|
Panch Mahals
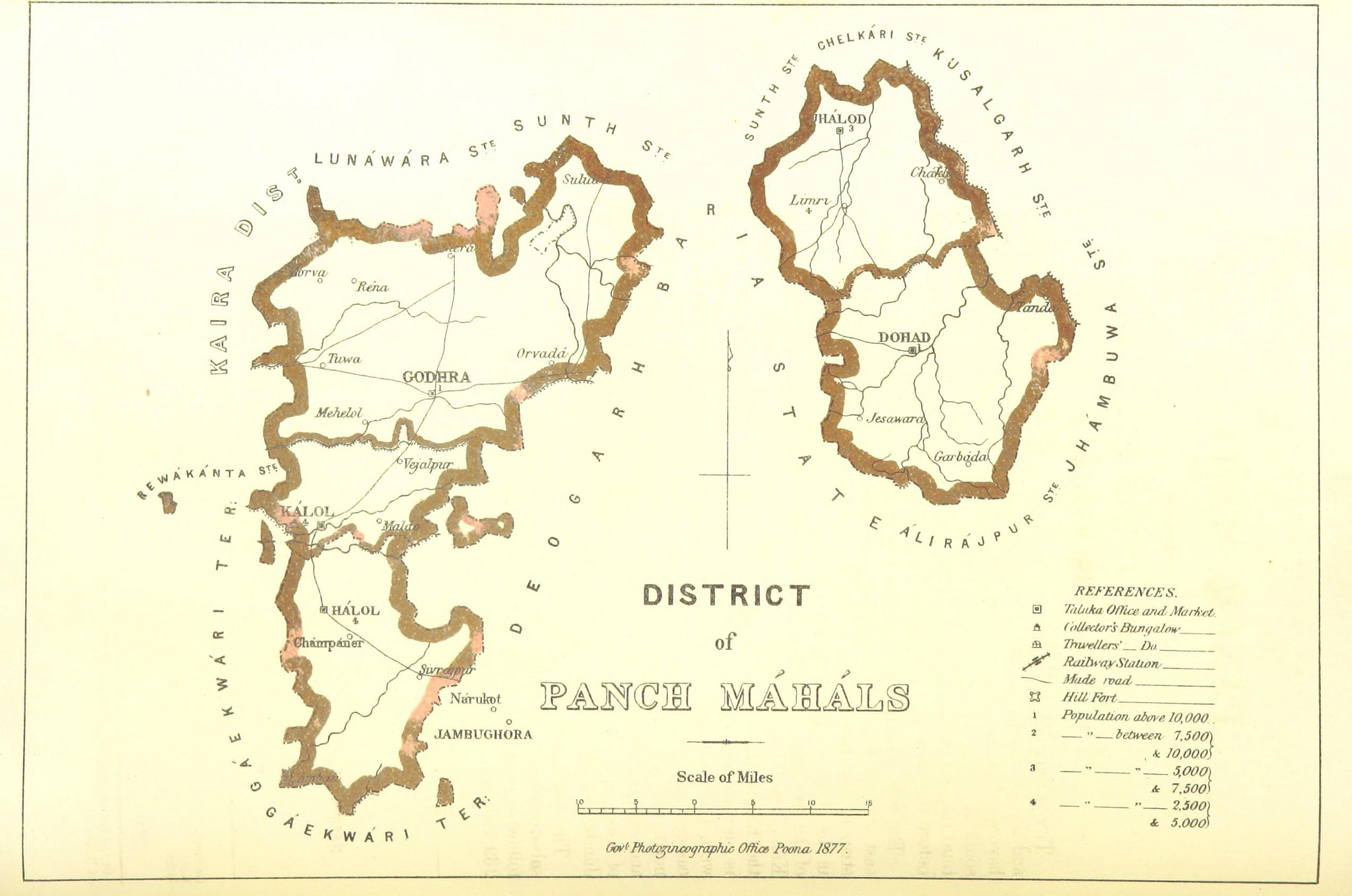
Panchmahal, also known as Panch Mahals, is a district in the eastern portion of Gujarat State western India. ''Panch-mahal'' means "five tehsils/talukas" (5 sub-divisions), and refers to the five sub-divisions that were transferred by the Maharaja Jivajirao Scindia of Gwalior State to the British: Godhra, Dahod, Halol, Kalol and Jhalod, Devgadh Baria. The district had a population of 2,390,776 of which 12.51% were urban as of 2001. The district is located on eastern end of the state. It is bordered by Dahod district to the north-east & east, Vadodara district to the southwest and Chhota Udaipur district to southeast, Kheda district to the west and Mahisagar district to the north. Name ''Panch-mahal'' is a Hindustani or Gujarati word derived from Panch ("five") and Mahal which adopted from its original usage in Arabic for a place or type of building, later adopted in Hindi to refer to a province, district or its division, an estate etc. The district was originally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Districts Of Gujarat
The western Indian state Gujarat has 33 districts after several splits of the original 17 districts at the formation of the state in 1960. Kutch is the largest district of Gujarat while Dang is the smallest. Ahmedabad is the most populated district while Dang is the least. There are 252 Talukas (subdivisions of districts) in Gujarat. History 1960 Gujarat state was created on 1 May 1960, out of the 17 northern districts of Bombay State when that was split on a linguistic basis (also creating Marathi speaking Maharashtra). They are as follow : Ahmedabad, Amreli, Banaskantha, Bharuch, Bhavnagar, Dang, Jamnagar, Junagadh, Kheda, Kachchh, Mehsana, Panchmahal, Rajkot, Sabarkantha, Surat, Surendranagar and Vadodara. 1964 In 1964, Gandhinagar was formed from parts of Ahmedabad and Mehsana. 1966 In 1966, Valsad was split from Surat. 1997 On 2 October 1997, five new districts were created: * Anand was split from Kheda. *Dahod was split from Panchmahal. * Narmad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jhalod
Jhalod (also written as Zalod) is a large town of historical and commercial importance.Also it is second largest City after Dahod.Jhalod serves as administrative headquarters of Jhalod Taluka in Dahod District, Gujarat, India. It is situated on the eastern border of Gujarat, from the Kushalgarh Tehsil of Banswara District, Rajasthan, near the Titodi River. History It is believed that the town was founded by a Bhil king called Zhala Vasaiya, whose tombstone is still visible by the entrance of the Maniben School. The Bhil people believe that the Jhalod name originates from the Zalai Mata temple, which is consecrated to the town's goddess, Zalod. Before the establishment of the Sant Rampur state, the king of Sant Rampur lived in Jhalod, but after a clash with other Bhils, the court was moved to Santrampur. After Scindia of Gwalior gave the area to the British, the state became one of the original "Five Mahals" of the Panchmahal District within Bombay Province during the Raj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chauhans
Chauhan, historically ''Chahamana'', is a clan name historically associated with the various ruling Rajput families during the Medieval India in Rajasthan. Subclans Khichi, Hada, Songara, Bhadauria, Devda etc. are the branches or subclans of Chauhan Rajputs. Origin The word ''Chauhan'' is the vernacular form of the Sanskrit term ''Chahamana'' (IAST: Cāhamāna). Several Chauhan inscriptions name a legendary hero called Chahamana as their ancestor, but none of them state the period in which he lived. The earliest extant inscription that describes the origin of the Chauhans is the 1119 CE Sevadi inscription of Ratnapala, a ruler of the Naddula Chahamana dynasty. According to this inscription, the ancestor of the Chahamanas was born from the eye of Indra. The 1170 CE Bijolia rock inscription of the Shakambhari Chahamana king Someshvara states that his ancestor Samantaraja was born at Ahichchhatrapura (possibly modern Nagaur) in the gotra of sage Vatsa. The 1262 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chavda Dynasty
The Chavda ( IAST:Chávaḍá), also spelled Chawda or Chavada was a dynasty which ruled the region of modern-day Gujarat in India, from c. 690 to 942. Variants of the name for the dynasty include Chapotkatas, Chahuda and Chávoṭakas. During the seventh century, Panchasar was the capital of the Chavda ruler Jayaśekhara. In c. 697, Panchasar was attacked and Jayaśekhara was killed. His wife had fled and she gave birth to Vanraja, who would go on to be the founder (746 or 765) of the city of Aṇahilaváḍa and most prominent ruler of the dynasty. According to ''Prabandhachintámaṇi'', he ruled for 60 years. He was succeeded by Yogaraja (ruled 35 years), followed by Kshemraja (25 years), Bhuyada (29 years), Virsimha (25 years) and Ratnaditya (15 years). Ratnaditya was succeeded by Samantsimha (also known as Chuyadadeva) who ruled seven years. Samantsimha did not have any children so he adopted his nephew Mularaja who overthrew him in 942 and established the Chaulukya dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vanraj Chavda
Vanaraja (IAST: Vanarāja Cāvaḍā) was the most prominent king of the Chavda dynasty who ruled Gujarat from c. 746 CE to c. 780 CE. Life Early life Kṛishṇabhaṭṭa’s (also known as Kṛṣṇakavi) ''Ratnamālā'' () says that in 695/696 CE (Samvat 752) Jayaśekhara, the Cāvaḍā king of Pañcāsara, a village (in modern-day Patan district, Gujarat), was attacked by the Chaulukya king Bhūvaḍa of Kalyāna-kaṭaka in Kanyākubja (probably Kanauj) and slain by Bhūvaḍa in battle. Before his death Jayaśekhara, he sent his pregnant wife Rūpasundarī to the forest in charge of her brother Surapāla, one of his chief warriors who now turned to banditry. After Jayaśekhara’s death on the battlefield, Rūpasundarī gave birth to a son named Vanarāja. This tradition is of dubious validity, as there is no city called Kalyāna-kaṭaka near Kanauj, and the Cālukya capital of Kalyāṇa in the Deccan was only founded in the 11th century, about 250 years after the ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavagadh Hill
Pavagadh Hill is situated within a plain in Panchmahal district, Gujarat, western India. A volcanic eruption occurred in the region approximately 500 million years ago and the etymology of Pavagadh is associated with this eruption: ''Pav-gadh'' means "one fourth hill" or "fire-hill". At its base is the historical city of Champaner, while the hill station of Pavagadh was built upon the volcanic cone itself. With Champaner, Pavagadh hill forms the Champaner-Pavagadh Archaeological Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site which is spread over an area of more than . Known for its forts, there are also dozens of heritage structures on the hill. The site is east of Vadodara and south of Godhra. Faith based legend surrounding Pavagadh formation suggests that the right foot of Sati is believed to have fallen at Pavagadh, thus forming a deep valley and the God later on "sent a large hill as per the request of Rishi Vishwamitra to fill up this deep valley so that the sage's sacred cows do not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champaner
Champaner is a historical city in the state of Gujarat, in western India. It is located in Panchmahal district, 47 kilometres from the city of Vadodara. The city was briefly the capital of the Sultanate of Gujarat. History Champaner is named after Champa Bhil, a last Bhil king of Champaner. Champa Bhil built Champaner Fort He also established Champaner. During 1405, after Champa Bhil, Rajputs occupied Champaner. By the later 15th century, the Khichi Chauhan Rajputs held Pavagadh fort above the town of Champaner. The young Sultan of Gujarat, Mahmud Begada, deciding to attack Champaner, started towards it with his army on 4 December 1482. After defeating the Champaner army, Mahmud captured the town and besieged Pavagadh, the well-known hill-fortress, above Champaner, where king Jayasimha had taken refuge. He captured the Pavagadh fort on 21 November 1484, after a siege of 20 months. He then spent 23 years rebuilding and embellishing Champaner, which he renamed Muhammadabad, afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co. KG, Berlin/Boston, 2011. Having emerged in the 1st century, it is named after the Arabs, Arab people; the term "Arab" was initially used to describe those living in the Arabian Peninsula, as perceived by geographers from ancient Greece. Since the 7th century, Arabic has been characterized by diglossia, with an opposition between a standard Prestige (sociolinguistics), prestige language—i.e., Literary Arabic: Modern Standard Arabic (MSA) or Classical Arabic—and diverse vernacular varieties, which serve as First language, mother tongues. Colloquial dialects vary significantly from MSA, impeding mutual intelligibility. MSA is only acquired through formal education and is not spoken natively. It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindustani Language
Hindustani (; Devanagari: , * * * * ; Perso-Arabic: , , ) is the '' lingua franca'' of Northern and Central India and Pakistan. Hindustani is a pluricentric language with two standard registers, known as Hindi and Urdu. Thus, the language is sometimes called Hindi–Urdu. Despite these standard registers, colloquial speech in Hindustani often exists on a spectrum between these standards. Ancestors of the language were known as ''Hindui'', ''Hindavi'', ''Zabān-e Hind'' (), ''Zabān-e Hindustan'' (), ''Hindustan ki boli'' (), Rekhta, and Hindi. Its regional dialects became known as ''Zabān-e Dakhani'' in southern India, ''Zabān-e Gujari'' () in Gujarat, and as ''Zabān-e Dehlavi'' or Urdu around Delhi. It is an Indo-Aryan language, deriving its base primarily from the Western Hindi dialect of Delhi, also known as Khariboli. Hindustani is a pluricentric language, best characterised as a continuum between two standardised registers: Modern Standard Hindi and Modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahisagar District
Mahisagar district is a district in the state of Gujarat in India that came into being on 26 January 2013, becoming the 28th district of the state. The district has been carved out of the Panchmahal district and the Kheda district. District Name Mahisagar given from "Mahi River". Lunawada is the district headquarters of Mahisagar. It started its operation in full-fledged from 15 August 2013. Demographics At the time of the 2011 census, Mahisagar district had a population of 9,94,624, of which 105,987 (10.66%) lived in urban areas. Mahisagar had a sex ratio of 947 females per 1000 males. Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes make up 50,862 (5.11%) and 350,217 (35.21%) of the population respectively. Hindus are in majority with 933,421, while Muslims are 58,546. Gujarati Gujarati may refer to: * something of, from, or related to Gujarat, a state of India * Gujarati people, the major ethnic group of Gujarat * Gujarati language, the Indo-Aryan language spoken by them * Guja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kheda District
Kheda District is one of the thirty-three districts of Gujarat state in western India. Its central city, Kheda, is the administrative headquarters of the district. History Formerly known as Kaira district, it was divided in two with the southern part becoming Anand district in 1997. The Charotar region of Kaira consisted of four talukas (sub-districts): Nadiad, Anand, Borsad, and Petlad. When the district was divided, Nadiad Taluka went with Kheda district and the other three with Anand district. Today, Kheda has eleven talukas. Balasinor and Virpur, once in Kheda district, were moved to the newly formed Mahisagar district in 2013. During the Indian independence movement in the first half of the 20th century, the Patidars of the Charotar region and other areas in Kaira resisted the British in a number of standoffs, notably the Kaira anti-tax campaign of 1913, the Kheda Satyagraha of 1918, the Borsad Satyagraha of 1923, and the Bardoli Satyagraha of 1928. Demographics A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chhota Udaipur
Chhota Udaipur is a town and a municipality in Chhota Udaipur district in the state of Gujarat, India. It is the headquarters of Chhota Udaipur district. History Chhota Udaipur was originally ruled by Bhil king , The last Bhil king of Chhota Udaipur was Kaliya Bhil in 1484. Chhota Udaipur was the capital of the erstwhile Princely State of Chhota Udaipur, founded in 1743 by Rawal Udeysinhji, a descendant of Patai Rawal of Champaner. This state was a First class state under Rewa Kantha Agency and merged with the Union of India on 10 March 1948. Rulers (title Maharaja Maharawal) * 1762 – 1771 Arsisinhji * 1771 – 1777 Hamirsinhji II * 1777 – 1822 Bhimsinhji * 1822 – 1851 Gumansinhji * 1851 – 1881 Jitsinhji * 1881 – 1895 Motisinhji * 1895 – 29 Aug 1923 Fatehsinhji (b. 1884 – d. 1923) * 29 Aug 1923 – 15 Oct 1946 Natwarsinhji Fatehsinhji ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)




