one. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balangay
A Balangay, or barangay is a type of lashed-lug boat built by joining planks edge-to-edge using pins, dowels, and fiber lashings. They are found throughout the Philippines and were used largely as trading ships up until the colonial era. The oldest known balangay are the Butuan boats, which have been carbon-dated to 320 AD and were recovered from several sites in Butuan, Agusan del Norte. Balangay were the first wooden watercraft excavated in Southeast Asia. Balangay are celebrated annually in the Balanghai Festival of Butuan City. Names ''Balangay'' was one of the first native words the Europeans learned in the Philippines. The Venetian chronicler Antonio Pigafetta, who was with Ferdinand Magellan when setting foot in the Philippines in 1521 called the native boats ''balangai'' or ''balanghai''. This word appears as either ''balangay'' or ''barangay'', with the same meaning, in all the major languages of the Philippines. Early colonial Spanish dictionaries make it clear t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangka (boat)
Bangka are various native watercraft of the Philippines. It originally referred to small double-outrigger dugout canoes used in rivers and shallow coastal waters, but since the 18th century, it has expanded to include larger lashed-lug ships, with or without outriggers. Though the term used is the same throughout the Philippines, "bangka" can refer to a very diverse range of boats specific to different regions. Bangka was also spelled as banca, panca, or panga (Grammatical gender, m. banco, panco, pango) in Spanish language, Spanish. It is also known archaically as wikt:sakayan, sakayan (also spelled sacayan). Etymology Bangka is derived from Proto-Malayo-Polynesian ''*baŋkaʔ'', with cognates including Kavalan language, Kavalan ''bangka'', Mori language, Mori ''bangka'', and Sumbawa language, Sumbawa ''bangka''. It is a Doublet (linguistics), doublet of two other protoforms referring to boats: Proto-Austronesian ''*qabaŋ'' and Proto-Central-Malayo-Polynesian ''*waŋka''. Ulti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |