|
Palisading (biology)
In histopathology, a palisade is a single layer of relatively long cells, arranged loosely perpendicular to a surface and parallel to each other. A rosette is a palisade in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. A pseudorosette is a perivascular radial arrangement of neoplastic cells around a small blood vessel. Rosette A ''rosette'' is a cell formation in a halo or spoke-and-wheel arrangement, surrounding a central core or hub. The central hub may consist of an empty-appearing lumen or a space filled with cytoplasmic processes. The cytoplasm of each of the cells in the rosette is often wedge-shaped with the apex directed toward the central core: the nuclei of the cells participating in the rosette are peripherally positioned and form a ring or halo around the hub. Pathogenesis Rosettes may be considered primary or secondary manifestations of tumor architecture. Primary rosettes form as a characteristic growth pattern of a given tumor type wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
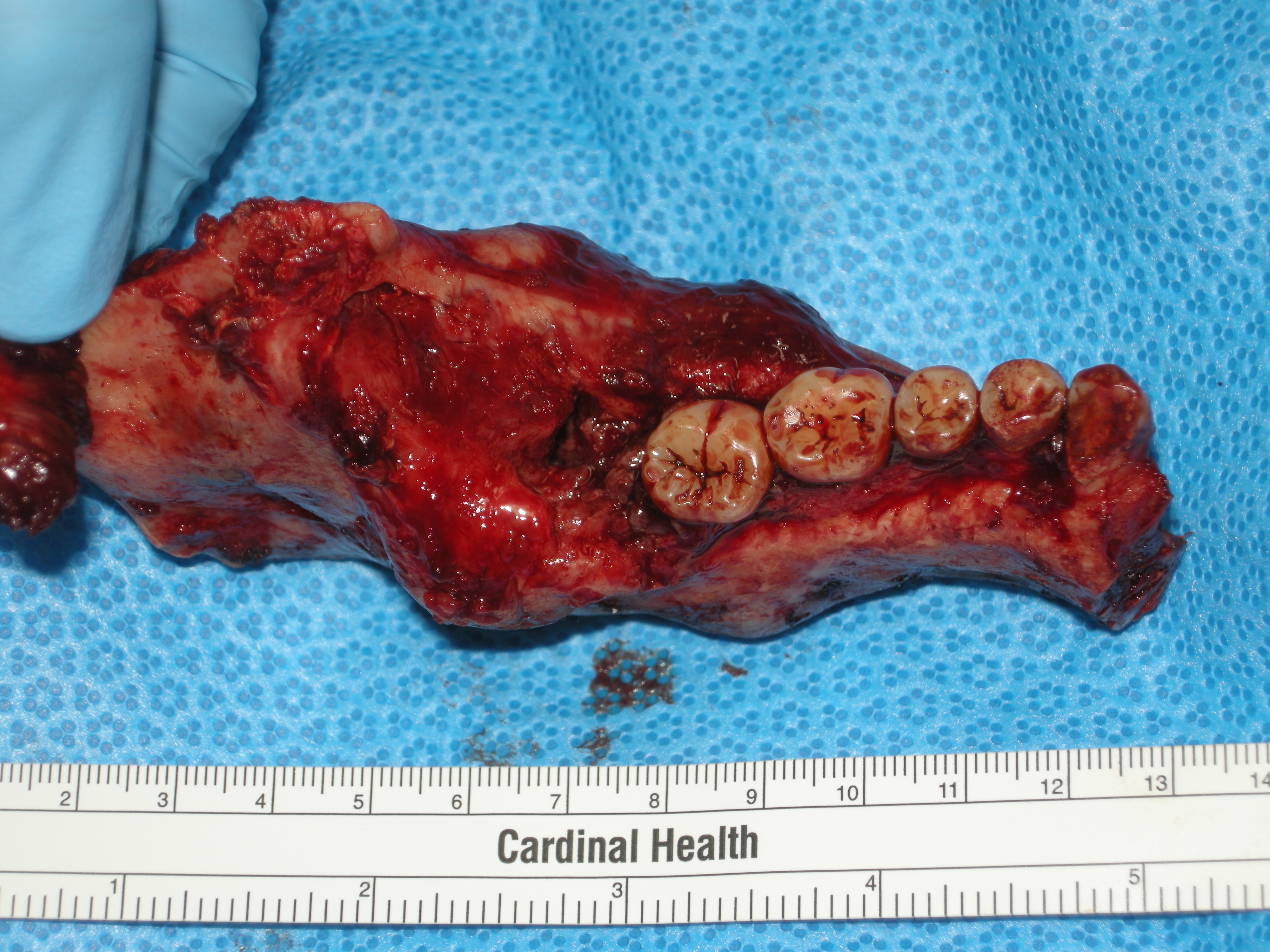
Ameloblastoma - High Mag
Ameloblastoma is a rare, benign or cancerous tumor of odontogenic epithelium (ameloblasts, or outside portion, of the Tooth development, teeth during development) much more commonly appearing in the human mandible, lower jaw than the maxilla, upper jaw. It was recognized in 1827 by Cusack. This type of odontogenic neoplasm was designated as an ''adamantinoma'' in 1885 by the French physician Louis-Charles Malassez. It was finally renamed to the modern name ''ameloblastoma'' in 1930 by Ivey and Churchill. While these tumors are rarely malignant or metastatic (that is, they rarely spread to other parts of the body), and progress slowly, the resulting lesions can cause severe abnormalities of the face and jaw leading to severe disfiguration. Additionally, as abnormal cell growth easily infiltrates and destroys surrounding bony tissues, wide surgical excision is required to treat this disorder. If an aggressive tumor is left untreated, it can obstruct the nasal and oral airways making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Flexner
Simon Flexner, M.D. (March 25, 1863 in Louisville, Kentucky – May 2, 1946) was a physician, scientist, administrator, and professor of experimental pathology at the University of Pennsylvania (1899–1903). He served as the first director of the Rockefeller Institute for Medical Research (1901–1935) (later developed as Rockefeller University) and a trustee of the Rockefeller Foundation. He was also a friend and adviser to John D. Rockefeller Jr. Among Flexner's most important achievements are studies into poliomyelitis and the development of serum treatment for meningitis. Among his lab assistants were Hideyo Noguchi and Cornelius Rhoads, later directors of Memorial Hospital and the Sloan-Kettering Institute, respectively. The bacteria species ''Shigella flexneri'' was named in recognition of Flexner. In addition, Flexner was the first to describe Flexner-Wintersteiner rosettes, a characteristic finding in retinoblastoma, a type of cancer. Early life and career Simon was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palisading In Basal Cell Cancer
A palisade is a steel or wooden fence or wall of variable height, usually used as a defensive structure. Palisade, palisades or palisading also may refer to: Software * PALISADE (software), an open source cross platform software library that provides implementations of lattice-based cryptography building blocks and homomorphic encryption schemes Geology * Columnar basalt, a common extrusive igneous (volcanic) rock formed from the rapid cooling of basaltic lava exposed at or very near the surface of a planet ** List of places with columnar jointed volcanics ;United States * The Palisades (Hudson River), cliffs along the Hudson River in the US states of New York and New Jersey * Palisades Sill, an intrusive igneous body that forms the cliffs largely following the southern portion of the Hudson River * Palisades (California Sierra), a group of peaks in the Sierra Nevada range of east-central California ** Palisade Glacier, California * The Palisades (Napa County), a mountain rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Homer Wright
James Homer Wright (April 8, 1869 – January 3, 1928) was an early and influential American pathologist, who was chief of pathology at Massachusetts General Hospital from 1896 to 1926. Wright was born in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. In 1915, he joined with Richard C. Cabot to begin publication of the ''Case Records of the Massachusetts General Hospital''. These began regular publication as the ''Boston Medical and Surgical Journal'' which later became the ''New England Journal of Medicine''. In 1924, Wright, along with Frank B. Mallory, published ''Pathological Technique: A Practical Manual for the Pathological Laboratory''. The book saw eight editions and for many years was the standard textbook in the field. He is the Wright in Wright's stain, and the Homer Wright rosettes associated with neuroblastoma. See also *Romanowsky stain Romanowsky staining, also known as Romanowsky–Giemsa staining, is a prototypical staining technique that was the forerunner of several disti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor is a malignant (cancerous) neural crest tumor. It is a rare tumor, usually occurring in children and young adults under 25 years of age. The overall 5 year survival rate is about 53%. It gets its name because the majority of the cells in the tumor are derived from neuroectoderm, but have not developed and differentiated in the way a normal neuron would, and so the cells appear "primitive".PNET belongs to the Ewing family of tumors. Genetics Using gene transfer of SV40 large T-antigen in neuronal precursor cells of rats, a brain tumor model was established. The PNETs were histologically indistinguishable from the human counterparts and have been used to identify new genes involved in human brain tumor carcinogenesis. The model was used to confirm p53 as one of the genes involved in human medulloblastomas, but since only about 10% of the human tumors showed mutations in that gene, the model can be used to identify the other binding partners of SV40 L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medulloblastoma
Medulloblastoma is a common type of primary brain cancer in children. It originates in the part of the brain that is towards the back and the bottom, on the floor of the skull, in the cerebellum, or posterior fossa. The brain is divided into two main parts, the larger cerebrum on top and the smaller cerebellum below towards the back. They are separated by a membrane called the tentorium. Tumors that originate in the cerebellum or the surrounding region below the tentorium are, therefore, called infratentorial. Historically medulloblastomas have been classified as a primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET), but it is now known that medulloblastoma is distinct from supratentorial PNETs and they are no longer considered similar entities. Medulloblastomas are invasive, rapidly growing tumors that, unlike most brain tumors, spread through the cerebrospinal fluid and frequently metastasize to different locations along the surface of the brain and spinal cord. Metastasis all the way dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuroblastoma
Neuroblastoma (NB) is a type of cancer that forms in certain types of nerve tissue. It most frequently starts from one of the adrenal glands but can also develop in the neck, chest, abdomen, or spine. Symptoms may include bone pain, a lump in the abdomen, neck, or chest, or a painless bluish lump under the skin. Typically, neuroblastoma occurs due to a genetic mutation occurring during early development. Rarely, it may be due to a mutation inherited from a person's parents. Environmental factors have not been found to be involved. Diagnosis is based on a tissue biopsy. Occasionally, it may be found in a baby by ultrasound during pregnancy. At diagnosis, the cancer has usually already spread. The cancer is divided into low-, intermediate-, and high-risk groups based on a child's age, cancer stage, and what the cancer looks like. Treatment and outcomes depends on the risk group a person is in. Treatments may include observation, surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or stem cell t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuropil
Neuropil (or "neuropile") is any area in the nervous system composed of mostly unmyelinated axons, dendrites and glial cell processes that forms a synaptically dense region containing a relatively low number of cell bodies. The most prevalent anatomical region of neuropil is the brain which, although not completely composed of neuropil, does have the largest and highest synaptically concentrated areas of neuropil in the body. For example, the neocortex and olfactory bulb both contain neuropil. White matter, which is mostly composed of myelinated axons (hence its white color) and glial cells, is generally not considered to be a part of the neuropil. Neuropil (pl. neuropils) comes from the Greek: ''neuro'', meaning "tendon, sinew; nerve" and ''pilos'', meaning "felt". The term's origin can be traced back to the late 19th century. Location Neuropil has been found in the following regions: outer neocortex layer, barrel cortex, inner plexiform layer and outer plexiform layer, poster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micrograph Of Homer Wright Pseudorosettes
A micrograph or photomicrograph is a photograph or digital image taken through a microscope or similar device to show a magnified image of an object. This is opposed to a macrograph or photomacrograph, an image which is also taken on a microscope but is only slightly magnified, usually less than 10 times. Micrography is the practice or art of using microscopes to make photographs. A micrograph contains extensive details of microstructure. A wealth of information can be obtained from a simple micrograph like behavior of the material under different conditions, the phases found in the system, failure analysis, grain size estimation, elemental analysis and so on. Micrographs are widely used in all fields of microscopy. Types Photomicrograph A light micrograph or photomicrograph is a micrograph prepared using an optical microscope, a process referred to as ''photomicroscopy''. At a basic level, photomicroscopy may be performed simply by connecting a camera to a microscope, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugo Wintersteiner
Hugo or HUGO may refer to: Arts and entertainment * ''Hugo'' (film), a 2011 film directed by Martin Scorsese * Hugo Award, a science fiction and fantasy award named after Hugo Gernsback * Hugo (franchise), a children's media franchise based on a troll ** ''Hugo'' (game show), a television show that first ran from 1990 to 1995 ** ''Hugo'' (video game), several video games released between 1991 and 2000 * ''Hugo'' (stylised as ''hugo''), a 2022 album by British rapper Loyle Carner People and fictional characters * Victor Hugo, a French poet, novelist, and dramatist of the Romantic movement. * Hugo (name), including lists of people with Hugo as a given name or surname, as well as fictional characters * Hugo (musician), Thai-American actor and singer-songwriter Chulachak Chakrabongse (born 1981) Places in the United States * Hugo, Alabama, an unincorporated community * Hugo, Colorado, a Statutory Town * Hugo, Minnesota, a town * Hugo, Missouri, an unincorporated community * Hugo, O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgery, surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency (medicine), residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austrians
, pop = 8–8.5 million , regions = 7,427,759 , region1 = , pop1 = 684,184 , ref1 = , region2 = , pop2 = 345,620 , ref2 = , region3 = , pop3 = 197,990 , ref3 = , region4 = , pop4 = 40,300–65,090 , ref4 = , region5 = , pop5 = 45,530 , ref5 = , region6 = , pop6 = 21,600–25,000 , ref6 = , region7 = , pop7 = 20,000 , ref7 = , region8 = , pop8 = 16,331 , ref8 = , region9 = , pop9 = 15,771 , ref9 = , region10 = , pop10 = 14,000 , ref10 = , region11 = , pop11 = 12,000 , ref11 = , region12 = , pop12 = 10,000 , ref12 = , region13 = , pop13 = 9,800 , ref13 = , region14 = , pop14 = 9,044 , ref14 = , region15 = , pop15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_(14767301904).jpg)



